Immune Netw.
2014 Jun;14(3):156-163. 10.4110/in.2014.14.3.156.
Reduced Interleukin-17 and Transforming Growth Factor Beta Levels in Peripheral Blood as Indicators for Following the Course of Bladder Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Immunology and Microbiology, School of Medicine, Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Jahrom, Iran. baharlour@gmail.com
- 2Department of Nursing, School of Nursing, Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Jahrom, Iran.
- 3Department of Student Research Committee, School of Medicine, Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Jahrom, Iran.
- KMID: 2168027
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2014.14.3.156
Abstract
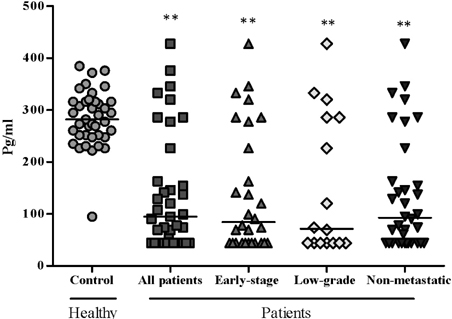
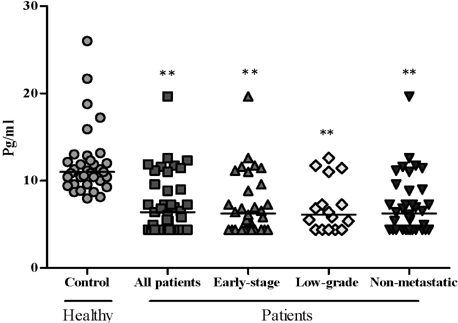
- Interleukin (IL) 17 is produced by T-helper (Th) 17 with a vigorous effect on cells of the immune system playing important roles in pathogenesis of immune-mediated diseases, including autoimmune disorders and cancers. Therefore, the aim of current study was to determine the serum levels of IL-6, IL-17, and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in Iranian bladder cancer patients, and to correlate them with disease status. Blood samples were collected from 40 bladder cancer patients and 38 healthy individuals with no history of malignancies or autoimmune disorders. The serum levels of IL-6, IL-17, and TGF-beta were measured by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The results showed that the levels of IL-17 (p<0.0001) and TGF-beta (p<0.0001) were significantly lower in the patients compared to the controls. No significant differences in the level of serum IL-6 (p=0.16) was observed between the patients and controls. In addition, demographic characteristics between control and patients groups were not significantly different. As most of the cases studied in this investigation were in stage I and II, it is concluded that reduced Th17-related cytokines can be used as indicators for following the course and clinical stages of bladder carcinoma progress and immune response to cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone I Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 2005; 175:5–14.2. Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva R, Wang YH, Wang Y, Hood L, Zhu Z, Tian Q, Dong C. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. 2005; 6:1133–1141.
Article3. Annunziato F, Cosmi L, Santarlasci V, Maggi L, Liotta F, Mazzinghi B, Parente E, Filì L, Ferri S, Frosali F, Giudici F, Romagnani P, Parronchi P, Tonelli F, Maggi E, Romagnani S. Phenotypic and functional features of human Th17 cells. J Exp Med. 2007; 204:1849–1861.
Article4. Peck A, Mellins ED. Breaking old paradigms: Th17 cells in autoimmune arthritis. Clin Immunol. 2009; 132:295–304.
Article5. Sfanos KS, Bruno TC, Maris CH, Xu L, Thoburn CJ, DeMarzo AM, Meeker AK, Isaacs WB, Drake CG. Phenotypic analysis of prostate-infiltrating lymphocytes reveals TH17 and Treg skewing. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:3254–3261.
Article6. Kryczek I, Wei S, Zou L, Altuwaijri S, Szeliga W, Kolls J, Chang A, Zou W. Cutting edge: Th17 and regulatory T cell dynamics and the regulation by IL-2 in the tumor microenvironment. J Immunol. 2007; 178:6730–6733.
Article7. Dong C. TH17 cells in development: an updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008; 8:337–348.
Article8. Nam JS, Terabe M, Kang MJ, Chae H, Voong N, Yang YA, Laurence A, Michalowska A, Mamura M, Lonning S, Berzofsky JA, Wakefield LM. Transforming growth factor beta subverts the immune system into directly promoting tumor growth through interleukin-17. Cancer Res. 2008; 68:3915–3923.
Article9. Shime H, Yabu M, Akazawa T, Kodama K, Matsumoto M, Seya T, Inoue N. Tumor-secreted lactic acid promotes IL-23/IL-17 proinflammatory pathway. J Immunol. 2008; 180:7175–7183.
Article10. Passos ST, Silver JS, OHara AC, Sehy D, Stumhofer JS, Hunter CA. IL-6 promotes NK cell production of IL-17 during toxoplasmosis. J Immunol. 2010; 184:1776–1783.
Article11. Mucida D, Cheroutre H. TGFbeta and retinoic acid intersect in immune-regulation. Cell Adh Migr. 2007; 1:142–144.12. Bettelli E, Korn T, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. Induction and effector functions of T(H)17 cells. Nature. 2008; 453:1051–1057.
Article13. Fossiez F, Djossou O, Chomarat P, Flores-Romo L, Ait-Yahia S, Maat C, Pin JJ, Garrone P, Garcia E, Saeland S, Blanchard D, Gaillard C, Das Mahapatra B, Rouvier E, Golstein P, Banchereau J, Lebecque S. T cell interleukin-17 induces stromal cells to produce proinflammatory and hematopoietic cytokines. J Exp Med. 1996; 183:2593–2603.
Article14. Murugaiyan G, Saha B. Protumor vs antitumor functions of IL-17. J Immunol. 2009; 183:4169–4175.
Article15. Zhang B, Rong G, Wei H, Zhang M, Bi J, Ma L, Xue X, Wei G, Liu X, Fang G. The prevalence of Th17 cells in patients with gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008; 374:533–537.
Article16. Honorati MC, Neri S, Cattini L, Facchini A. Interleukin-17, a regulator of angiogenic factor release by synovial fibroblasts1. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14:345–352.
Article17. Jeon SH, Chae BC, Kim HA, Seo GY, Seo DW, Chun GT, Kim NS, Yie SW, Byeon WH, Eom SH, Ha KS, Kim YM, Kim PH. Mechanisms underlying TGF-ß1-induced expression of VEGF and Flk-1 in mouse macrophages and their implications for angiogenesis. J Leukoc Biol. 2007; 81:557–566.
Article18. Wang L, Yi T, Kortylewski M, Pardoll DM, Zeng D, Yu H. IL-17 can promote tumor growth through an IL-6-Stat3 signaling pathway. J Exp Med. 2009; 206:1457–1464.
Article19. Radosavljevic G, Ljujic B, Jovanovic I, Srzentic Z, Pavlovic S, Zdravkovic N, Milovanovic M, Bankovic D, Knezevic M, Acimovic LJ, Arsenijevic N. Interleukin-17 may be a valuable serum tumor marker in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Neoplasma. 2010; 57:135–144.
Article20. Jovanovic DV, Di Battista JA, Martel-Pelletier J, Jolicoeur FC, He Y, Zhang M, Mineau F, Pelletier JP. IL-17 stimulates the production and expression of proinflammatory cytokines, IL-beta and TNF-alpha, by human macrophages. J Immunol. 1998; 160:3513–3521.21. Muranski P, Boni A, Antony PA, Cassard L, Irvine KR, Kaiser A, Paulos CM, Palmer DC, Touloukian CE, Ptak K, Gattinoni L, Wrzesinski C, Hinrichs CS, Kerstann KW, Feigenbaum L, Chan CC, Restifo NP. Tumor-specific Th17-polarized cells eradicate large established melanoma. Blood. 2008; 112:362–373.
Article22. Ankathatti Munegowda M, Deng Y, Mulligan SJ, Xiang J. Th17 and Th17-stimulated CD8+ T cells play a distinct role in Th17-induced preventive and therapeutic antitumor immunity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011; 60:1473–1484.
Article23. Kolahdoozan S, Sadjadi A, Radmard AR, Khademi H. Five common cancers in Iran. Arch Iran Med. 2010; 13:143–146.24. Zhang JP, Yan J, Xu J, Pang XH, Chen MS, Li L, Wu C, Li SP, Zheng L. Increased intratumoral IL-17-producing cells correlate with poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J Hepatol. 2009; 50:980–989.
Article25. Zhang B, Rong G, Wei H, Zhang M, Bi J, Ma L, Xue X, Wei G, Liu X, Fang G. The prevalence of Th17 cells in patients with gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008; 374:533–537.
Article26. Zhu X, Mulcahy LA, Mohammed RA, Lee AH, Franks HA, Kilpatrick L, Yilmazer A, Paish EC, Ellis IO, Patel PM, Jackson AM. IL-17 expression by breast-cancer-associated macrophages: IL-17 promotes invasiveness of breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res. 2008; 10:R95.
Article27. Kato T, Furumoto H, Ogura T, Onishi Y, Irahara M, Yamano S, Kamada M, Aono T. Expression of IL-17 mRNA in ovarian cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001; 282:735–738.
Article28. Chi LJ, Lu HT, Li GL, Wang XM, Su Y, Xu WH, Shen BZ. Involvement of T helper type 17 and regulatory T cell activity in tumour immunology of bladder carcinoma. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010; 161:480–489.
Article29. Lee JJ, Chang YL, Lai WL, Ko JY, Kuo MY, Chiang CP, Azuma M, Chen CW, Chia JS. Increased prevalence of interleukin-17-producing CD4XMLLink_XYZ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2011; 33:1301–1308.
Article30. Kwon KA, Kim SH, Oh SY, Lee S, Han JY, Kim KH, Goh RY, Choi HJ, Park KJ, Roh MS, Kim HJ, Kwon HC, Lee JH. Clinical significance of preoperative serum vascular endothelial growth factor, interleukin-6, and C-reactive protein level in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 2010; 10:203.
Article31. Ravishankaran P, Karunanithi R. Clinical significance of preoperative serum interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein level in breast cancer patients. World J Surg Oncol. 2011; 9:18.
Article32. Chen MF, Lin PY, Wu CF, Chen WC, Wu CT. IL-6 expression regulates tumorigenicity and correlates with prognosis in bladder cancer. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e61901.
Article33. Yang L, Qi Y, Hu J, Tang L, Zhao S, Shan B. Expression of Th17 cells in breast cancer tissue and its association with clinical parameters. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2012; 62:153–159.
Article34. Weaver CT, Hatton RD. Interplay between the TH17 and TReg cell lineages: a (co-) evolutionary perspective. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9:883–889.
Article35. Khatami M. Inflammation, aging, and cancer: tumoricidal versus tumorigenesis of immunity: a common denominator mapping chronic diseases. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2009; 55:55–79.
Article36. Erdman SE, Poutahidis T. Roles for inflammation and regulatory T cells in colon cancer. Toxicol Pathol. 2010; 38:76–87.
Article37. Connolly EC, Freimuth J, Akhurst RJ. Complexities of TGF-beta Targeted Cancer Therapy. Int J Biol Sci. 2012; 8:964–978.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Interleukin-17 on Production of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Cultured Rheumatoid Arthritis Synoviocytes
- Regulation of Tumor Immune Surveillance and Tumor Immune Subversion by TGF-beta
- Expressions of transforming growth factor beta in patients with rheumatioid arthritis and osteoarthritis
- Effects of Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 and Its Receptor on the Development, Recurrence and Progression of Human Bladder Cancer
- Changes of Interleukin-12 and Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 before and after Antipsychotic Treatments in Schizophrenic Patients