Int J Stem Cells.
2016 May;9(1):124-136. 10.15283/ijsc.2016.9.1.124.
Characterization of Senescence of Culture-expanded Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Latvian Biomedical Research and Study Centre, Riga, Latvia. dianal@biomed.lu.lv
- 2Children's Clinical University Hospital, Clinical Laboratory, Riga, Latvia.
- KMID: 2164169
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc.2016.9.1.124
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) are promising candidates in regenerative medicine. The need for in vitro propagation to obtain therapeutic quantities of the cells imposes a risk of impaired functionality due to cellular senescence. The aim of the study was to analyze in vitro senescence of previously cryopreserved human ADSCs subjected to serial passages in cell culture.
METHODS AND RESULTS
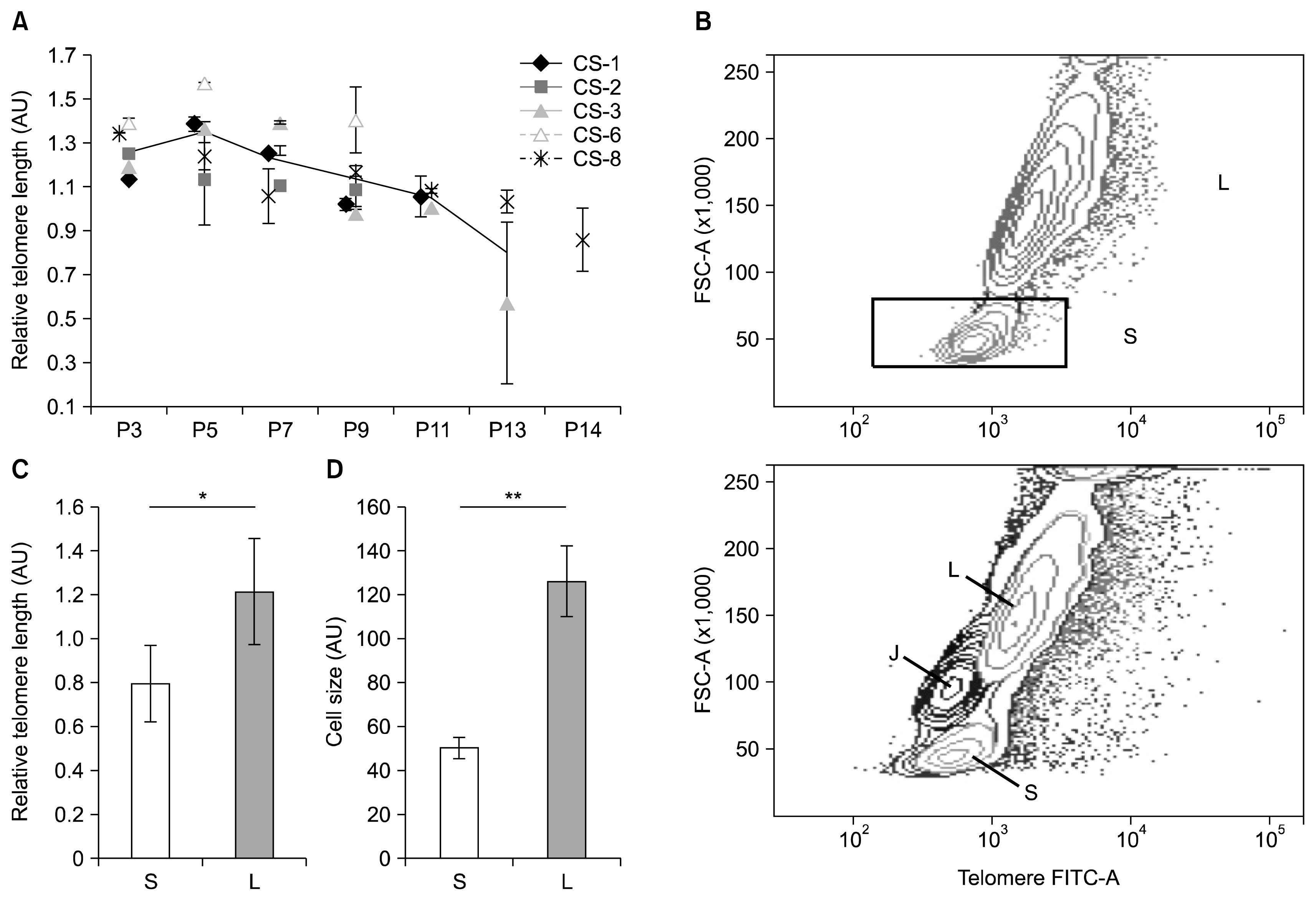
ADSC cultures from 8 donors were cultivated until proliferation arrest was reached. A gradual decline of ADSC fitness was observed by altered cell morphology, loss of proliferative, clonogenic and differentiation abilities and increased β-galactosidase expression all of which occurred in a donor-specific manner. Relative telomere length (RTL) analysis revealed that only three tested cultures encountered replicative senescence. The presence of two ADSC subsets with significantly different RTL and cell size was discovered. The heterogeneity of ADSC cultures was supported by the intermittent nature of aging seen in tested samples.
CONCLUSION
We conclude that the onset of in vitro senescence of ADSCs is a strongly donor-specific process which is complicated by the intricate dynamics of cell subsets present in ADSC population. This complexity needs to be carefully considered when elaborating protocols for personalized cellular therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA, Huang JI, Mizuno H, Alfonso ZC, Fraser JK, Benhaim P, Hedrick MH. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002; 13:4279–4295. DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E02-02-0105. PMID: 12475952. PMCID: 138633.
Article2. Fraser JK, Wulur I, Alfonso Z, Hedrick MH. Fat tissue: an underappreciated source of stem cells for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2006; 24:150–154. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2006.01.010. PMID: 16488036.
Article3. Ikegame Y, Yamashita K, Hayashi S, Mizuno H, Tawada M, You F, Yamada K, Tanaka Y, Egashira Y, Nakashima S, Yoshimura S, Iwama T. Comparison of mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue and bone marrow for ischemic stroke therapy. Cytotherapy. 2011; 13:675–685. DOI: 10.3109/14653249.2010.549122. PMID: 21231804.
Article4. Dulic V. Senescence regulation by mTOR. Methods Mol Biol. 2013; 965:15–35. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-62703-239-1_2. PMID: 23296649.
Article5. Hayflick L, Moorhead PS. The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res. 1961; 25:585–621. DOI: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90192-6. PMID: 13905658.
Article6. Shay JW, Wright WE. Hayflick, his limit, and cellular ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000; 1:72–76. DOI: 10.1038/35036093.
Article7. Ramirez RD, Morales CP, Herbert BS, Rohde JM, Passons C, Shay JW, Wright WE. Putative telomere-independent mechanisms of replicative aging reflect inadequate growth conditions. Genes Dev. 2001; 15:398–403. DOI: 10.1101/gad.859201. PMID: 11230148. PMCID: 312628.
Article8. Rochette PJ, Brash DE. Human telomeres are hypersensitive to UV-induced DNA Damage and refractory to repair. PLoS Genet. 2010; 6:e1000926. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000926. PMID: 20442874. PMCID: 2861706.
Article9. Yuan H, Kaneko T, Matsuo M. Relevance of oxidative stress to the limited replicative capacity of cultured human diploid cells: the limit of cumulative population doublings increases under low concentrations of oxygen and decreases in response to aminotriazole. Mech Ageing Dev. 1995; 81:159–168. DOI: 10.1016/0047-6374(95)01584-M. PMID: 8569280.
Article10. Roberson RS, Kussick SJ, Vallieres E, Chen SY, Wu DY. Escape from therapy-induced accelerated cellular senescence in p53-null lung cancer cells and in human lung cancers. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:2795–2803. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1270. PMID: 15805280.
Article11. Munro J, Barr NI, Ireland H, Morrison V, Parkinson EK. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce a senescence-like state in human cells by a p16-dependent mechanism that is independent of a mitotic clock. Exp Cell Res. 2004; 295:525–538. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.01.017. PMID: 15093749.
Article12. Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME, Beach D, Lowe SW. Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell. 1997; 88:593–602. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81902-9. PMID: 9054499.
Article13. Izadpanah R, Trygg C, Patel B, Kriedt C, Dufour J, Gimble JM, Bunnell BA. Biologic properties of mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow and adipose tissue. J Cell Biochem. 2006; 99:1285–1297. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.20904. PMID: 16795045. PMCID: 4048742.
Article14. Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, Acosta M, Scott G, Roskelley C, Medrano EE, Linskens M, Rubelj I, Pereira-Smith O, Peacocke M, Campisi J. A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995; 92:9363–9367. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9363. PMID: 7568133. PMCID: 40985.
Article15. Baxter MA, Wynn RF, Jowitt SN, Wraith JE, Fairbairn LJ, Bellantuono I. Study of telomere length reveals rapid aging of human marrow stromal cells following in vitro expansion. Stem Cells. 2004; 22:675–682. DOI: 10.1634/stemcells.22-5-675. PMID: 15342932.
Article16. Mao Z, Ke Z, Gorbunova V, Seluanov A. Replicatively senescent cells are arrested in G1 and G2 phases. Aging (Albany NY). 2012; 4:431–435. DOI: 10.18632/aging.100467.
Article17. Yu KR, Kang KS. Aging-related genes in mesenchymal stem cells: a mini-review. Gerontology. 2013; 59:557–563. DOI: 10.1159/000353857. PMID: 23970150.
Article18. Rufini A, Tucci P, Celardo I, Melino G. Senescence and aging: the critical roles of p53. Oncogene. 2013; 32:5129–5143. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.640. PMID: 23416979.
Article19. von Zglinicki T, Saretzki G, Ladhoff J, d’Adda di Fagagna F, Jackson SP. Human cell senescence as a DNA damage response. Mech Ageing Dev. 2005; 126:111–117. DOI: 10.1016/j.mad.2004.09.034.
Article20. Thomas DM, Yang HS, Alexander K, Hinds PW. Role of the retinoblastoma protein in differentiation and senescence. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003; 2:124–130. DOI: 10.4161/cbt.2.2.235. PMID: 12750549.
Article21. Qian Y, Chen X. Senescence regulation by the p53 protein family. Methods Mol Biol. 2013; 965:37–61. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-62703-239-1_3. PMID: 23296650. PMCID: 3784259.
Article22. Narita M, Nũnez S, Heard E, Narita M, Lin AW, Hearn SA, Spector DL, Hannon GJ, Lowe SW. Rb-mediated heterochromatin formation and silencing of E2F target genes during cellular senescence. Cell. 2003; 113:703–716. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00401-X. PMID: 12809602.
Article23. Ferbeyre G, de Stanchina E, Querido E, Baptiste N, Prives C, Lowe SW. PML is induced by oncogenic ras and promotes premature senescence. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:2015–2027. PMID: 10950866. PMCID: 316863.
Article24. Dhahbi JM, Atamna H, Boffelli D, Magis W, Spindler SR, Martin DI. Deep sequencing reveals novel microRNAs and regulation of microRNA expression during cell senescence. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e20509. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020509. PMID: 21637828. PMCID: 3102725.
Article25. Banas A, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y, Tokuhara M, Takeshita F, Osaki M, Kawamata M, Kato T, Okochi H, Ochiya T. IFATS collection: in vivo therapeutic potential of human adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells after transplantation into mice with liver injury. Stem Cells. 2008; 26:2705–2712. DOI: 10.1634/stemcells.2008-0034. PMID: 18535155.
Article26. Cho YB, Lee WY, Park KJ, Kim M, Yoo HW, Yu CS. Autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells for the treatment of Crohn’s fistula: a phase I clinical study. Cell Transplant. 2013; 22:279–285. DOI: 10.3727/096368912X656045.
Article27. Bogdanova A, Bērziņš U, Brūvere R, Eivazova G, Kozlovska T. Adipose-derived stem cells cultured in autologous serum maintain the characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells. Proc Latv Acad Sci, Sect B, Nat Exact Appl Sci. 2010; 64:106–113.
Article28. Digirolamo CM, Stokes D, Colter D, Phinney DG, Class R, Prockop DJ. Propagation and senescence of human marrow stromal cells in culture: a simple colony-forming assay identifies samples with the greatest potential to propagate and differentiate. Br J Haematol. 1999; 107:275–281. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1999.01715.x. PMID: 10583212.
Article29. Salama R, Sadaie M, Hoare M, Narita M. Cellular senescence and its effector programs. Genes Dev. 2014; 28:99–114. DOI: 10.1101/gad.235184.113. PMID: 24449267. PMCID: 3909793.
Article30. Evans-Galea MV, Wielgosz MM, Hanawa H, Srivastava DK, Nienhuis AW. Suppression of clonal dominance in cultured human lymphoid cells by addition of the cHS4 insulator to a lentiviral vector. Mol Ther. 2007; 15:801–809. PMID: 17299406.
Article31. Crook JM, Stacey GN. Setting quality standards for stem cell banking, research and translation: the international stem cell banking initiative. Ilic D, editor. Stem cell banking. New York City, NY, USA: Humana Press Inc;2014. p. 5–7.
Article32. Lee CC, Christensen JE, Yoder MC, Tarantal AF. Clonal analysis and hierarchy of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem and progenitor cells. Exp Hematol. 2010; 38:46–54. DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2009.11.001. PMCID: 2807618.
Article33. Rada T, Reis RL, Gomes ME. Distinct stem cells sub-populations isolated from human adipose tissue exhibit different chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation potential. Stem Cell Rev. 2011; 7:64–76. DOI: 10.1007/s12015-010-9147-0.
Article34. Cholewa D, Stiehl T, Schellenberg A, Bokermann G, Joussen S, Koch C, Walenda T, Pallua N, Marciniak-Czochra A, Suschek CV, Wagner W. Expansion of adipose mesenchymal stromal cells is affected by human platelet lysate and plating density. Cell Transplant. 2011; 20:1409–1422. DOI: 10.3727/096368910X557218. PMID: 21396157.
Article35. Winkler R, Perner B, Rapp A, Durm M, Cremer C, Greulich KO, Hausmann M. Labelling quality and chromosome morphology after low temperature FISH analysed by scanning far-field and near-field optical microscopy. J Microsc. 2003; 209:23–33. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2818.2003.01101.x. PMID: 12535181.
Article36. Baerlocher GM, Mak J, Tien T, Lansdorp PM. Telomere length measurement by fluorescence in situ hybridization and flow cytometry: tips and pitfalls. Cytometry. 2002; 47:89–99. DOI: 10.1002/cyto.10053. PMID: 11813198.
Article37. Noh HB, Ahn HJ, Lee WJ, Kwack KB, Kwon YD. The molecular signature of in vitro senescence in human mesenchymal stem cells. Genes Genomics. 2010; 32:87–93. DOI: 10.1007/s13258-010-0868-x.
Article38. Samsonraj RM, Raghunath M, Hui JH, Ling L, Nurcombe V, Cool SM. Telomere length analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells by quantitative PCR. Gene. 2013; 519:348–355. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.01.039. PMID: 23380569.
Article39. Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB, Harley CB, Shay JW, Lichtsteiner S, Wright WE. Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science. 1998; 279:349–352. DOI: 10.1126/science.279.5349.349. PMID: 9454332.
Article40. Treff NR, Su J, Taylor D, Scott RT Jr. Telomere DNA deficiency is associated with development of human embryonic aneuploidy. PLoS Genet. 2011; 7:e1002161. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002161. PMID: 21738493. PMCID: 3128107.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Concise Review: Differentiation of Human Adult Stem Cells Into Hepatocyte-like Cells In vitro
- Nervonic Acid Inhibits Replicative Senescence of Human Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Adipose-derived stem cells: characterization and clinical application
- Evaluation of Bone Marrow-derived Stem Cells and Adipose-derived Stem Cells Co-cultured on Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells: A Pilot Study
- Adipose Tissue Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells