Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Dec;39(6):971-979. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.6.971.
The Effects of Body Mass Composition and Cushion Type on Seat-Interface Pressure in Spinal Cord Injured Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. asc88@cnuh.co.kr
- KMID: 2165624
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.6.971
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the effects of body mass composition and cushion type on seat-interface pressure in spinal cord injured (SCI) patients and healthy subjects.
METHODS
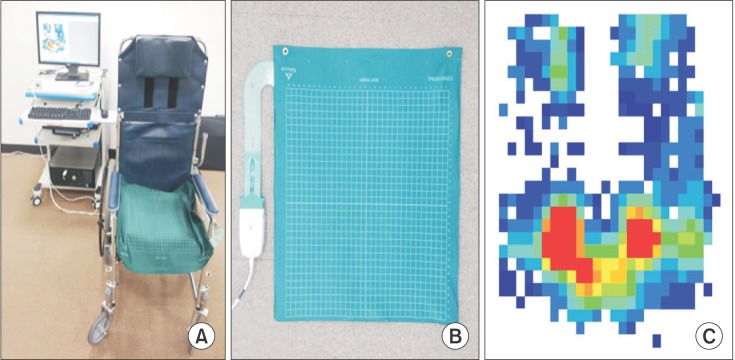
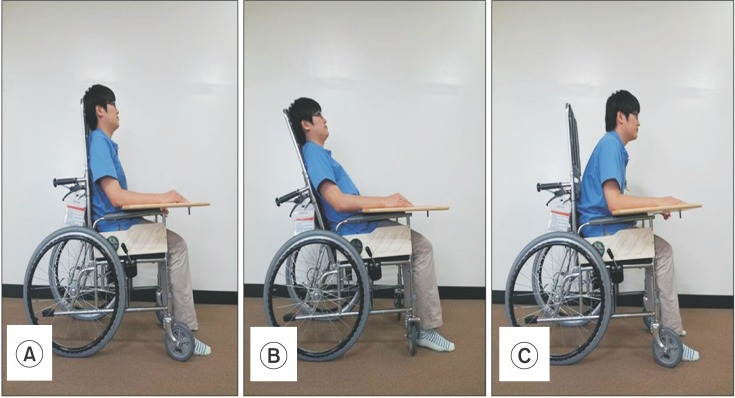
Twenty SCI patients and control subjects were included and their body mass composition measured. Seat-interface pressure was measured with participants in an upright sitting posture on a wheelchair with three kinds of seat cushion and without a seat cushion. We also measured the pressure with each participant in three kinds of sitting postures on each air-filled cushion. We used repeated measure ANOVA, the Mann-Whitney test, and Spearman correlation coefficient for statistical analysis.
RESULTS
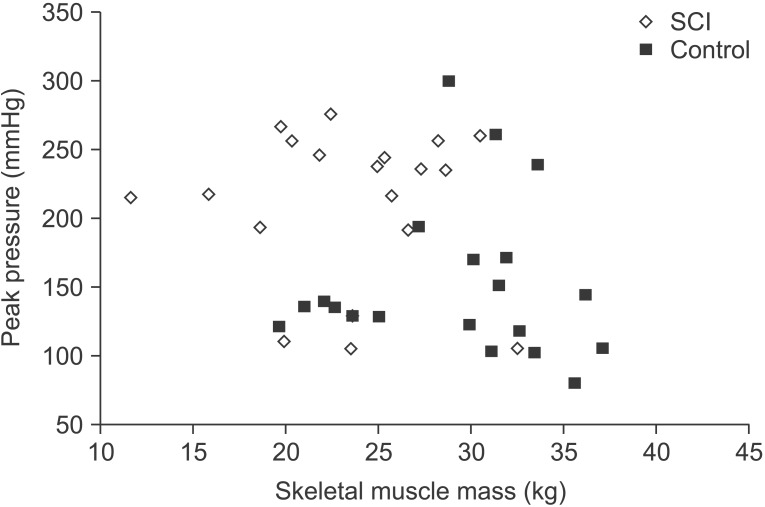
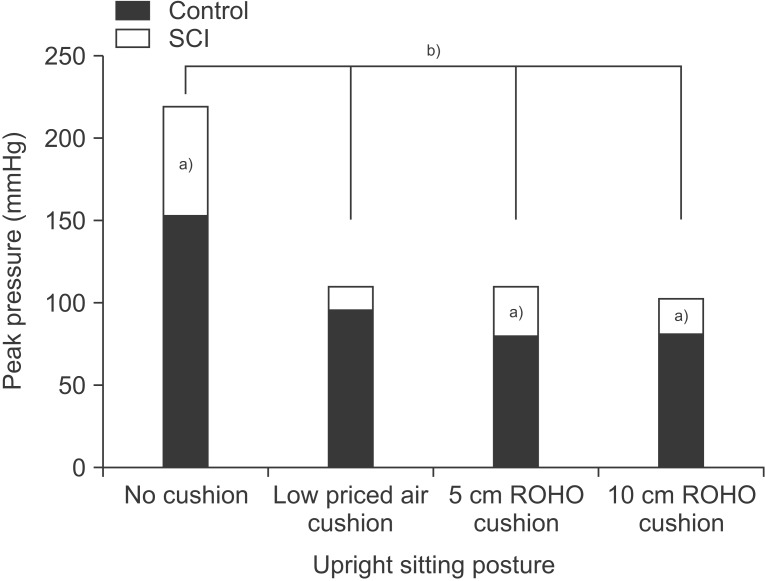
The total skeletal muscle mass and body water in the lower extremities were significantly higher in the control group, whilst body fat was significantly higher in the SCI group. However, the seat-interface pressure and body mass composition were not significantly correlated in both groups. Each of the three types of seat cushion resulted in significant reduction in the seat-interface pressure. The SCI group had significantly higher seatinterface pressure than the control group regardless of cushion type or sitting posture. The three kinds of sitting posture did not result in a significant reduction of seat-interface pressure.
CONCLUSION
We confirmed that the body mass composition does not have a direct effect on seat-interface pressure. However, a reduction of skeletal muscle mass and body water can influence the occurrence of pressure ulcers. Furthermore, in order to minimize seat-interface pressure, it is necessary to apply a method fitted to each individual rather than a uniform method.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel. Pressure ulcers in America: prevalence, incidence, and implications for the future. An executive summary of the National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel monograph. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2001; 14:208–215. PMID: 11902346.2. Mawson AR, Biundo JJ Jr, Neville P, Linares HA, Winchester Y, Lopez A. Risk factors for early occurring pressure ulcers following spinal cord injury. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1988; 67:123–127. PMID: 3377890.
Article3. Olin JW, Beusterien KM, Childs MB, Seavey C, McHugh L, Griffiths RI. Medical costs of treating venous stasis ulcers: evidence from a retrospective cohort study. Vasc Med. 1999; 4:1–7. PMID: 10355863.
Article4. Gordon MD, Gottschlich MM, Helvig EI, Marvin JA, Richard RL. Review of evidenced-based practice for the prevention of pressure sores in burn patients. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2004; 25:388–410. PMID: 15353931.
Article5. Reddy M, Gill SS, Rochon PA. Preventing pressure ulcers: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006; 296:974–984. PMID: 16926357.
Article6. Aissaoui R, Kauffmann C, Dansereau J, de Guise JA. Analysis of pressure distribution at the body-seat interface in able-bodied and paraplegic subjects using a deformable active contour algorithm. Med Eng Phys. 2001; 23:359–367. PMID: 11551812.
Article7. Burns SP, Betz KL. Seating pressures with conventional and dynamic wheelchair cushions in tetraplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999; 80:566–571. PMID: 10326923.
Article8. Gil-Agudo A, De la Pena-Gonzalez A, Del Ama-Espinosa A, Perez-Rizo E, Diaz-Dominguez E, Sanchez-Ramos A. Comparative study of pressure distribution at the user-cushion interface with different cushions in a population with spinal cord injury. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009; 24:558–563.
Article9. Coggrave MJ, Rose LS. A specialist seating assessment clinic: changing pressure relief practice. Spinal Cord. 2003; 41:692–695. PMID: 14639449.
Article10. Ragan R, Kernozek TW, Bidar M, Matheson JW. Seat-interface pressures on various thicknesses of foam wheelchair cushions: a finite modeling approach. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 83:872–875. PMID: 12048671.
Article11. Gefen A. Tissue changes in patients following spinal cord injury and implications for wheelchair cushions and tissue loading: a literature review. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2014; 60:34–45. PMID: 24515983.12. Stinson MD, Porter-Armstrong A, Eakin P. Seat-interface pressure: a pilot study of the relationship to gender, body mass index, and seating position. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 84:405–409. PMID: 12638109.
Article13. Elsner JJ, Gefen A. Is obesity a risk factor for deep tissue injury in patients with spinal cord injury? J Biomech. 2008; 41:3322–3331. PMID: 19026415.
Article14. Sopher R, Nixon J, Gorecki C, Gefen A. Exposure to internal muscle tissue loads under the ischial tuberosities during sitting is elevated at abnormally high or low body mass indices. J Biomech. 2010; 43:280–286. PMID: 19762029.
Article15. Hamanami K, Tokuhiro A, Inoue H. Finding the optimal setting of inflated air pressure for a multi-cell air cushion for wheelchair patients with spinal cord injury. Acta Med Okayama. 2004; 58:37–44. PMID: 15157010.16. Brienza DM, Karg PE. Seat cushion optimization: a comparison of interface pressure and tissue stiffness characteristics for spinal cord injured and elderly patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998; 79:388–394. PMID: 9552103.
Article17. Gutierrez EM, Alm M, Hultling C, Saraste H. Measuring seating pressure, area, and asymmetry in persons with spinal cord injury. Eur Spine J. 2004; 13:374–379. PMID: 14639505.
Article18. Linder-Ganz E, Shabshin N, Itzchak Y, Yizhar Z, Siev-Ner I, Gefen A. Strains and stresses in sub-dermal tissues of the buttocks are greater in paraplegics than in healthy during sitting. J Biomech. 2008; 41:567–580. PMID: 18054024.
Article19. Thorfinn J, Sjoberg F, Lidman D. Sitting pressure and perfusion of buttock skin in paraplegic and tetraplegic patients, and in healthy subjects: a comparative study. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2002; 36:279–283. PMID: 12477086.
Article20. Yuen HK, Garrett D. Comparison of three wheelchair cushions for effectiveness of pressure relief. Am J Occup Ther. 2001; 55:470–475. PMID: 11723993.
Article21. Hobson DA. Comparative effects of posture on pressure and shear at the body-seat interface. J Rehabil Res Dev. 1992; 29:21–31. PMID: 1432724.
Article22. Kim DA, Yi SH, Lee BS, Lim MH, Ryh BJ, Kim HC, et al. Impact of sitting time on seat-interface pressure of spinal cord injured patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2009; 33:614–618.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Impact of Sitting Time on Seat-Interface Pressure of Spinal Cord Injured Patients
- The Effects of Pressure Relief Methods at Wheelchair Seated Spinal Cord Injured Patients
- Pressure Relieving Effect of Adding a Pelvic Well Pad to a Wheelchair Cushion in Individuals With Spinal Cord Injury
- Clinical Utility of a Special Mattress in the Prevention of Pressure Ulcers
- The Effects of Growth Hormone on Quality of Life and Metabolism of Spinal Cord Injured Patients