Yonsei Med J.
2013 Jul;54(4):1053-1057. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.4.1053.
Novel Mutations in the UNC13D Gene Carried by a Chinese Neonate with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, PR China. Y_M_TANG@zju.edu.cn
- KMID: 2158245
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.4.1053
Abstract
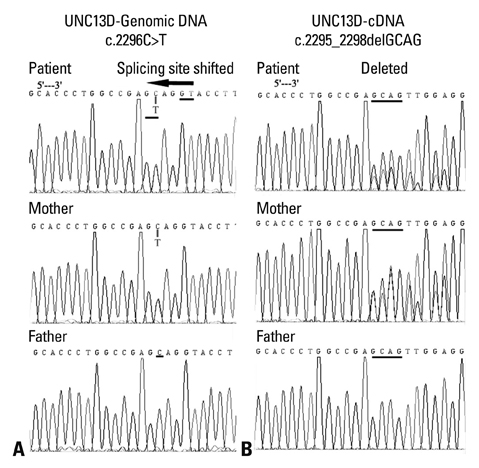
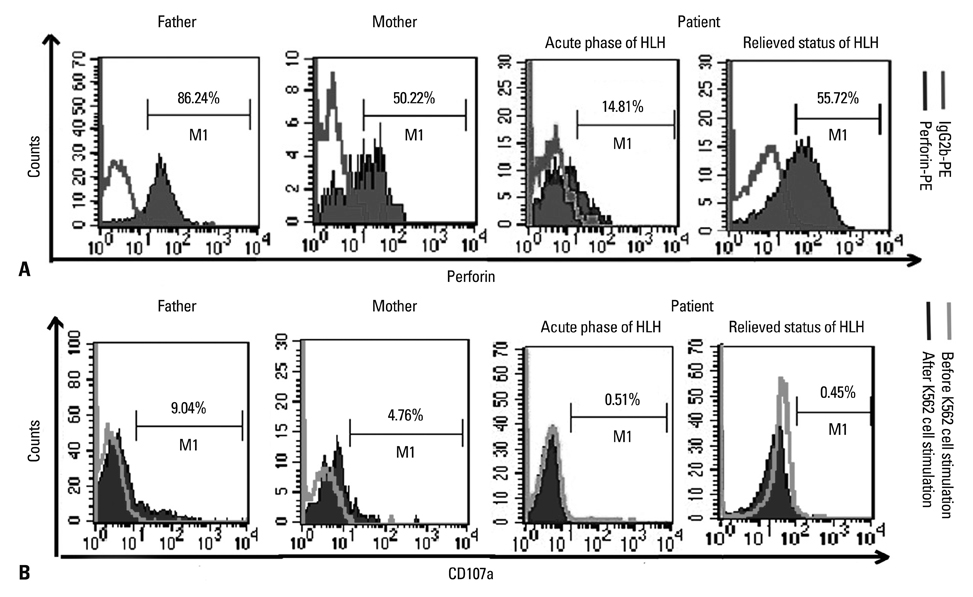
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in different ethnicities has been described in the literature, but few cases in patients of Chinese descent have been reported. Here, we describe the case of a Chinese neonate presenting with HLH carrying novel, compound heterozygous mutations of the UNC13D gene, including [c.2295_2298delGCAG, p.Glu765Aspfs*27] in exon 23, c.-250C>T, c.1+30G>A, c.279C>T, c.888G>C, c.18+36A>G, c.20-48T>C, c.1977C>T, c.2296C>T, c.24-46C>T, c.26-9_26-8insC, c.2599A>G, c.28+48C>T and c.3198A>G, some of which have not been reported in the literature. Cytokine profile analyses were performed in this patient, and the results were consistent with our previous findings in HLH patients. Cytokine profile monitoring may be helpful in differentiating among various clinical phases of HLH.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhizhuo H, Junmei X, Yuelin S, Qiang Q, Chunyan L, Zhengde X, et al. Screening the PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, SH2D1A, XIAP, and ITK gene mutations in Chinese children with Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2012; 58:410–414.
Article2. Murata Y, Yasumi T, Shirakawa R, Izawa K, Sakai H, Abe J, et al. Rapid diagnosis of FHL3 by flow cytometric detection of intraplatelet Munc13-4 protein. Blood. 2011; 118:1225–1230.
Article3. Stepp SE, Dufourcq-Lagelouse R, Le Deist F, Bhawan S, Certain S, Mathew PA, et al. Perforin gene defects in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Science. 1999; 286:1957–1959.
Article4. Feldmann J, Callebaut I, Raposo G, Certain S, Bacq D, Dumont C, et al. Munc13-4 is essential for cytolytic granules fusion and is mutated in a form of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL3). Cell. 2003; 115:461–473.
Article5. zur Stadt U, Schmidt S, Kasper B, Beutel K, Diler AS, Henter JI, et al. Linkage of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) type-4 to chromosome 6q24 and identification of mutations in syntaxin 11. Hum Mol Genet. 2005; 14:827–834.
Article6. zur Stadt U, Rohr J, Seifert W, Koch F, Grieve S, Pagel J, et al. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 5 (FHL-5) is caused by mutations in Munc18-2 and impaired binding to syntaxin 11. Am J Hum Genet. 2009; 85:482–492.
Article7. Bryceson YT, Pende D, Maul-Pavicic A, Gilmour KC, Ufheil H, Vraetz T, et al. A prospective evaluation of degranulation assays in the rapid diagnosis of familial hemophagocytic syndromes. Blood. 2012; 119:2754–2763.
Article8. Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, et al. HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007; 48:124–131.
Article9. Zhang K, Biroschak J, Glass DN, Thompson SD, Finkel T, Passo MH, et al. Macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis is associated with MUNC13-4 polymorphisms. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:2892–2896.
Article10. Yoon HS, Kim HJ, Yoo KH, Sung KW, Koo HH, Kang HJ, et al. UNC13D is the predominant causative gene with recurrent splicing mutations in Korean patients with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Haematologica. 2010; 95:622–626.
Article11. van Egmond ME, Vermeulen RJ, Peeters-Scholte CM, Augoustides-Savvopoulou P, Abbink F, Boelens JJ, et al. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a pediatric patient diagnosed by brain magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropediatrics. 2011; 42:191–193.
Article12. Tang Y, Xu X, Song H, Yang S, Shi S, Wei J, et al. Early diagnostic and prognostic significance of a specific Th1/Th2 cytokine pattern in children with haemophagocytic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 2008; 143:84–91.
Article13. Tang Y, Liao C, Xu X, Song H, Shi S, Yang S, et al. Evaluation of Th1/Th2 cytokines as a rapid diagnostic tool for severe infection in paediatric haematology/oncology patients by the use of cytometric bead array technology. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011; 17:1666–1673.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple Ecthyma Gangrenosum in a Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Patient
- Two Cases of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Following Kikuchi's Disease
- A Case of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Presenting with Neck Mass in a Child
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis secondary to histoplasmosis
- Genetic and clinical characteristics of pediatric patients with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis