Cancer Res Treat.
2008 Jun;40(2):45-52.
Cyclin D1 Overexpression, p16 Loss, and pRb Inactivation Play a Key Role in Pulmonary Carcinogenesis and have a Prognostic Implication for the Long-term Survival in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. myongnh@dankook.ac.kr
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: We investigated the immunoexpressions of cyclin D1, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 and phosphorylated retinoblastoma (p-pRb) proteins in non- small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) to demonstrate their key roles in tumorigenesis, their relationship with the clinicopathologic factors, and their prognostic influences on the long-term survival.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
115 surgically resected NSCLCs were immunohistochemically stained for the G1/S cell cycle proteins, with using a tissue microarray. The correlation between their immunoexpressions and the clinicopathologic prognostic factors, their inter-relationships and their single or combined effects on the long-term survival (over 5 years) were statistically analyzed by SPSS15.0.
RESULTS
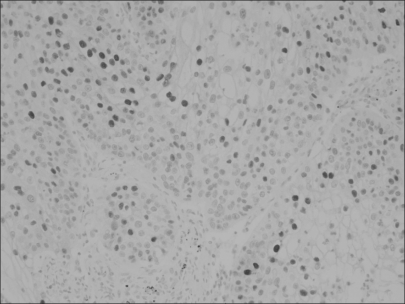
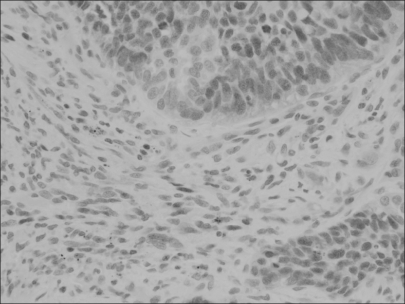
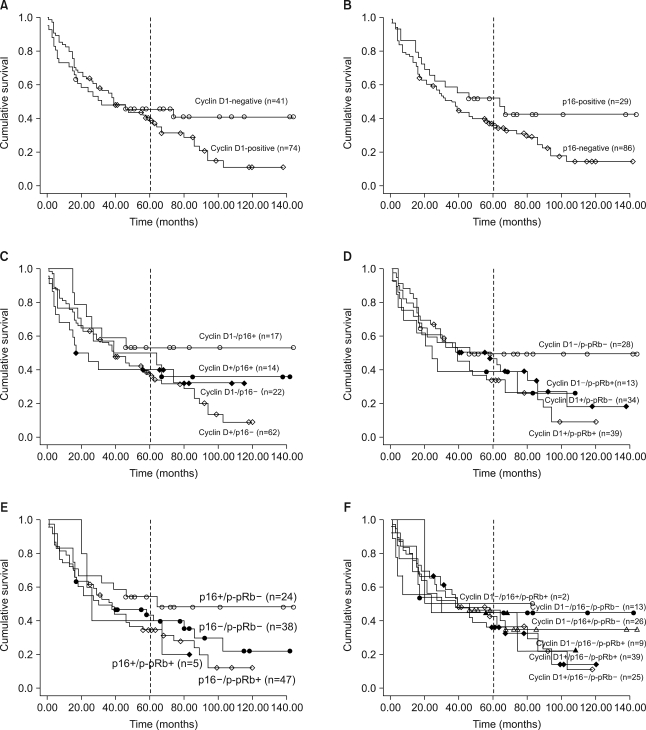
Loss of p16 was found in 75% of the cases and cyclin D1 overexpression and phosphorylated pRb (p-pRb) were found in 64% and 46%, respectively. Cyclin D1 overexpression was correlated with the p16 loss and pRb inactivation by phosphorylation. The p16 loss was tightly associated with p-pRb. The Kaplan-Meier survival curves disclosed that the cyclin D1-positive group and the p16-negative group showed a rapid decline of survival at the point of about 5 years after surgery and thereafter. The combined actions of cyclin D1 overexpression, loss of p16 and pRb inactivation tended to have an adverse influence on the prolonged survival.
CONCLUSIONS
The observation that cyclin D1 overexpression, p16 loss and pRb inactivation were largely found in NSCLCs suggests that they play an important role in pulmonary carcinogenesis. Also, their inverse or positive correlations indicate that the G1/S cell cycle proteins may act alternatively or synergistically on the mechanisms by which tumor cells escape the G1 restriction point. Finally, their solitary or combined actions might have a long-term effect on the survival.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cell Cycle Proteins
Cell Transformation, Neoplastic
Cyclin D1
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p16
Cyclins
G1 Phase Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Lung
Phosphorylation
Proteins
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma Protein
Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
United Nations
Cell Cycle Proteins
Cyclin D1
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p16
Cyclins
Proteins
Retinoblastoma Protein
Figure
Reference
-
2. Michalides R. Prognosis of GI cell-cycle regulators: useful for predicting course of disease and for assessment of therapy in cancer. J Pathol. 1999; 188:341–343. PMID: 10440742.3. Marchetti A, Doglioni C, Barbareschi M, Buttitta F, Pellegrini S, Gaeta P, et al. Cyclin D1 and retinoblastoma susceptibility gene alterations in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 1998; 75:187–192. PMID: 9462706.
Article4. Zhou JX, Niehans GA, Shar A, Rubins JB, Frizelle SP, Kratzke RA. Mechanisms of G1 checkpoint loss in resected early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2001; 32:27–38. PMID: 11282426.
Article5. Kang Y, Ozbun LL, Angdisen J, Moody TW, Prentice M, Diwan BA, et al. Altered expression of G1/S regulatory genes occurs early and frequently in transforming growth factor-(1 heterozygous mice. Carcinogenesis. 2002; 23:1217–1227. PMID: 12117781.6. Burke L, Flieder DB, Guinee DG, Brambilla E, Freedman AN, Bennett WP, et al. Prognostic implications of molecular and immunohistochemical profiles of the Rb and p53 cell cycle regulatory pathways in primary non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:232–234. PMID: 15671551.7. Kratzke RA, Greatens TM, Rubins JB, Maddaus MA, Niewoehner DE, Niehans GA, et al. Rb and p16INK4a expression in resected non-small cell lung tumors. Cancer Res. 1996; 56:3415–3420. PMID: 8758904.8. Shapiro GI, Edwards CD, Kobzik L, Godleski J, Richards W, Sugarbaker DJ, et al. Reciprocal Rb inactivation and p16INK4 expression in primary lung cancers and cell lines. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:505–509. PMID: 7834618.9. Brambilla E, Moro D, Gazzeri S, Brambilla C. Alterations of expression of Rb, p16INK4A and cyclin D1 in non-small cell lung carcinoma and their clinical significance. J Pathol. 1999; 188:351–360. PMID: 10440744.
Article10. Roesch A, Becker B, Meyer S, Hafner C, Johannes Wild P, Landthaler M, et al. Overexpression and hyperphosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein in the progression of malignant melanoma. Mod Pathol. 2005; 18:565–572. PMID: 15502804.
Article11. Kitagawa M, Higashi H, Jung HK, Suzuki-Takahashi I, Ikeda M, Tamai K, et al. The consensus motif for phosphorylation by cyclin D1-Cdk4 is different from that for phosphorylation by cyclin A/E-Cdk2. EMBO J. 1996; 15:7060–7069. PMID: 9003781.
Article12. Epposito V, Baldi A, Tonini G, Vincenzi B, Santini M, Ambrogi V, et al. Analysis of cell cycle regulator proteins in non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2004; 57:58–63. PMID: 14693837.13. Mohamed S, Yasufuku K, Hiroshima K, Nakajima T, Yoshida S, Suzuki M, et al. Prognostic implications of cell cycle-related proteins in primary respectable pathologic N2 nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2007; 109:2506–2514. PMID: 17487846.14. Huang CI, Taki T, Higashiyama M, Kohno N, Miyake M. p16 protein expression is associated with a poor prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Br J Cancer. 2000; 82:374–380. PMID: 10646891.
Article15. Kaye FJ. RB and cyclin dependent kinase pathways: defining a distinction between Rb and p16 loss in lung cancer. Oncogene. 2001; 21:6908–6914. PMID: 12362273.
Article16. Betticher DC, White GRM, Volanthen S, Liu X, Kappeler A, Altermatt HJ, et al. G1 control gene status is frequently altered in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 1997; 74:556–562. PMID: 9355981.17. Sakaguchi M, Fujii Y, Hirabayashi H, Yoon HE, Komoto Y, Que T, et al. Inversely correlated expression of p16 and Rb protein in non-small cell lung cancers: an immunohistocxhemical study. Int J Cancer. 1996; 65:442–445. PMID: 8621224.18. Lukas J, Aagaard L, Strauss M, Bartek J. Oncogenic aberrations of p16INK4/CDKN2 and cyclin D1 cooperate to deregulate G1 control. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:4818–4823. PMID: 7585513.19. Serrano M, Hannon GJ, Beach D. A new regulatory motif in cell-cylce control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature (Lond.). 1994; 366:704–707. PMID: 8259215.20. Betticher DC, Heighway J, Hasleton PS, Altermatt HJ, Ryder WDJ, Cenry T, et al. Prognostic significance of CCND1(cyclin D1) overexpression in primary resected non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 1996; 73:294–300. PMID: 8562333.21. Schauer E, Siriwardana S, Langan TA, Sclafani RA. Cyclin D1 overexpression vs. retinoblastoma inactivation: Implications for growth control evasion in non-small cell and small cell lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994; 91:7827–7831. PMID: 8052667.
Article22. Betticher DC, Heighway J, Thatcher N, Hasleton PS. Abnormal expression of CCND1 and RB1 in resection margin epithelia of lung cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 1997; 75:1761–1768. PMID: 9192978.23. Lonardo F, Rusch V, Langenfeld J, Dmitrovsky E, Klimstra DS. Overexpression of cyclin D1 and E is frequent in bronchial preneoplasia and precedes squamous cell carcinoma development. Cancer Res. 1999; 59:2470–2476. PMID: 10344760.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Functional Inactivation of pRb Associated with Cyclin D1- and Cyclin-dependent Kinase 4 Overexpression Plays A Key Role in Human Pituitary Tumorigenesis
- Expression of pRb, p16, Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E in Infiltrating Duct Carcinoma of the Breast
- Expression of p16 Protein and Cyclin D1 Protein in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas
- Expression of pRb, p53, p16 and Cyclin D1 and Their Clinical Implications in Urothelial Carcinoma
- Expression of G1/S Phase Checkpoint Proteins in Breast Carcinoma: Relationship to Clinicopathologic Factors andSurvival Rate