Yonsei Med J.
2018 Sep;59(7):852-856. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.7.852.
IgE Cross-Reactivity between Humulus japonicus and Humulus lupulus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac, jeongky@yuhs.ac
- 2Research and Development Department, Lofarma S.p.A, Viale Cassala, Milan, Italy.
- KMID: 2428911
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.7.852
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Japanese hop (Humulus japonicus) is a major cause of weed pollinosis in East Asia. However, supplies of commercial allergen extract from this plant have not met clinical demand. The pollen of common hop (Humulus lupulus), a closely related species, may provide an alternative source if there is strong IgE cross-reactivity between these two species. We aimed to compare the IgE cross-reactivity and allergenicity of common hop and Japanese hop pollen.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cross-reactivity was measured by inhibition ELISA. One- and two-dimensional (2D) gel analyses combined with IgE immunoblotting and mass spectrometry [liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS)] were performed to detect IgE-reactive pollen components.
RESULTS
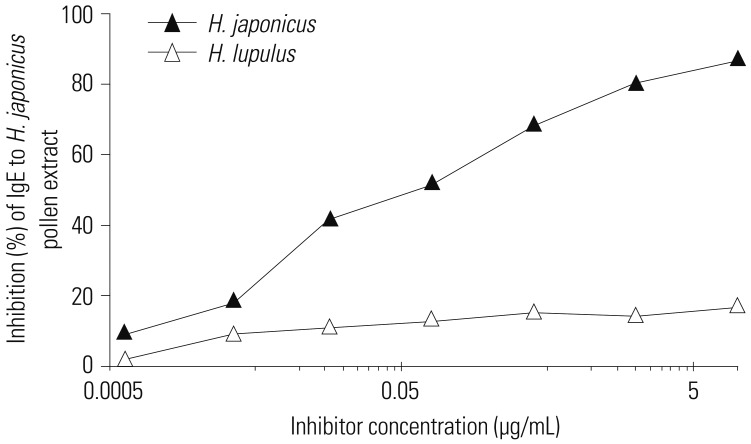
Up to 16.7% of IgE reactivity to Japanese hop was inhibited by common hop. A 12-kDa protein component of Japanese hop pollen that showed the most potent IgE reaction was absent from common hop. Six IgE-reactive components from Japanese hop were detected by 2D gel electrophoresis and LC-ESI-MS/MS, but showed low Mascot scores, preventing positive identification.
CONCLUSION
No significant IgE cross-reaction was observed for Japanese and common hop pollen allergens. Development of allergy diagnostic and immunotherapeutic reagents based on Japanese hop pollen are urgently needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Allergens
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Chromatography
Electrophoresis, Gel, Two-Dimensional
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Equipment and Supplies
Far East
Humans
Humulus*
Hypersensitivity
Immunoblotting
Immunoglobulin E*
Indicators and Reagents
Mass Spectrometry
Plants
Pollen
Rhinitis, Allergic, Seasonal
Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Allergens
Immunoglobulin E
Indicators and Reagents
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park HS, Nahm DH, Suh CH, Lee SM, Choi SY, Jung KS, et al. Evidence of Hop Japanese pollinosis in Korea: IgE sensitization and identification of allergenic components. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 100:475–479. PMID: 9338540.
Article2. Park HJ, Lee JH, Park KH, Kim KR, Han MJ, Choe H, et al. A six-year study on the changes in airborne pollen counts and skin positivity rates in Korea: 2008–2013. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:714–720. PMID: 26996572.
Article3. Wang XY, Ma TT, Wang XY, Zhuang Y, Wang XD, Ning HY, et al. Prevalence of pollen-induced allergic rhinitis with high pollen exposure in grasslands of northern China. Allergy. 2018; 73:1232–1243. PMID: 29322523.
Article4. Cui L, Yin J. Association of serum specific IgE levels with asthma in autumn pollen-induced allergic rhinitis: a retrospective analysis. J Asthma. 2018; 4. 18. [Epub]. DOI: 10.1080/02770903.2018.1466316.
Article5. Jeong KY, Son M, Choi SY, Park KH, Park HJ, Hong CS, et al. Standardization of weed pollen extracts, Japanese hop and mugwort, in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:399–406. PMID: 26847293.
Article6. Codina R, Crenshaw RC, Lockey RF. Considerations about pollen used for the production of allergen extracts. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015; 3:676–682. PMID: 26004305.
Article7. Esch RE. Allergen source materials and quality control of allergenic extracts. Methods. 1997; 13:2–13. PMID: 9281463.
Article8. Spiewak R, Gòra A, Dutkiewicz J. Work-related skin symptoms and type I allergy among eastern-Polish farmers growing hops and other crops. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2001; 8:51–56. PMID: 11426925.9. Reeb-Whitaker CK, Bonauto DK. Respiratory disease associated with occupational inhalation to hop (Humulus lupulus) during harvest and processing. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014; 113:534–538. PMID: 25216973.10. Jung CG, Yang EM, Lee JH, Kim HM, Park HS. Evaluation of the allergenic relationship between Humulus japonicus and Humulus lupulus pollen allergens. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017; 5:217–222.11. Park JW, Ko SH, Kim CW, Jeoung BJ, Hong CS. Identification and characterization of the major allergen of the Humulus japonicus pollen. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999; 29:1080–1086. PMID: 10457112.12. Burastero SE. Pollen-cross allergenicity mediated by panallergens: a clue to the patho-genesis of multiple sensitizations. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2006; 5:203–209. PMID: 17168790.
Article13. Tao AL, He SH. Cloning, expression, and characterization of pollen allergens from Humulus scandens (Lour) Merr and Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005; 26:1225–1232. PMID: 16174439.14. Jeong KY, Han IS, Choi SY, Lee JH, Lee JS, Hong CS, et al. Allergenicity of recombinant profilins from Japanese hop, Humulus japonicus. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2013; 23:345–350.15. Hong Q, Zhou S, Zhao H, Peng J, Li Y, Shang Y, et al. Allergenicity of recombinant Humulus japonicus pollen allergen 1 after combined exposure to ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Environ Pollut. 2018; 234:707–715. PMID: 29241157.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the allergenic relationship between Humulus japonicus and Humulus lupulus pollen allergens
- Cross - reactivity between pollens in patients sensitlzed to multiple pollens
- Standardization of Weed Pollen Extracts, Japanese Hop and Mugwort, in Korea
- Methanol extracts of Humulus japonicus induced apoptosis in human FaDu hypopharynx squamous carcinoma cells
- Optimized mixture of hops rho iso-alpha acids-rich extract and acacia proanthocyanidins-rich extract reduces insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and improves glucose and insulin control in db/db mice