Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 Jul;7(4):384-392. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.4.384.
IgE Reactivity of the Dog Lipocalin Allergen Can f 4 and the Development of a Sandwich ELISA for Its Quantification
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Microbiology, Institute of Clinical Medicine and Biocenter Kuopio, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio Campus, Finland. Marja.Rytkonen-Nissinen@uef.fi
- 2Institute of Dentistry, School of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio Campus, Finland.
- 3Department of Pulmonary Diseases, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland.
- 4Institute of Biomedicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio Campus, Finland.
- 5Institute of Biotechnology, Viikki Biocenter, University of Helsinki, Finland.
- KMID: 2166686
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.4.384
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Divergent results on the IgE reactivity of dog-allergic subjects to Can f 4 have been reported. The aim of this study was to evaluate the significance of Can f 4 in dog allergy and to develop an immunochemical method for measuring Can f 4 content in environmental samples.
METHODS
We purified the natural dog allergen Can f 4 from a dog dander extract by monoclonal antibody-based affinity chromatography and generated its variant in a recombinant form. Sixty-three dog-allergic patients and 12 nonallergic control subjects were recruited in the study. The IgE-binding capacity of natural Can f 4 and its recombinant variant was assessed by ELISA, immunoblotting, and skin prick tests (SPT).
RESULTS
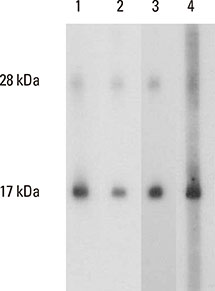
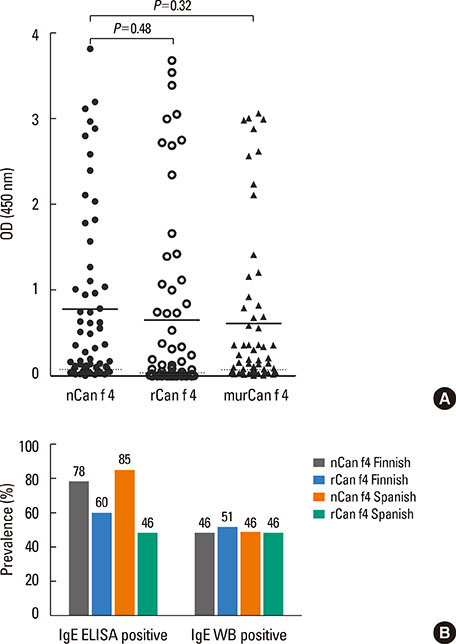
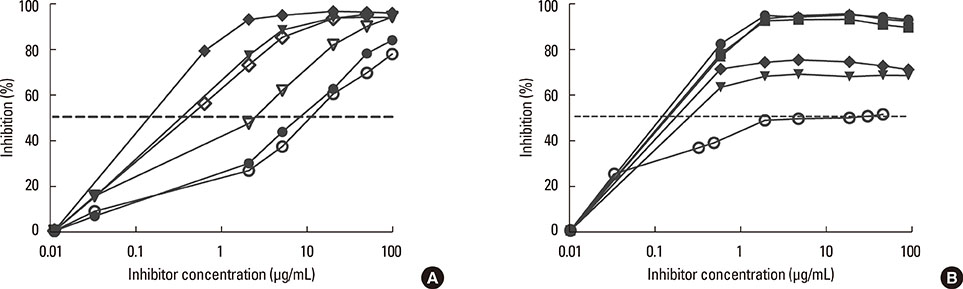
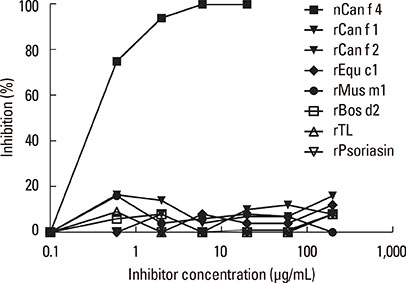
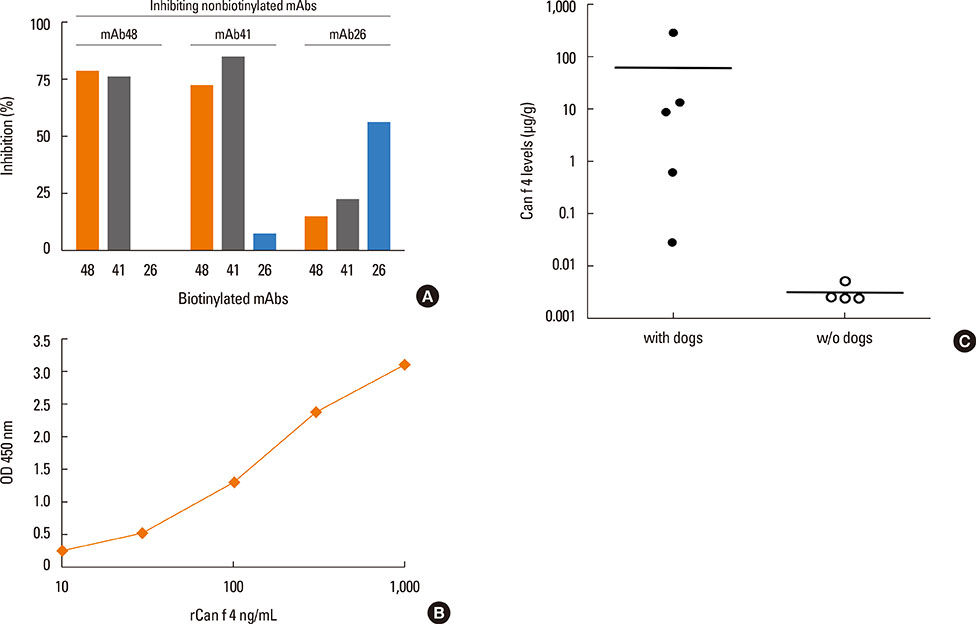
Eighty-one percent of the dog-allergic patients showed a positive result to the immunoaffinity-purified natural Can f 4 in IgE ELISA, but only 46% in IgE immunoblotting. Respective results with the recombinant Can f 4 variant were 54% and 49%. SPT results reflected those obtained in ELISA and immunoblotting. The overall IgE reactivity of the immunoaffinity-purified natural Can f 4 was found to depend strongly on the integrity of the allergen's conformation. A sandwich ELISA based on monoclonal antibodies was found to be functional for measuring Can f 4 in environmental samples.
CONCLUSIONS
Can f 4 is a major allergen of dog together with Can f 1 and Can f 5. In combination with other dog allergens, it improves the reliability of allergy tests in dog allergy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Perzanowski MS, Rönmark E, Nold B, Lundbäck B, Platts-Mills TA. Relevance of allergens from cats and dogs to asthma in the northernmost province of Sweden: schools as a major site of exposure. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 103:1018–1024.2. Partti-Pellinen K, Marttila O, Mäkinen-Kiljunen S, Haahtela T. Occurrence of dog, cat, and mite allergens in public transport vehicles. Allergy. 2000; 55:65–68.3. Bufford JD, Reardon CL, Li Z, Roberg KA, DaSilva D, Eggleston PA, et al. Effects of dog ownership in early childhood on immune development and atopic diseases. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:1635–1643.4. Munir AK, Einarsson R, Schou C, Dreborg SK. Allergens in school dust. I. The amount of the major cat (Fel d I) and dog (Can f I) allergens in dust from Swedish schools is high enough to probably cause perennial symptoms in most children with asthma who are sensitized to cat and dog. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993; 91:1067–1074.5. World Health Organization. International Union of Immunological Societies, Allergen Nomenclature- Sub-committee. Allergen nomenclature [Internet]. [place unknown]: Allergen Nomenclature Sub-committee;cited 2014 Dec 12. Available from: http://www.allergen.org.6. Konieczny A, Morgenstern JP, Bizinkauskas CB, Lilley CH, Brauer AW, Bond JF, et al. The major dog allergens, Can f 1 and Can f 2, are salivary lipocalin proteins: cloning and immunological characterization of the recombinant forms. Immunology. 1997; 92:577–586.7. Saarelainen S, Taivainen A, Rytkönen-Nissine M, Auriola S, Immonen A, Mäntyjärvi R, et al. Assessment of recombinant dog allergens Can f 1 and Can f 2 for the diagnosis of dog allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:1576–1582.8. Mattsson L, Lundgren T, Olsson P, Sundberg M, Lidholm J. Molecular and immunological characterization of Can f 4: a dog dander allergen cross-reactive with a 23 kDa odorant-binding protein in cow dander. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010; 40:1276–1287.9. Hilger C, Swiontek K, Arumugam K, Lehners C, Hentges F. Identification of a new major dog allergen highly cross-reactive with Fel d 4 in a population of cat- and dog-sensitized patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:1149–1151.10. Pandjaitan B, Swoboda I, Brandejsky-Pichler F, Rumpold H, Valenta R, Spitzauer S. Escherichia coli expression and purification of recombinant dog albumin, a cross-reactive animal allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 105:279–285.11. Mattsson L, Lundgren T, Everberg H, Larsson H, Lidholm J. Prostatic kallikrein: a new major dog allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:362–368.12. Ylönen J, Mäntyjärvi R, Taivainen A, Virtanen T. IgG and IgE antibody responses to cow dander and urine in farmers with cow-induced asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992; 22:83–90.13. van Ree R, van Leeuwen WA, Bulder I, Bond J, Aalberse RC. Purified natural and recombinant Fel d 1 and cat albumin in in vitro diagnostics for cat allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 104:1223–1230.14. Saarelainen S, Rytkönen-Nissinen M, Rouvinen J, Taivainen A, Auriola S, Kauppinen A, et al. Animal-derived lipocalin allergens exhibit immunoglobulin E cross-reactivity. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:374–381.15. Kauppinen A, Peräsaari J, Taivainen A, Kinnunen T, Saarelainen S, Rytkönen-Nissinen M, et al. Association of HLA class II alleles with sensitization to cow dander Bos d 2, an important occupational allergen. Immunobiology. 2012; 217:8–12.16. Zeiler T, Mäntyjärvi R, Rautiainen J, Rytkönen-Nissinen M, Vilja P, Taivainen A, et al. T cell epitopes of a lipocalin allergen colocalize with the conserved regions of the molecule. J Immunol. 1999; 162:1415–1422.17. O'Connell KL, Stults JT. Identification of mouse liver proteins on two-dimensional electrophoresis gels by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of in situ enzymatic digests. Electrophoresis. 1997; 18:349–359.18. Niemi MH, Rytkönen-Nissinen M, Jänis J, Virtanen T, Rouvinen J. Structural aspects of dog allergies: the crystal structure of a dog dander allergen Can f 4. Mol Immunol. 2014; 61:7–15.19. Rautiainen J, Auriola S, Rouvinen J, Kauppinen J, Zeiler T, Novikov D, et al. Molecular and crystal properties of Bos d 2, an allergenic protein of the lipocalin family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998; 247:746–750.20. Porre S, Heinonen S, Mäntyjärvi R, Rytkönen-Nissinen M, Perola O, Rautiainen J, et al. Psoriasin, a calcium-binding protein with chemotactic properties is present in the third trimester amniotic fluid. Mol Hum Reprod. 2005; 11:87–92.21. Zeiler T, Taivainen A, Rytkönen M, Rautiainen J, Karjalainen H, Mäntyjärvi R, et al. Recombinant allergen fragments as candidate preparations for allergen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 100:721–727.22. Rautiainen J, Rytkönen M, Virtanen T, Pentikäinen J, Zeiler T, Mäntyjärvi R. BDA20, a major bovine dander allergen characterized at the sequence level, is Bos d 2. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 100:251–252.23. Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW. NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012; 9:671–675.24. Zampieri S, Ghirardello A, Doria A, Tonello M, Bendo R, Rossini K, et al. The use of Tween 20 in immunoblotting assays for the detection of autoantibodies in connective tissue diseases. J Immunol Methods. 2000; 239:1–11.25. Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979; 76:4350–4354.26. Zeng FY, Oka JA, Weigel PH. Renaturation and ligand blotting of the major subunit of the rat asialoglycoprotein receptor after denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Glycobiology. 1996; 6:247–255.27. Aalberse JA, Meijer Y, Derksen N, van der Palen-Merkus T, Knol E, Aalberse RC. Moving from peanut extract to peanut components: towards validation of component-resolved IgE tests. Allergy. 2013; 68:748–756.28. Ylönen J, Mäntyjärvi R, Taivainen A, Virtanen T. Comparison of the antigenic and allergenic properties of three types of bovine epithelial material. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1992; 99:112–117.29. Ball T, Linhart B, Sonneck K, Blatt K, Herrmann H, Valent P, et al. Reducing allergenicity by altering allergen fold: a mosaic protein of Phl p 1 for allergy vaccination. Allergy. 2009; 64:569–580.30. Moldaver D, Larché M. Immunotherapy with peptides. Allergy. 2011; 66:784–791.31. Kauppinen J, Zeiler T, Rautiainen J, Rytkönen-Nissinen M, Taivainen A, Mäntyjärvi R, et al. Mutant derivatives of the main respiratory allergen of cow are less allergenic than the intact molecule. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999; 29:989–996.32. Hattori M, Hiramatsu K, Kurata T, Nishiura M, Takahashi K, Ametani A, et al. Complete refolding of bovine beta-lactoglobulin requires disulfide bond formation under strict conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005; 1752:154–165.33. Takai T, Yokota T, Yasue M, Nishiyama C, Yuuki T, Mori A, et al. Engineering of the major house dust mite allergen Der f 2 for allergen-specific immunotherapy. Nat Biotechnol. 1997; 15:754–758.34. Schramm G, Bufe A, Petersen A, Haas H, Merget R, Schlaak M, et al. Discontinuous IgE-binding epitopes contain multiple continuous epitope regions: results of an epitope mapping on recombinant Hol l 5, a major allergen from velvet grass pollen. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:331–341.35. Varshney S, Goldblum RM, Kearney C, Watanabe M, Midoro-Horiuti T. Major mountain cedar allergen, Jun a 1, contains conformational as well as linear IgE epitopes. Mol Immunol. 2007; 44:2781–2785.36. Rouvinen J, Jänis J, Laukkanen ML, Jylhä S, Niemi M, Päivinen T, et al. Transient dimers of allergens. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e9037.37. Schöll I, Kalkura N, Shedziankova Y, Bergmann A, Verdino P, Knittelfelder R, et al. Dimerization of the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 is important for its in vivo IgE-cross-linking potential in mice. J Immunol. 2005; 175:6645–6650.38. Reese G, Ballmer-Weber BK, Wangorsch A, Randow S, Vieths S. Allergenicity and antigenicity of wild-type and mutant, monomeric, and dimeric carrot major allergen Dau c 1: destruction of conformation, not oligomerization, is the roadmap to save allergen vaccines. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:944–951.39. Japaridze T, Senda A, Nozaki H, Yanagida M, Suzuki T, Ganzorig K, et al. Cloning, monoclonal antibody production, and bodily distribution pattern of a bovine lipocalin. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012; 76:712–720.40. Gu Y, Liu Q, Chen P, Guo C, Liu Y, Zhao Y, et al. Characterization of the oligomerization and ligand-binding properties of recombinant rat lipocalin 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1834:1–7.41. Rautiainen J, Auriola S, Konttinen A, Virtanen T, Rytkönen-Nissinen M, Zeiler T, et al. Two new variants of the lipocalin allergen Bos d 2. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2001; 763:91–98.42. Virtanen T, Kinnunen T, Rytkönen-Nissinen M. Mammalian lipocalin allergens--insights into their enigmatic allergenicity. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 42:494–504.43. Smith W, Butler AJ, Hazell LA, Chapman MD, Pomés A, Nickels DG, et al. Fel d 4, a cat lipocalin allergen. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:1732–1738.44. Nilsson OB, Binnmyr J, Zoltowska A, Saarne T, van Hage M, Grönlund H. Characterization of the dog lipocalin allergen Can f 6: the role in cross-reactivity with cat and horse. Allergy. 2012; 67:751–757.45. Madhurantakam C, Nilsson OB, Uchtenhagen H, Konradsen J, Saarne T, Högbom E, et al. Crystal structure of the dog lipocalin allergen Can f 2: implications for cross-reactivity to the cat allergen Fel d 4. J Mol Biol. 2010; 401:68–83.46. Mussalo-Rauhamaa H, Reijula K, Malmberg M, Mäkinen-Kiljunen S, Lapinlampi T. Dog allergen in indoor air and dust during dog shows. Allergy. 2001; 56:878–882.47. Vredegoor DW, Willemse T, Chapman MD, Heederik DJ, Krop EJ. Can f 1 levels in hair and homes of different dog breeds: lack of evidence to describe any dog breed as hypoallergenic. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 130:904–909.e7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- IgE Binding Reactivity of Peptide Fragments of Bla g 4, a Major German Cockroach Allergen
- Validation of measurement of house dust mite-specific IgE antibodies in serum using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- Identification of Tyrophagus putrescentiae allergens and evaluation of cross-reactivity with Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus
- Monoclonal Antibodies to Recombinant Fag e 3 Buckwheat Allergen and Development of a Two-site ELISA for Its Quantification
- IgE Cross-Reactivity between Humulus japonicus and Humulus lupulus