Anat Cell Biol.
2010 Sep;43(3):185-193. 10.5115/acb.2010.43.3.185.
Effects of hypothyroidism on cell proliferation and neuroblasts in the hippocampal dentate gyrus in a rat model of type 2 diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, College of Veterinary Medicine, and Research Institute for Veterinary Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. ysyoon@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biomedical Sciences, College of Health Sciences, Marquette University, Milwaukee, USA.
- 3Department of Neurobiology, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2168873
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2010.43.3.185
Abstract
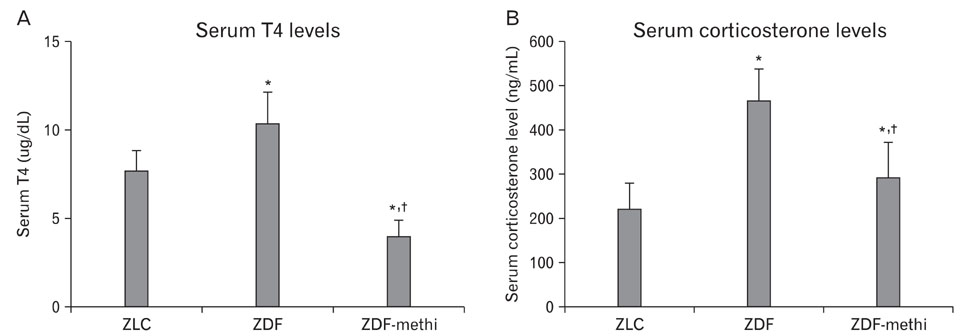
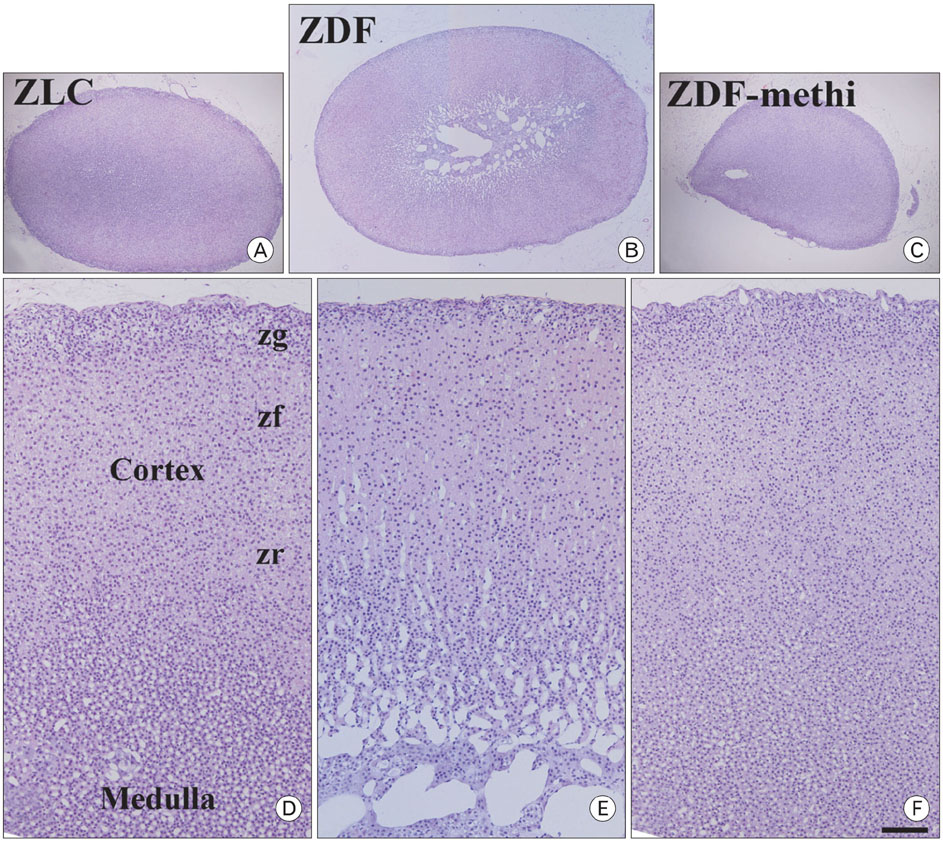
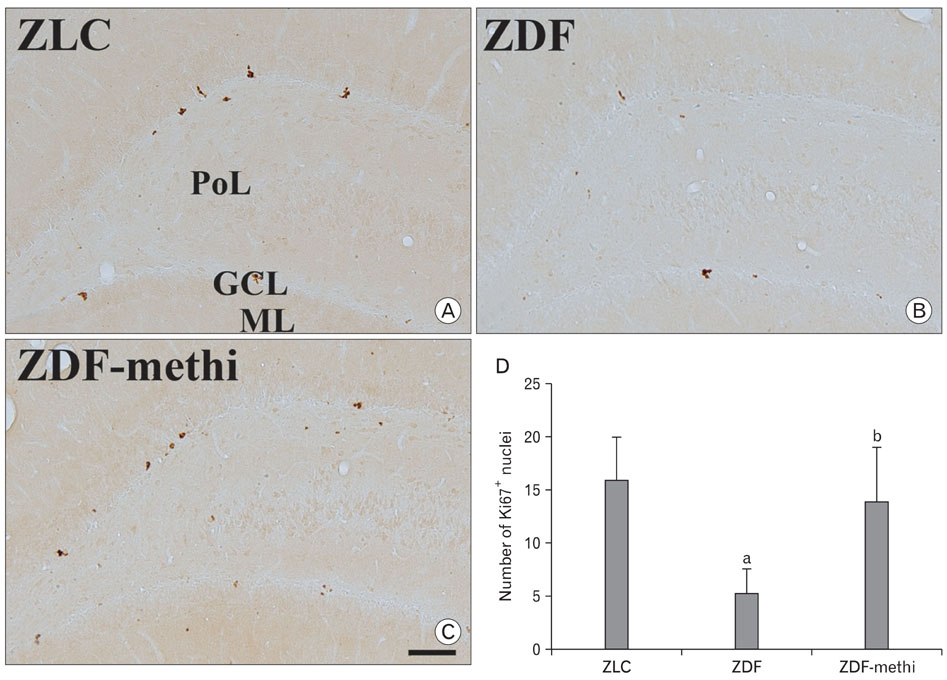
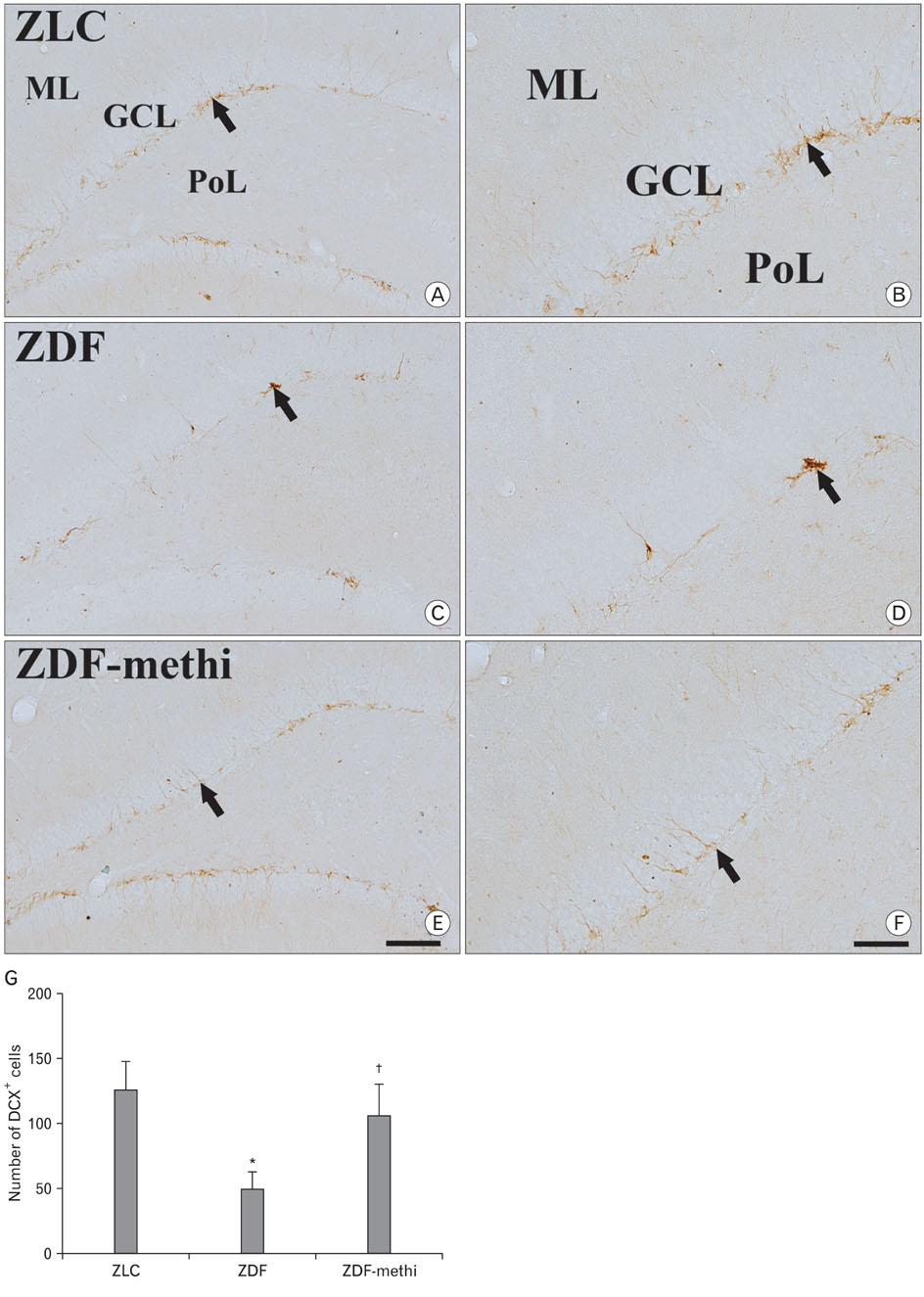
- We observed how the hypothyroid state affects diabetic states and modifies cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG). For this, 0.03% methimazole, an anti-thyroid drug, was administered to 7-week-old, pre-diabetic Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats by drinking water for 5 weeks, and the animals were sacrificed at 12 weeks of age. At this age, corticosterone levels were significantly increased in the ZDF rats compared to those in the control (Zucker lean control, ZLC) rats. Methimazole (methi) treatment in the ZDF rats (ZDF-methi rats) significantly decreased corticosterone levels and diabetes-induced hypertrophy of adrenal glands. In the DG, Ki67 (a marker for cell proliferation)- and doublecortin (DCX, a marker for neuronal progenitors)-immunoreactive cells were much lower in the ZDF rats than those in the ZLC rats. However, in ZDF-methi rats, numbers of Ki67- and DCX-immunoreactive cells were similar to those in the ZLC rats. These suggest that methi significantly reduces diabetes-induced hypertrophy of the adrenal gland and alleviates the diabetes-induced reduction of cell proliferation and neuronal progenitors in the DG.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aizawa K, Ageyama N, Yokoyama C, Hisatsune T. Age-dependent alteration in hippocampal neurogenesis correlates with learning performance of macaque monkeys. Exp Anim. 2009. 58:403–407.2. Ambrogini P, Cuppini R, Ferri P, et al. Thyroid hormones affect neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult rat. Neuroendocrinology. 2005. 81:244–253.3. Ausó E, Lavado-Autric R, Cuevas E, Del Rey FE, Morreale De Escobar G, Berbel P. A moderate and transient deficiency of maternal thyroid function at the beginning of fetal neocorticogenesis alters neuronal migration. Endocrinology. 2004. 145:4037–4047.4. Beauquis J, Roig P, Homo-Delarche F, De Nicola A, Saravia F. Reduced hippocampal neurogenesis and number of hilar neurones in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice: reversion by antidepressant treatment. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. 23:1539–1546.5. Bernal J, Guadaño-Ferraz A, Morte B. Perspectives in the study of thyroid hormone action on brain development and function. Thyroid. 2003. 13:1005–1012.6. Carageorgiou H, Pantos C, Zarros A, et al. Changes in acetylcholinesterase, Na+,K+-ATPase, and Mg2+-ATPase activities in the frontal cortex and the hippocampus of hyper- and hypothyroid adult rats. Metabolism. 2007. 56:1104–1110.7. Cooper DS. Antithyroid drugs. N Engl J Med. 2005. 352:905–917.8. Cooper-Kuhn CM, Kuhn HG. Is it all DNA repair? Methodological considerations for detecting neurogenesis in the adult brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2002. 134:13–21.9. Cuevas E, Ausó E, Telefont M, Morreale de Escobar G, Sotelo C, Berbel P. Transient maternal hypothyroxinemia at onset of corticogenesis alters tangential migration of medial ganglionic eminence-derived neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. 22:541–551.10. Etgen GJ, Oldham BA. Profiling of Zucker diabetic fatty rats in their progression to the overt diabetic state. Metabolism. 2000. 49:684–688.11. Gispen WH, Biessels GJ. Cognition and synaptic plasticity in diabetes mellitus. Trends Neurosci. 2000. 23:542–549.12. Hastings NB, Gould E. Rapid extension of axons into the CA3 region by adult-generated granule cells. J Comp Neurol. 1999. 413:146–154.13. Hibbe T, Kiesel U, Kolb-Bachofen V, Kolb H. Methimazole treatment aggravates low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1991. 11:53–58.14. Hwang IK, Kim IY, Kim YN, et al. Effects of methimazole on the onset of type 2 diabetes in leptin receptor-deficient rats. J Vet Med Sci. 2009. 71:275–280.15. Hwang IK, Yi SS, Kim YN, et al. Reduced hippocampal cell differentiation in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus in a rat model of type II diabetes. Neurochem Res. 2008. 33:394–400.16. Jackson-Guilford J, Leander JD, Nisenbaum LK. The effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on cell proliferation in the rat dentate gyrus. Neurosci Lett. 2000. 293:91–94.17. Joëls M. Role of corticosteroid hormones in the dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res. 2007. 163:355–370.18. Karl C, Couillard-Despres S, Prang P, et al. Neuronal precursor-specific activity of a human doublecortin regulatory sequence. J Neurochem. 2005. 92:264–282.19. Landfield PW, Waymire JC, Lynch G. Hippocampal aging and adrenocorticoids: quantitative correlations. Science. 1978. 202:1098–1102.20. Lee PR, Brady D, Koenig JI. Thyroid hormone regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor subunit mRNA expression in adult brain. J Neuroendocrinol. 2003. 15:87–92.21. Magariños AM, McEwen BS. Experimental diabetes in rats causes hippocampal dendritic and synaptic reorganization and increased glucocorticoid reactivity to stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000. 97:11056–11061.22. Matsushita M, Tamura K, Osada S, Kogo H. Effect of troglitazone on the excess testosterone and LH secretion in thyroidectomized, insulin-resistant, type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Endocrine. 2005. 27:301–305.23. Mennemeier M, Garner RD, Heilman KM. Memory, mood and measurement in hypothyroidism. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1993. 15:822–831.24. Montaron MF, Drapeau E, Dupret D, et al. Lifelong corticosterone level determines age-related decline in neurogenesis and memory. Neurobiol Aging. 2006. 27:645–654.25. Montero-Pedrazuela A, Venero C, Lavado-Autric R, et al. Modulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis by thyroid hormones: implications in depressive-like behavior. Mol Psychiatry. 2006. 11:361–671.26. Narayanan CH, Narayanan Y. Cell formation in the motor nucleus and mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal nerve of rats made hypothyroid by propylthiouracil. Exp Brain Res. 1985. 59:257–266.27. Patel AJ, Hayashi M, Hunt A. Selective persistent reduction in choline acetyltransferase activity in basal forebrain of the rat after thyroid deficiency during early life. Brain Res. 1987. 422:182–185.28. Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 2007. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press.29. Piroli GG, Grillo CA, Reznikov LR, et al. Corticosterone impairs insulin-stimulated translocation of GLUT4 in the rat hippocampus. Neuroendocrinology. 2007. 85:71–80.30. Ryan CM, Geckle MO. Circumscribed cognitive dysfunction in middle-aged adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000. 23:1486–1493.31. Silva JE, Bianco SD. Thyroid-adrenergic interactions: physiological and clinical implications. Thyroid. 2008. 18:157–165.32. Siwak-Tapp CT, Head E, Muggenburg BA, Milgram NW, Cotman CW. Neurogenesis decreases with age in the canine hippocampus and correlates with cognitive function. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2007. 88:249–259.33. Smith JW, Evans AT, Costall B, Smythe JW. Thyroid hormones, brain function and cognition: a brief review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2002. 26:45–60.34. Song HJ, Stevens CF, Gage FH. Neural stem cells from adult hippocampus develop essential properties of functional CNS neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2002. 5:438–445.35. Stanfield BB, Trice JE. Evidence that granule cells generated in the dentate gyrus of adult rats extend axonal projections. Exp Brain Res. 1988. 72:399–406.36. Stranahan AM, Arumugam TV, Cutler RG, Lee K, Egan JM, Mattson MP. Diabetes impairs hippocampal function through glucocorticoid-mediated effects on new and mature neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2008. 11:309–317.37. Tamura K, Osada S, Matsushita M, Abe K, Kogo H. Changes in ovarian steroidogenesis in insulin-resistant, type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats after thyroidectomy and gonadotropin treatment. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. 513:151–157.38. Tohei A. Studies on the functional relationship between thyroid, adrenal and gonadal hormones. J Reprod Dev. 2004. 50:9–20.39. Tohei A, Akai M, Tomabechi T, Mamada M, Taya K. Adrenal and gonadal function in hypothyroid adult male rats. J Endocrinol. 1997. 152:147–154.40. Tohei A, Imai A, Watanabe G, Taya K. Influence of thiouracil-induced hypothyroidism on adrenal and gonadal functions in adult female rats. J Vet Med Sci. 1998. 60:439–446.41. Trudeau F, Gagnon S, Massicotte G. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity and glutamate receptor regulation: influences of diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. 490:177–186.42. Watts LM, Manchem VP, Leedom TA, et al. Reduction of hepatic and adipose tissue glucocorticoid receptor expression with antisense oligonucleotides improves hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in diabetic rodents without causing systemic glucocorticoid antagonism. Diabetes. 2005. 54:1846–1853.43. Weng Q, Saita E, Watanabe G, et al. Effect of methimazole-induced hypothyroidism on adrenal and gonadal functions in male Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica). J Reprod Dev. 2007. 53:1335–1341.44. Wilcoxon JS, Nadolski GJ, Samarut J, Chassande O, Redei EE. Behavioral inhibition and impaired spatial learning and memory in hypothyroid mice lacking thyroid hormone receptor alpha. Behav Brain Res. 2007. 177:109–116.45. Williams GR. Neurodevelopmental and neurophysiological actions of thyroid hormone. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008. 20:784–794.46. Zucker LM, Zucker TF. Fatty, a new mutation in the rat. J Hered. 1961. 52:275–278.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetes on Cell Proliferation and Neuronal Differentiation in the Dentate Gyrus; Correlation with Memory Impairment
- Protective Effect of Shenqi-wan on Traumatic Brain Injury-induced Delayed Apoptosis in Rat Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus
- Vanillin and 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol attenuate cognitive impairment and the reduction of cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the dentate gyrus in a mouse model of scopolamine-induced amnesia
- Low Dose Radiation Overcomes Diabetes-induced Suppression of Hippocampal Neuronal Cell Proliferation in Rats
- Vardenafil Increases Cell Proliferation in the Dentate Gyrus through Enhancement of Serotonin Expression in the Rat Dorsal Raphe