J Vet Sci.
2015 Mar;16(1):75-85. 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.1.75.
Canine model of ischemic stroke with permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion: clinical features, magnetic resonance imaging, histopathology, and immunohistochemistry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju 660-701, Korea. jungdi@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathobiology, Small Animal Tumor Diagnostic Center, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea.
- 3Laboratory of Veterinary Dermatology and Neurology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea.
- 4Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, School of Dentistry, DRI and Brain Korea 21 Program, Seoul National University, Seoul 110-749, Korea.
- KMID: 2160823
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2015.16.1.75
Abstract
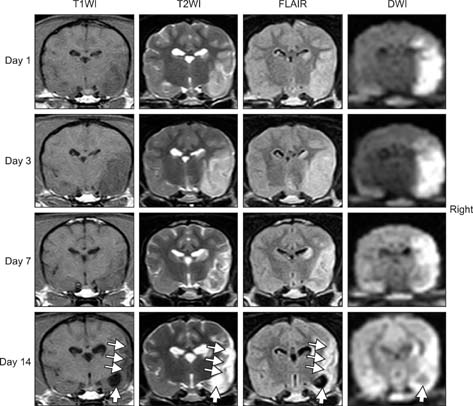
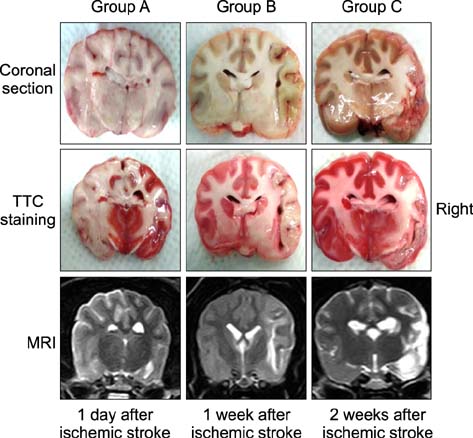
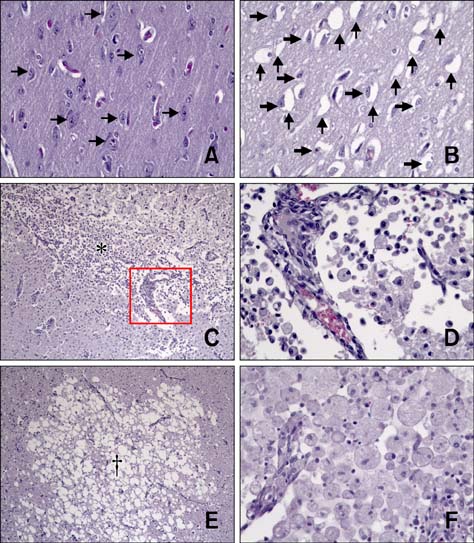
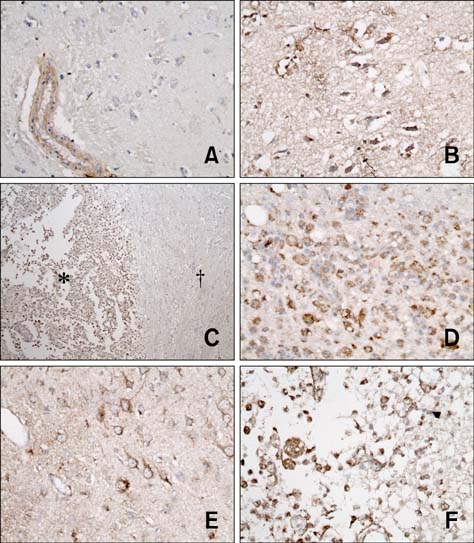
- The purpose of this study was to identify time-related changes in clinical, MRI, histopathologic, and immunohistochemical findings associated with ischemic stroke in dogs. Additionally, the association of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and tissue levels of interleukin (IL)-6 with clinical prognosis was assessed. Ischemic stroke was induced by permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in nine healthy experimental dogs. The dogs were divided into three groups according to survival time and duration of the experimental period: group A (survived only 1 day), group B (1-week experimental period), and group C (2-week experimental period). Neurologic status was evaluated daily. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed according to a predetermined schedule. Concentration of IL-6 in CSF was measured serially after ischemic stroke. Postmortem examination was performed for all experimental dogs. During histopathological examination, variable degrees of cavitation and necrosis due to neuronal cytopathic effects, such as pyknotic nuclei and cytoplasmic shrinkage, were observed on the affected side of the cerebral cortex in all dogs. Immunohistochemistry specific for IL-6 showed increased expression in the ischemic lesions. CSF IL-6 concentrations and ischemic lesion volumes 1 day after ischemic stroke were significantly higher in group A compared to groups B and C.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of ischemic brain infarction over time in a canine stroke model
Sooyoung Choi, Daji Noh, Youngwhan Kim, Inseong Jeong, Hojung Choi, Youngwon Lee, Kija Lee
J Vet Sci. 2018;19(1):137-143. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2018.19.1.137.
Reference
-
1. Arsene D, Vasilescu F, Toader C, Bălan A, Popa C, Ardeleanu C. Clinico-pathological correlations in fatal ischemic stroke. An immunohistochemical study of human brain penumbra. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011; 52:29–38.2. Ayata C, Ropper AH. Ischaemic brain oedema. J Clin Neurosci. 2002; 9:113–124.
Article3. Baciqaluppi M, Comi G, Hermann DM. Animal models of ischemic stroke. Part one: modeling risk factors. Open Neurol J. 2010; 4:26–33.
Article4. Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Germano SM, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski HM. Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke. 1986; 17:1304–1308.
Article5. Boltze J, Förschler A, Nitzsche B, Waldmin D, Hoffmann A, Boltze CM, Dreyer AY, Goldammer A, Reischauer A, Härtig W, Geiger KD, Barthel H, Emmrich F, Gille U. Permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in sheep: a novel large animal model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2008; 28:1951–1964.
Article6. Bremer AM, Watanabe O, Bourke RS. Artificial embolization of the middle cerebral artery in primates. Description of an experimental model with extracranial technique. Stroke. 1975; 6:387–390.
Article7. Carmichael ST. Rodent models of focal stroke: size, mechanism, and purpose. NeuroRx. 2005; 2:396–409.
Article8. Chuaqui R, Tapia J. Histologic assessment of the age of recent brain infarcts in man. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993; 52:481–489.
Article9. Garcia JH, Kamijyo Y. Cerebral infarction. Evolution of histopathological changes after occlusion of a middle cerebral artery in primates. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1974; 33:408–421.10. Garcia JH, Kalimo H, Kamijyo Y, Trump BF. Cellular events during partial cerebral ischemia. I. Electron microscopy of feline cerebral cortex after middle-cerebral-artery occlusion. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1977; 25:191–206.11. Garosi LS. Cerebrovascular disease in dogs and cats. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2010; 40:65–79.
Article12. Hill JK, Gunion-Rinker L, Kulhanek D, Lessov N, Kim S, Clark WM, Dixon MP, Nishi R, Stenzel-Poore MP, Eckenstein FP. Temporal modulation of cytokine expression following focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Brain Res. 1999; 820:45–54.
Article13. Jiang Q, Zhang RL, Zhang ZG, Ewing JR, Divine GW, Chopp M. Diffusion-, T2-, and perfusion-weighted nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of middle cerebral artery embolic stroke and recombinant tissue plasminogen activator intervention in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1998; 18:758–767.
Article14. Kang BT, Lee JH, Jung DI, Park C, Gu SH, Jeon HW, Jang DP, Lim CY, Quan FS, Kim YB, Cho ZH, Woo EJ, Park HM. Canine model of ischemic stroke with permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion: clinical and histopathological findings. J Vet Sci. 2007; 8:369–376.
Article15. Kang BT, Jang DP, Gu SH, Lee JH, Jung DI, Lim CY, Kim HJ, Kim YB, Kim HJ, Woo EJ, Cho ZH, Park HM. MRI features in a canine model of ischemic stroke: correlation between lesion volume and neurobehavioral status during the subacute stage. Comp Med. 2009; 59:459–464.16. Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A, Hofer M. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: therapeutic approaches. J Transl Med. 2009; 7:97.
Article17. Lambertsen KL, Biber K, Finsen B. Inflammatory cytokines in experimental and human stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012; 32:1677–1698.
Article18. Lansberg MG, Tong DC, Norbash AM, Yenari MA, Moseley ME. Intra-arterial rtPA treatment of stroke assessed by diffusion- and perfusion-weighted MRI. Stroke. 1999; 30:678–680.
Article19. Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology. 1986; 161:401–407.
Article20. Mena H, Cadavid D, Rushing EJ. Human cerebral infarct: a proposed histopathologic classification based on 137 cases. Acta Neuropathol. 2004; 108:524–530.
Article21. Menzies SA, Hoff JT, Betz AL. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats: a neurological and pathological evaluation of a reproducible model. Neurosurgery. 1992; 31:100–106.22. Nakanishi M, Niidome T, Matsuda S, Akaike A, Kihara T, Sugimoto H. Microglia-derived interleukin-6 and leukaemia inhibitory factor promote astrocytic differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells. Eur J Neurosci. 2007; 25:649–658.
Article23. Panarello GL, Dewey CW, Barone G, Stefanacci JD. Magnetic resonance imaging of two suspected cases of global brain ischemia. J Vet Emerg Crit Care. 2004; 14:269–277.
Article24. Righi M, Mori L, De Libero G, Sironi M, Biondi A, Mantovani A, Donini SD, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P. Monokine production by microglial cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1989; 19:1443–1448.
Article25. Riou EM, Amlie-Lefond C, Echenne B, Farmer M, Sébire G. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis in the diagnosis and treatment of arterial ischemic stroke. Pediatr Neurol. 2008; 38:1–9.
Article26. Sairanen T, Carpén O, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Paetau A, Turpeinen U, Kaste M, Lindsberg PJ. Evolution of cerebral tumor necrosis factor-XMLLink_XYZ production during human ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2001; 32:1750–1758.
Article27. Sandoval KE, Witt KA. Blood-brain barrier tight junction permeability and ischemic stroke. Neurobiol Dis. 2008; 32:200–219.
Article28. Schwamm LH, Koroshetz WJ, Sorensen AG, Wang B, Copen WA, Budzik R, Rordorf G, Buonanno FS, Schaefer PW, Gonzalez RG. Time course of lesion development in patients with acute stroke: serial diffusion- and hemodynamicweighted magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke. 1998; 29:2268–2276.
Article29. Sorjonen DC. Total protein, albumin quota, and electrophoretic patterns in cerebrospinal fluid of dogs with central nervous system disorders. Am J Vet Res. 1987; 48:301–305.30. Suzuki S, Tanaka K, Nogawa S, Nagata E, Ito D, Dembo T, Fukuuchi Y. Temporal profile and cellular localization of interleukin-6 protein after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999; 19:1256–1262.
Article31. Suzuki S, Tanaka K, Suzuki N. Ambivalent aspects of interleukin-6 in cerebral ischemia: inflammatory versus neurotrophic aspects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009; 29:464–479.
Article32. Takano K, Carano RA, Tatlisumak T, Meiler M, Sotak CH, Kleinert HD, Fisher M. Efficacy of intra-arterial and intravenous prourokinase in an embolic stroke model evaluated by diffusion-perfusion magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology. 1998; 50:870–875.
Article33. Tarkowski E, Rosengren L, Blomstrand C, Wikkelsö C, Jensen C, Ekholm S, Tarkowski A. Early intrathecal production of interleukin-6 predicts the size of brain lesion in stroke. Stroke. 1995; 26:1393–1398.
Article34. Tarkowski E, Rosengren L, Blomstrand C, Wikkelsö C, Jensen C, Ekholm S, Tarkowski A. Intrathecal release of proand anti-inflammatory cytokines during stroke. Clin Exp Immunol. 1997; 110:492–499.35. Vandevelde M, Spano JS. Cerebrospinal fluid cytology in canine neurologic disease. Am J Vet Res. 1977; 38:1827–1832.36. Warach S, Gaa J, Siewert B, Wielopolski P, Edelman RR. Acute human stroke studied by whole brain echo planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 1995; 37:231–241.
Article37. Wexler BC. Pathophysiological responses to acute cerebral ischemia in the gerbil. Stroke. 1972; 3:71–78.
Article38. Yamasaki Y, Matsuura N, Shozuhara H, Onodera H, Itoyama Y, Kogure K. Interleukin-1 as a pathogenetic mediator of ischemic brain damage in rats. Stroke. 1995; 26:676–681.
Article39. Zaremba J, Losy J. Early TNF-α levels correlate with ischaemic stroke severity. Acta Neurol Scand. 2001; 104:288–295.
Article40. Zhang L, Cheng H, Shi J, Chen J. Focal epidural cooling reduces the infarction volume of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in swine. Surg Neurol. 2007; 67:117–121.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Canine model of ischemic stroke with permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion: clinical and histopathological findings
- Increased Expressions of eNBC and NHE1 in Ischemic Penumbra after Permanent Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
- Acute Ischemic Stroke Involving Both Anterior and Posterior Circulation Treated by Endovascular Revascularization for Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion via Persistent Primitive Trigeminal Artery
- Intracranial Cerebrovascular Revascularization(Extracranial-Intracranial Arterial Bypass, EIAB)
- Animal Model of Cerebral Ischemia