J Vet Sci.
2015 Jun;16(2):187-194. 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.2.187.
The role of rpoS, hmp, and ssrAB in Salmonella enterica Gallinarum and evaluation of a triple-deletion mutant as a live vaccine candidate in Lohmann layer chickens
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine and Institute of Veterinary Science, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 200-701, Korea. twhahn@kangwon.ac.kr
- 2Department of Microbiology and Immunology, School of Dentistry, Chosun University, Gwangju 501-759, Korea. isbang@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2164528
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2015.16.2.187
Abstract
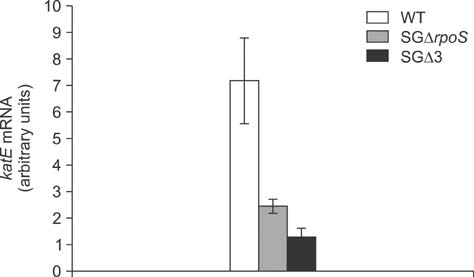
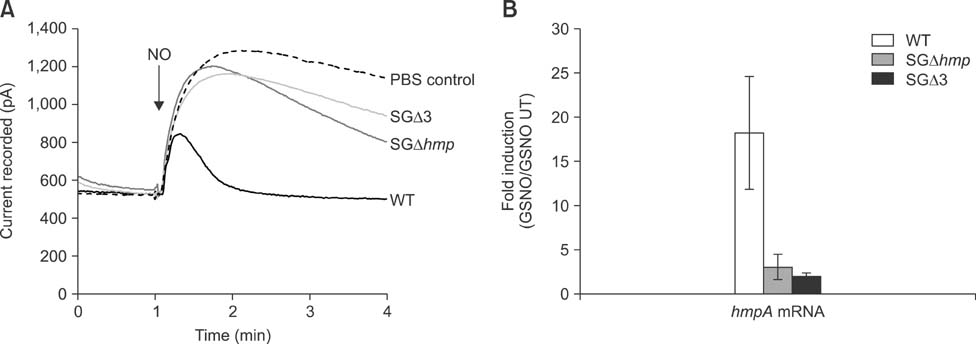
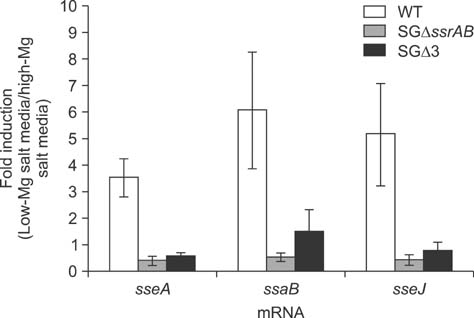
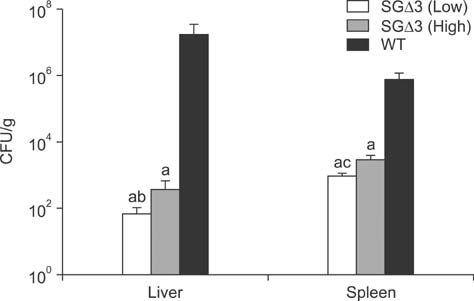
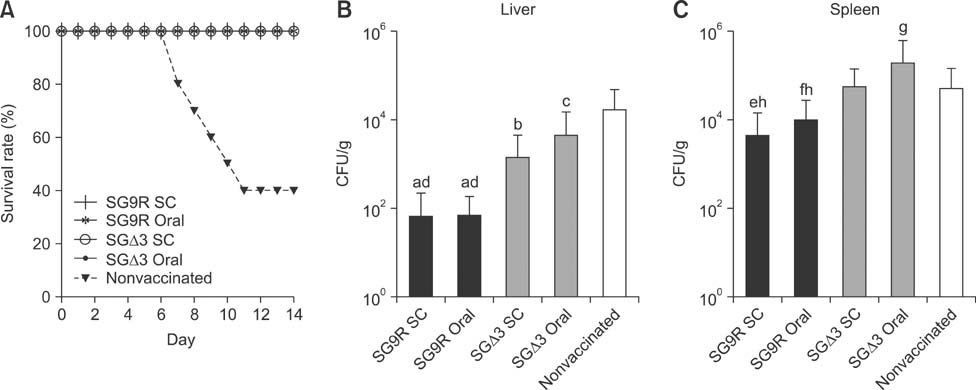
- Salmonella enterica Gallinarum (SG) causes fowl typhoid (FT), a septicemic disease in avian species. We constructed deletion mutants lacking the stress sigma factor RpoS, the nitric oxide (NO)-detoxifying flavohemoglobin Hmp, and the SsrA/SsrB regulator to confirm the functions of these factors in SG. All gene products were fully functional in wild-type (WT) SG whereas mutants harboring single mutations or a combination of rpoS, hmp, and ssrAB mutations showed hypersusceptibility to H2O2, loss of NO metabolism, and absence of Salmonella pathogenicity island (SPI)-2 expression, respectively. A triple-deletion mutant, SGDelta3 (SGDeltarpoSDeltahmpDeltassrAB), was evaluated for attenuated virulence and protection efficacy in two-week-old Lohmann layer chickens. The SGDelta3 mutant did not cause any mortality after inoculation with either 1 x 10(6) or 1 x 10(8) colony-forming units (CFUs) of bacteria. Significantly lower numbers of salmonellae were recovered from the liver and spleen of chickens inoculated with the SGDelta3 mutant compared to chickens inoculated with WT SG. Vaccination with the SGDelta3 mutant conferred complete protection against challenge with virulent SG on the chickens comparable to the group vaccinated with a conventional vaccine strain, SG9R. Overall, these results indicate that SGDelta3 could be a promising candidate for a live Salmonella vaccine against FT.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Administration, Oral
Animals
Bacterial Proteins/*genetics/immunology
*Chickens
Female
Poultry Diseases/*immunology/microbiology
Salmonella Infections, Animal/*immunology/microbiology
Salmonella Vaccines/administration & dosage/genetics/*immunology
Salmonella enterica/immunology/*physiology
Vaccines, Attenuated/administration & dosage/genetics/immunology
Virulence
Bacterial Proteins
Salmonella Vaccines
Vaccines, Attenuated
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bang IS, Frye JG, McClelland M, Velayudhan J, Fang FC. Alternative sigma factor interactions in Salmonella: σE and σH promote antioxidant defenses by enhancing σS levels. Mol Microbiol. 2005; 56:811–823.
Article2. Bang IS, Liu L, Vazquez-Torres A, Crouch ML, Stamler JS, Fang FC. Maintenance of nitric oxide and redox homeostasis by the Salmonella flavohemoglobin Hmp. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:28039–28047.
Article3. Barrow PA, Freitas Neto OC. Pullorum disease and fowl typhoid-new thoughts on old diseases: a review. Avian Pathol. 2011; 40:1–13.
Article4. Bouzoubaa K, Nagaraja KV, Kabbaj FZ, Newman JA, Pomeroy BS. Feasibility of using proteins from Salmonella gallinarum vs. 9R live vaccine for the prevention of fowl typhoid in chickens. Avian Dis. 1989; 33:385–391.
Article5. Boyen F, Pasmans F, Van Immerseel F, Morgan E, Botteldoorn N, Heyndrickx M, Volf J, Favoreel H, Hernalsteens JP, Ducatelle R, Haesebrouck F. A limited role for SsrA/B in persistent Salmonella Typhimurium infections in pigs. Vet Microbiol. 2008; 128:364–373.
Article6. Coynault C, Robbe-Saule V, Norel F. Virulence and vaccine potential of Salmonella typhimurium mutants deficient in the expression of the RpoS (σS) regulon. Mol Microbiol. 1996; 22:149–160.
Article7. Datsenko KA, Wanner BL. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97:6640–6645.
Article8. Deiwick J, Nikolaus T, Erdogan S, Hensel M. Environmental regulation of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1999; 31:1759–1773.
Article9. Fang FC, Libby SJ, Buchmeier NA, Loewen PC, Switala J, Harwood J, Guiney DG. The alternative σ factor KatF (RpoS) regulates Salmonella virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992; 89:11978–11982.10. Foley SL, Johnson TJ, Ricke SC, Nayak R, Danzeisen J. Salmonella pathogenicity and host adaptation in chicken-associated serovars. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013; 77:582–607.
Article11. Forrester MT, Foster MW. Protection from nitrosative stress: a central role for microbial flavohemoglobin. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012; 52:1620–1633.
Article12. Hart TW. Some observations concerning the S-nitroso and S-phenylsulphonyl derivatives of L-cysteine and glutathione. Tetrahedron Lett. 1985; 26:2013–2016.
Article13. Jeong JH, Song M, Park SI, Cho KO, Rhee JH, Choy HE. Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum requires ppGpp for internalization and survival in animal cells. J Bacteriol. 2008; 190:6340–6350.
Article14. Jones MA, Wigley P, Page KL, Hulme SD, Barrow PA. Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum requires the Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system but not the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 type III secretion system for virulence in chickens. Infect Immun. 2001; 69:5471–5476.
Article15. Kazmierczak MJ, Wiedmann M, Boor KJ. Alternative sigma factors and their roles in bacterial virulence. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005; 69:527–543.
Article16. Kwon HJ, Cho SH. Pathogenicity of SG 9R, a rough vaccine strain against fowl typhoid. Vaccine. 2011; 29:1311–1318.
Article17. Löber S, Jäckel D, Kaiser N, Hensel M. Regulation of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 genes by independent environmental signals. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006; 296:435–447.
Article18. Morgan E, Campbell JD, Rowe SC, Bispham J, Stevens MP, Bowen AJ, Barrow PA, Maskell DJ, Wallis TS. Identification of host-specific colonization factors of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Mol Microbiol. 2004; 54:994–1010.
Article19. Pasmans F, Van Immerseel F, Heyndrickx M, Martel A, Godard C, Wildemauwe C, Ducatelle R, Haesebrouck F. Host adaptation of pigeon isolates of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium variant Copenhagen phage type 99 is associated with enhanced macrophage cytotoxicity. Infect Immun. 2003; 71:6068–6074.
Article20. Robbe-Saule V, Algorta G, Rouilhac I, Norel F. Characterization of the RpoS status of clinical isolates of Salmonella enterica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003; 69:4352–4358.
Article21. Seo YS, Lee SH, Shin EK, Kim SJ, Jung R, Hahn TW. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis genotyping of Salmonella gallinarum and comparison with random amplified polymorphic DNA. Vet Microbiol. 2006; 115:349–357.
Article22. Silva EN, Snoeyenbos GH, Weinack OM, Smyser CF. Studies on the use of 9R strain of Salmonella gallinarum as a vaccine in chickens. Avian Dis. 1981; 25:38–52.
Article23. Smith HW. The immunity to Salmonella gallinarum infection in chickens produced by live cultures of members of the Salmonella genus. J Hyg (Lond). 1956; 54:433–439.
Article24. Van Immerseel F, Studholme DJ, Eeckhaut V, Heyndrickx M, Dewulf J, Dewaele I, Van Hoorebeke S, Haesebrouck F, Van Meirhaeghe H, Ducatelle R, Paszkiewicz K, Titball RW. Salmonella Gallinarum field isolates from laying hens are related to the vaccine strain SG9R. Vaccine. 2013; 31:4940–4945.
Article25. Waterman SR, Holden DW. Functions and effectors of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system. Cell Microbiol. 2003; 5:501–511.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Protection Against Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum, and Salmonella Enteritidis Infection in Layer Chickens Conferred by a Live Attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium Strain
- Protective efficacy and immune responses by homologous prime-booster immunizations of a novel inactivated Salmonella Gallinarum vaccine candidate
- Comparative evaluation of the murine immune responses to Salmonella enterica serovars Enteritidis, Gallinarum and Typhimurium infection
- Development and evaluation of protective capacity of Salmonella Enteritidis polyphosphate kinase-deleted and temperature-sensitive mutant
- Establishment of a live vaccine strain against fowl typhoid and paratyphoid