Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2017 Sep;9(5):417-422. 10.4168/aair.2017.9.5.417.
Monoclonal Antibodies to Recombinant Fag e 3 Buckwheat Allergen and Development of a Two-site ELISA for Its Quantification
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2383989
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2017.9.5.417
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Buckwheat is a major cause of anaphylaxis, and Fag e 3 is the key major allergen in buckwheat. However, an immunoassay system for the quantification of Fag e 3 has yet to be developed.
METHODS
We developed a 2-site enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) produced against recombinant Fag e 3. We applied this ELISA to quantify native Fag e 3 in total buckwheat extract.
RESULTS
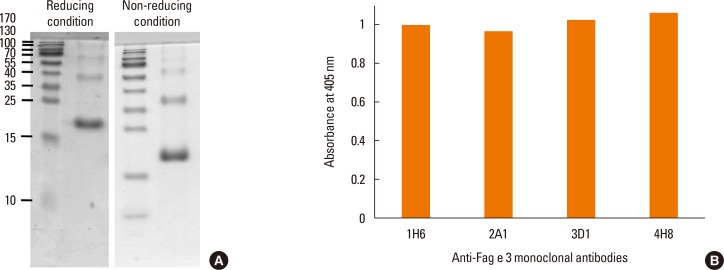
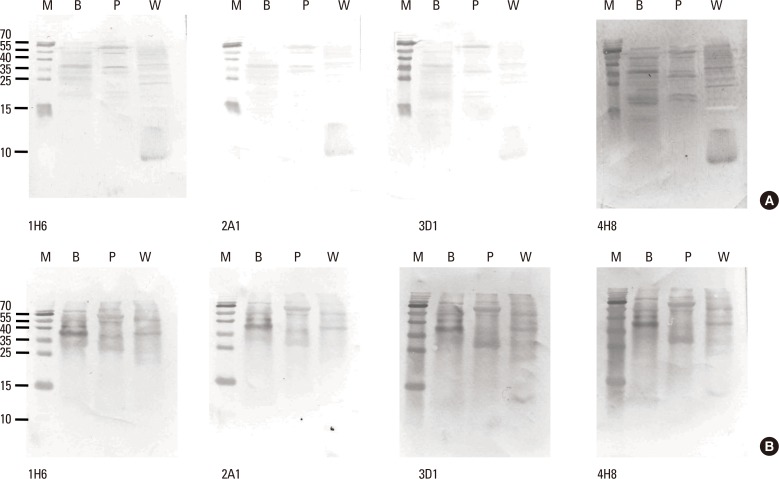
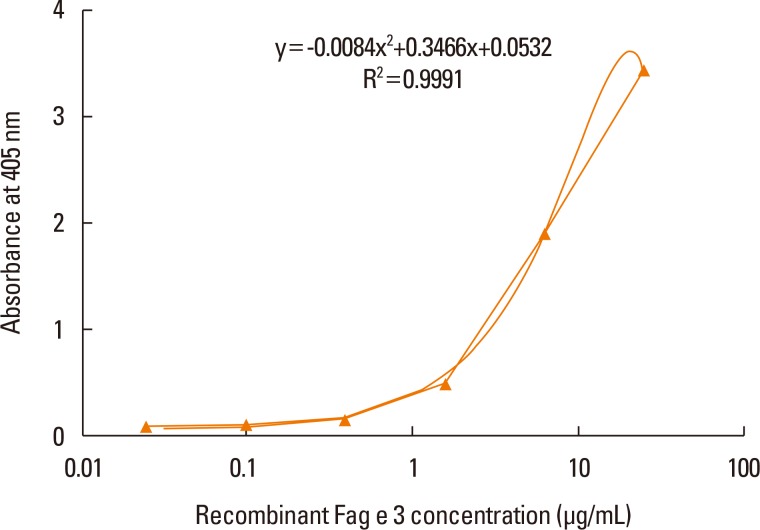
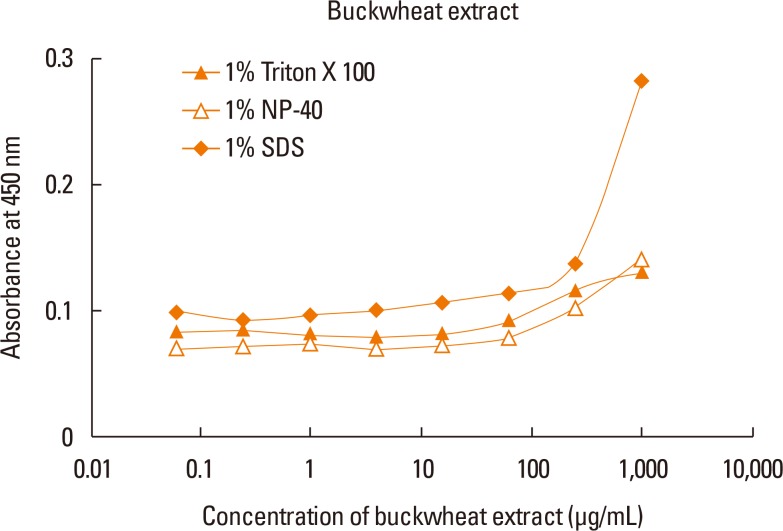
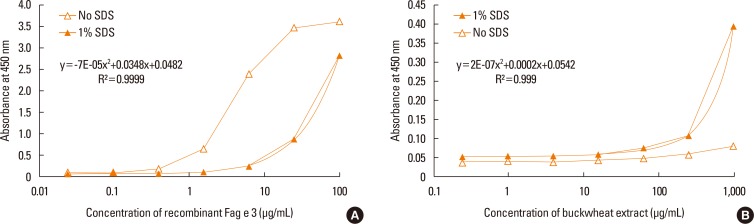
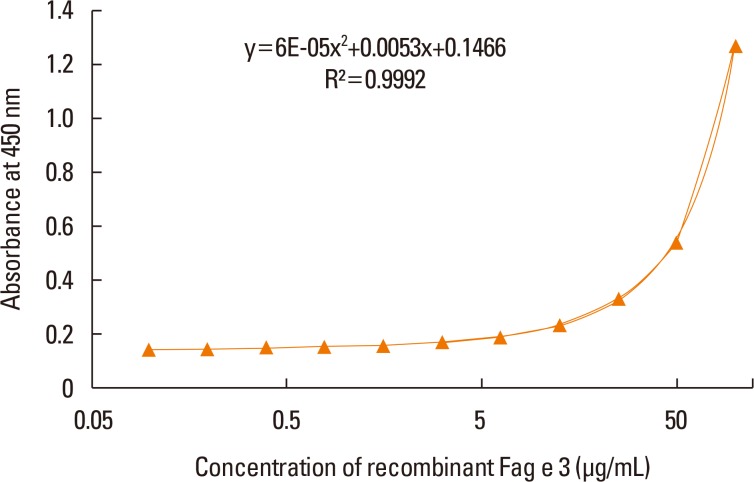
Four clones of mAbs were produced, and all recognized vicilin allergens not only from buckwheat, but also from peanut and walnut. However, the ELISA using these antibodies was only able to quantify Fag e 3 in the total extract after addition of 1% sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) and heating, which facilitated dissociation of the allergen. The detection limit of the developed 2-site ELISA was 0.8 µg/mL. The measurement of Fag e 3 in the total extract of buckwheat showed that approximately 12% of protein in total buckwheat extract was Fag e 3.
CONCLUSIONS
We have developed an ELISA system for the quantification of the group 3 buckwheat allergen, Fag e 3, specifically. This assay will be useful for standardization of buckwheat allergens and monitoring of buckwheat contamination in foods.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Han SM, Heo YR. Changes of prevalence of food allergy in elementary school student and perception of it in school nutritionist in Korea, 1995–2015. J Nutr Health. 2016; 49:8–17.
Article2. Kim SR, Park HJ, Park KH, Lee JH, Park JW. IgE sensitization patterns to commonly consumed foods determined by skin prick test in Korean adults. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:1197–1201. PMID: 27478328.
Article3. Lee SY, Ahn K, Kim J, Jang GC, Min TK, Yang HJ, et al. A multicenter retrospective case study of anaphylaxis triggers by age in Korean children. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016; 8:535–540. PMID: 27582405.
Article4. Chandrupatla CV, Kundu RV, Aronson IK. Buckwheat allergy and atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005; 53:356–357. PMID: 16021142.
Article5. Heffler E, Nebiolo F, Asero R, Guida G, Badiu I, Pizzimenti S, et al. Clinical manifestations, co-sensitizations, and immunoblotting profiles of buckwheat-allergic patients. Allergy. 2011; 66:264–270. PMID: 20804471.
Article6. Taylor SL, Baumert JL. Worldwide food allergy labeling and detection of allergens in processed foods. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2015; 101:227–234. PMID: 26022883.
Article7. Park JW, Kang DB, Kim CW, Ko SH, Yum HY, Kim KE, et al. Identification and characterization of the major allergens of buckwheat. Allergy. 2000; 55:1035–1041. PMID: 11097313.
Article8. Choi SY, Sohn JH, Lee YW, Lee EK, Hong CS, Park JW. Characterization of buckwheat 19-kD allergen and its application for diagnosing clinical reactivity. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007; 144:267–274. PMID: 17641547.
Article9. Maruyama N, Sato S, Yanagida N, Cabanos C, Ito K, Borres MP, et al. Clinical utility of recombinant allergen components in diagnosing buckwheat allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016; 4:322–323.e3. PMID: 26776372.
Article10. Koeberl M, Clarke D, Lopata AL. Next generation of food allergen quantification using mass spectrometric systems. J Proteome Res. 2014; 13:3499–3509. PMID: 24824675.
Article11. Jeong KY, Hong CS, Lee JS, Park JW. Optimization of allergen standardization. Yonsei Med J. 2011; 52:393–400. PMID: 21488181.
Article12. Shewry PR, Napier JA, Tatham AS. Seed storage proteins: structures and biosynthesis. Plant Cell. 1995; 7:945–956. PMID: 7640527.
Article13. Villalta D, Conte M, Asero R, Da Re M, Stella S, Martelli P. Isolated IgE reactivity to native walnut vicilin-like protein (nJug r 2) on ISACTM microarray is due to cross-reactive carbohydrate epitopes. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013; 51:1991–1995. PMID: 23585182.14. Barre A, Sordet C, Culerrier R, Rancé F, Didier A, Rougé P. Vicilin allergens of peanut and tree nuts (walnut, hazelnut and cashew nut) share structurally related IgE-binding epitopes. Mol Immunol. 2008; 45:1231–1240. PMID: 18029017.
Article15. Badenoch-Jones J, Spencer D, Higgins TJ, Millerd A. The role of glycosylation in storage-protein synthesis in developing pea seeds. Planta. 1981; 153:201–209. PMID: 24276822.
Article16. Yang ZH, Li C, Li YY, Wang ZH. Effects of Maillard reaction on allergenicity of buckwheat allergen Fag t 3 during thermal processing. J Sci Food Agric. 2013; 93:1510–1515. PMID: 23165788.
Article17. Pomés A, Vinton R, Chapman MD. Peanut allergen (Ara h 1) detection in foods containing chocolate. J Food Prot. 2004; 67:793–798. PMID: 15083733.18. Shin DS, Compadre CM, Maleki SJ, Kopper RA, Sampson H, Huang SK, et al. Biochemical and structural analysis of the IgE binding sites on Ara h 1, an abundant and highly allergenic peanut protein. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:13753–13759. PMID: 9593717.19. de Jong EC, Van Zijverden M, Spanhaak S, Koppelman SJ, Pellegrom H, Penninks AH. Identification and partial characterization of multiple major allergens in peanut proteins. Clin Exp Allergy. 1998; 28:743–751. PMID: 9677140.
Article20. Pomés A, Helm RM, Bannon GA, Burks AW, Tsay A, Chapman MD. Monitoring peanut allergen in food products by measuring Ara h 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:640–645. PMID: 12642850.
Article21. Perry TT, Conover-Walker MK, Pomés A, Chapman MD, Wood RA. Distribution of peanut allergen in the environment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:973–976. PMID: 15131582.
Article22. Lee SY, Lee KS, Hong CH, Lee KY. Three cases of childhood nocturnal asthma due to buckwheat allergy. Allergy. 2001; 56:763–766. PMID: 11488670.
Article23. Park HS, Nahm DH. Buckwheat flour hypersensitivity: an occupational asthma in a noodle maker. Clin Exp Allergy. 1996; 26:423–427. PMID: 8732239.
Article24. Wensing M, Knulst AC, Piersma S, O'Kane F, Knol EF, Koppelman SJ. Patients with anaphylaxis to pea can have peanut allergy caused by cross-reactive IgE to vicilin (Ara h 1). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:420–424. PMID: 12589366.
Article25. Matsuda R, Yoshioka Y, Akiyama H, Aburatani K, Watanabe Y, Matsumoto T, et al. Interlaboratory evaluation of two enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits for the detection of egg, milk, wheat, buckwheat, and peanut in foods. J AOAC Int. 2006; 89:1600–1608. PMID: 17225608.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunoblot Analysis of Hypoallergenic Buckwheat with Monoclonal Antibodies to Raw Buckwheat
- Monoclonal antibodies to recombinant Der p 2, a major house dust mite allergen: specificity, epitope analysis and development of two-site capture ELISA
- Production of Recombinant Buckwheat Allergen
- IgE Reactivity of the Dog Lipocalin Allergen Can f 4 and the Development of a Sandwich ELISA for Its Quantification
- Detection of Hepatitis B Virus X Antigen and Anti-X Antibody in Sera of HBV Infected Patients by ELISA using Recombinant X Proteins Expressed in E. coli and Anti-HBx Monoclonal Antibodies