Standardization of House Dust Mite Extracts in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Environmental Medical Biology and Institute of Tropical Medicine, Arthropods of Medical Importance Resource Bank, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Center for Immunology and Pathology, Korea National Institute of Health, Cheongwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2167022
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2012.4.6.346
Abstract
- PURPOSE
House dust mites are the most important cause of respiratory allergy in Korea. Standardization of allergen extracts is essential for improving diagnostics and immunotherapeutics. This study was undertaken to evaluate the allergenicity of standardized house dust mite allergen extracts from Korean house dust mite isolates.
METHODS
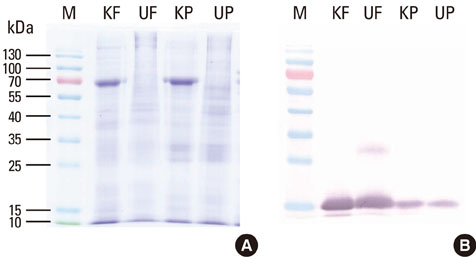
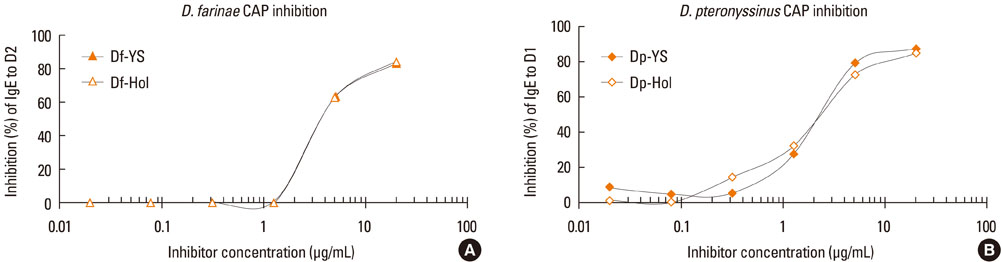
Allergen extracts were prepared from cultured Korean house dust mites (Dermatophagoides farinae and D. pteronyssinus). Allergenic activities of Korean house dust mite extracts were compared to standardized extracts from a company in the United States whose allergen concentrations were expressed as Allergy Units (AUs). Specifically, we compared group 1 and 2 major allergens using two-site enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits and an in vivo intradermal test.
RESULTS
Major allergen concentrations were 17.0 microg/mg (5.0 microg/mg of Der f 1 and 12.0 microg/mg of Der f 2) for a D. farinae extract and 24.0 microg/mg (11.6 microg/mg of Der p 1 and 12.4 microg/mg of Der p 2) for a D. pteronyssinus extract. Using chloramphenicol (CAP) inhibition assays, AUs were 12.5 AU/microg for a D. farinae extract and 12.8 AU/microg for a D. pteronyssinus extract. Allergenic activities were 3- to 4-fold stronger when assessed by intradermal skin tests for in vivo standardization.
CONCLUSIONS
Allergen extracts were prepared from Korean house dust mites and the allergenicities of the extracts were estimated using AU measurements. House dust mite extracts prepared in this study could be utilized as a reference material, which will be useful for the development of diagnostic and immunotherapeutic reagents in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Allergens
Antigens, Dermatophagoides
Arthropod Proteins
Chloramphenicol
Cysteine Endopeptidases
Dust
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Hypersensitivity
Indicators and Reagents
Korea
Pyroglyphidae
Skin Tests
United States
Allergens
Antigens, Dermatophagoides
Arthropod Proteins
Chloramphenicol
Cysteine Endopeptidases
Dust
Indicators and Reagents
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Comparison between Newly Developed and Commercial Inhalant Skin Prick Test Reagents Using In Vivo and In Vitro Methods
Sang Chul Lee, Da Woon Sim, Jongsun Lee, Kyoung Yong Jeong, Kyung Hee Park, Jae-Hyun Lee, Jung Dong Kim, Jung-Won Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(13):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e101.Different Responses in Induction of Allergen Specific Immunoglobulin G4 and IgE-Blocking Factors for Three Mite Subcutaneous Immunotherapy Products
Kyung Hee Park, Sang Chul Lee, Young Woong Son, Kyoung Yong Jeong, Yoo Seob Shin, Jung U Shin, Da Woon Sim, Hye Jung Park, Jae-Hyun Lee, Kwang Hoon Lee, Jung-Won Park
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(6):1427-1434. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1427.Influence of the Adjuvants and Genetic Background on the Asthma Model Using Recombinant Der f 2 in Mice
Yoon-Seok Chang, Yoon-Keun Kim, Seong Gyu Jeon, Sae-Hoon Kim, Sun-Sin Kim, Heung-Woo Park, Kyung-Up Min, You-Young Kim, Sang-Heon Cho
Immune Netw. 2013;13(6):295-300. doi: 10.4110/in.2013.13.6.295.Allergen standardization
Jung-Won Park, Kyoung Yong Jeong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(4):191-196. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.4.191.
Reference
-
1. Jeong KY, Hong CS, Yong TS. Domestic arthropods and their allergens. Protein Pept Lett. 2007. 14:934–942.2. Ree HI, Jeon SH, Lee IY, Hong CS, Lee DK. Fauna and geographical distribution of house dust mites in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1997. 35:9–17.3. Thomas WR, Heinrich TK, Smith WA, Hales BJ. Pyroglyphid house dust mite allergens. Protein Pept Lett. 2007. 14:943–953.4. Weghofer M, Thomas WR, Kronqvist M, Mari A, Purohit A, Pauli G, Horak F, Grönlund H, van Hage M, Valenta R, Vrtala S. Variability of IgE reactivity profiles among European mite allergic patients. Eur J Clin Invest. 2008. 38:959–965.5. Burazer L, Milovanovic K, Milovanovic M, Vuckovic O, Velickovic TC, Gavrovic-Jankulovic M. Impact of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus mite body raw material on house dust mite allergy diagnosis in a Serbian population. Med Vet Entomol. 2011. 25:77–83.6. Park HS, Nahm DH, Chae BW. Allergen standardization of Dermatophagoides farinae (D. farinae) extracts. Korean J Allergy. 1996. 16:19–25.7. Brunetto B, Tinghino R, Braschi MC, Antonicelli L, Pini C, Iacovacci P. Characterization and comparison of commercially available mite extracts for in vivo diagnosis. Allergy. 2010. 65:184–190.8. Jeong KY, Hong CS, Lee JS, Park JW. Optimization of allergen standardization. Yonsei Med J. 2011. 52:393–400.9. Jeong KY, Jin HS, Oh SH, Hong CS, Lee IY, Ree HI, Yong TS. Monoclonal antibodies to recombinant Der f 2 and development of a two-site ELISA sensitive to major Der f 2 isoallergen in Korea. Allergy. 2002. 57:29–34.10. Kim CW, Park JW, Hong CS. Allergen standardization of the whole body extracts of the Korean house dust mites by in vitro method. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 18:28–39.11. Kim CW, Park JW, Hong CS. Allergen standardization of whole body extract of Korean house dust mite by in vivo method. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 18:232–242.12. Park JW, Kim KS, Jin HS, Kim CW, Kang DB, Choi SY, Yong TS, Oh SH, Hong CS. Der p 2 isoallergens have different allergenicity, and quantification with 2-site ELISA using monoclonal antibodies is influenced by the isoallergens. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002. 32:1042–1047.13. Jeong KY, Lee IY, Yong TS, Lee JH, Kim EJ, Lee JS, Hong CS, Park JW. Sequence polymorphisms of Der f 1, Der p 1, Der f 2 and Der p 2 from Korean house dust mite isolates. Exp Appl Acarol. Forthcoming 2012.14. Gregory LG, Lloyd CM. Orchestrating house dust mite-associated allergy in the lung. Trends Immunol. 2011. 32:402–411.15. Jacquet A. The role of innate immunity activation in house dust mite allergy. Trends Mol Med. 2011. 17:604–611.16. Wan GH, Li CS, Lin RH. Airborne endotoxin exposure and the development of airway antigen-specific allergic responses. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000. 30:426–432.17. Tulic MK, Holt PG, Sly PD. Modification of acute and late-phase allergic responses to ovalbumin with lipopolysaccharide. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002. 129:119–128.18. Eisenbarth SC, Piggott DA, Huleatt JW, Visintin I, Herrick CA, Bottomly K. Lipopolysaccharide-enhanced, toll-like receptor 4-dependent T helper cell type 2 responses to inhaled antigen. J Exp Med. 2002. 196:1645–1651.19. Braun-Fahrländer C, Riedler J, Herz U, Eder W, Waser M, Grize L, Maisch S, Carr D, Gerlach F, Bufe A, Lauener RP, Schierl R, Renz H, Nowak D, von Mutius E. Allergy and Endotoxin Study Team. Environmental exposure to endotoxin and its relation to asthma in school-age children. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:869–877.20. Trivedi B, Valerio C, Slater JE. Endotoxin content of standardized allergen vaccines. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 111:777–783.21. Valerio CR, Murray P, Arlian LG, Slater JE. Bacterial 16S ribosomal DNA in house dust mite cultures. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 116:1296–1300.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Allergen standardization of whole body extract of Korean house dust mite by in vivo method
- Repellent effect of Mate tea and Jasmine tea against house dust mites (Dermatophagoides farinae and D. pteronyssinus)
- Distribution of House Dust Mites in the Bedroom of Patients with Allergic Rhinitis in Pusan Area
- Avian Mite Dermatitis: Observation of the Causative Mites and Clinical Findings
- Sensitization of house dust mites in the allergic patients and mite ecology in their house dusts