Blood Res.
2021 Jun;56(2):86-101. 10.5045/br.2021.2020308.
Genetic and clinical characteristics of pediatric patients with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 2Section of Immunogenetics, Department of Genetics, Research Center, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 3Department of Pediatric Allergy/Immunology, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 4Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 5College of Medicine, AlFaisal University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- 6Cell Therapy, Applied Genomics, King Hussein Cancer Center, Amman, Jordan
- 7King Abdullah International Medical Research Center (KAIMRC), King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, King Abdulaziz Medical City Hospital, Al-Ahsa, Saudi Arabia
- KMID: 2517005
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2021.2020308
Abstract
- Background
Our study was designed to investigate the frequencies and distributions of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) associated genes in Saudi patients.
Methods
FHL associated gene screening was performed on 87 Saudi patients who were diagnosed with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) between 1995 and 2014. The clinical and biochemical profiles were also retrospectively captured and analyzed.
Results
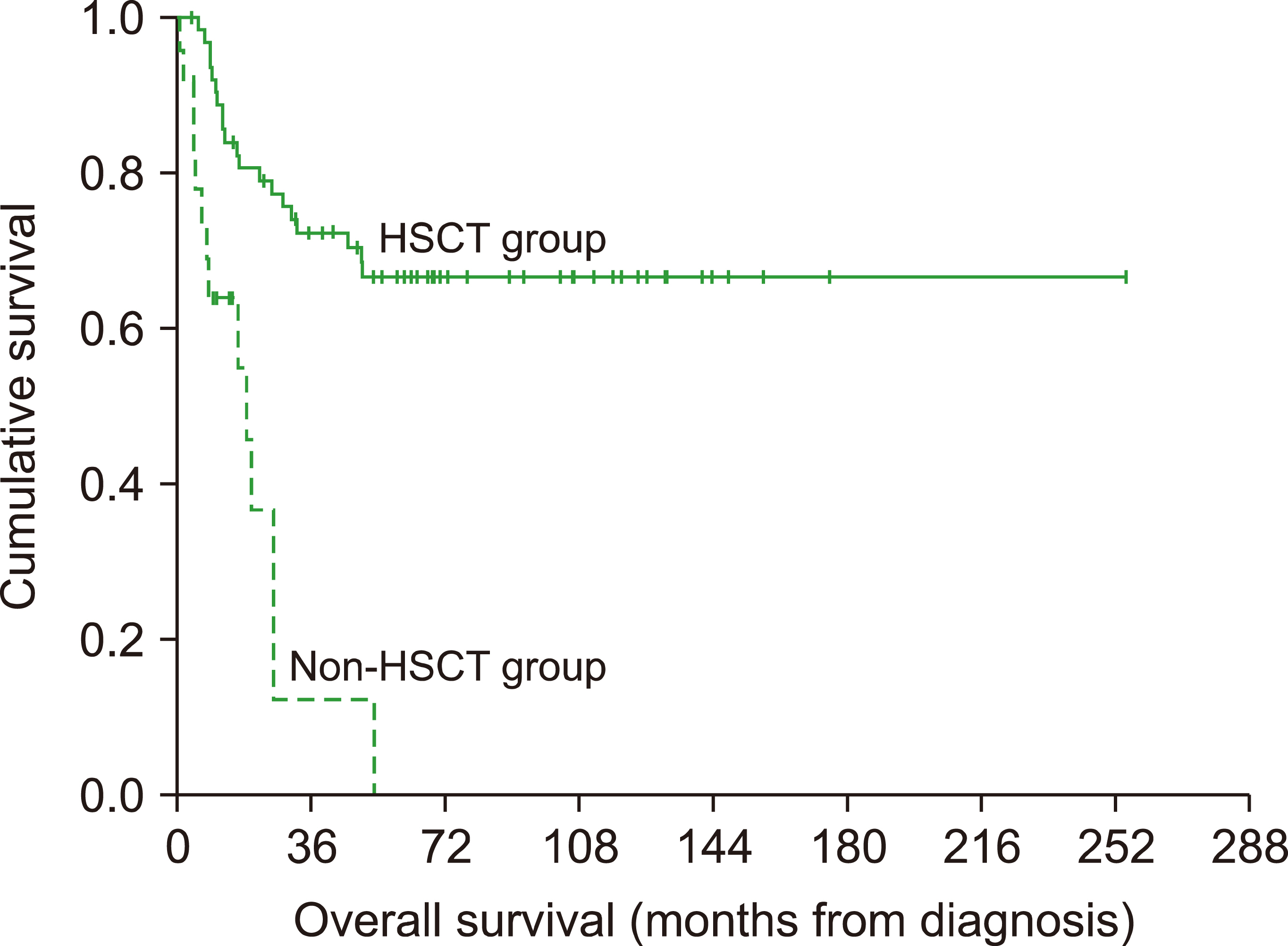
Homozygous mutations and mono-allelic variants were identified in 66 (75.9%) and 3 (3.5%) of the study participants, respectively. STXBP2 was the most frequently mutated gene (36% of patients) and mutations in STXBP2 and STX11 accounted for 58% of all FHL cases and demonstrated a specific geographical pattern. Patients in the FHL group presented at a significantly younger age than those belonging to the unknown-genetics group (median, 3.9 vs. 9.4 mo; P =0.005). The presenting clinical features were similar among the various genetic groups and the 5-year overall survival (OS) was 55.4% with a 5.6 year median follow-up. Patients with PRF1 mutations had a significantly poorer 5-year OS (21.4%, P =0.008) and patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplant (72.4%) had a significantly better 5-year OS (66.5% vs. 0%, P =0.001).
Conclusion
Our study revealed the predominance of the STXBP2 mutations in Saudi patients with FHL. A genetic diagnosis was possible in 80% of the cohort and our data showed improved survival in FHL patients who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chandrakasan S, Filipovich AH. 2013; Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: advances in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J Pediatr. 163:1253–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.06.053. PMID: 23953723.
Article2. Henter JI, Aricò M, Elinder G, Imashuku S, Janka G. 1998; Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 12:417–33. DOI: 10.1016/S0889-8588(05)70520-7. PMID: 9561910.3. Janka G, Imashuku S, Elinder G, Schneider M, Henter JI. 1998; Infection- and malignancy-associated hemophagocytic syndromes. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 12:435–44. DOI: 10.1016/S0889-8588(05)70521-9. PMID: 9561911.4. Janka GE. 1983; Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Eur J Pediatr. 140:221–30. DOI: 10.1007/BF00443367. PMID: 6354720.
Article5. Henter JI, Samuelsson-Horne A, Aricò M, et al. 2002; Treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with HLH-94 immuno-chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 100:2367–73. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2002-01-0172. PMID: 12239144.
Article6. Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, et al. 2007; HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 48:124–31. DOI: 10.1002/pbc.21039. PMID: 16937360.
Article7. Li Q, Wang K. 2017; InterVar: clinical interpretation of genetic variants by the 2015 ACMG-AMP guidelines. Am J Hum Genet. 100:267–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.01.004. PMID: 28132688. PMCID: PMC5294755.
Article8. Haddad E, Sulis ML, Jabado N, Blanche S, Fischer A, Tardieu M. 1997; Frequency and severity of central nervous system lesions in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood. 89:794–800. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V89.3.794. PMID: 9028310.
Article9. Aricò M, Janka G, Fischer A, et al. 1996; Hemophagocytic lympho-histiocytosis. Report of 122 children from the International Registry. FHL Study Group of the Histiocyte Society. Leukemia. 10:197–203. PMID: 8637226.10. Bertaina C, Bezzio S, Riva C. 2007; Late onset of familial hemophagocytic lympho-histiocytosis. Minerva Pediatr. 59:416–7. PMID: 17947849.11. Sieni E, Cetica V, Santoro A, et al. 2011; Genotype-phenotype study of familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3. J Med Genet. 48:343–52. DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2010.085456. PMID: 21248318. PMCID: PMC4115201.
Article12. Manno EC, Salfa I, Palma P, et al. 2014; Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3 diagnosed at school age: a case report. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 36:e128–30. DOI: 10.1097/MPH.0b013e318292bc7c. PMID: 23669735.13. Tabata R, Tabata C, Terada M, Nagai T. 2009; Hemophagocytic syndrome in elderly patients with underlying autoimmune diseases. Clin Rheumatol. 28:461–4. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-009-1086-2. PMID: 19165558.
Article14. Elyamany G, Alzahrani A, Elfaraidi H, et al. 2016; Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: single-center series of 12 cases from Saudi Arabia. Clin Med Insights Pediatr. 10:21–6. DOI: 10.4137/CMPed.S35853. PMID: 27081327. PMCID: PMC4822721.
Article15. zur Stadt U, Rohr J, Seifert W, et al. 2009; Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 5 (FHL-5) is caused by mutations in Munc18-2 and impaired binding to syntaxin 11. Am J Hum Genet. 85:482–92. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.09.005. PMID: 19804848. PMCID: PMC2756548.
Article16. Côte M, Ménager MM, Burgess A, et al. 2009; Munc18-2 deficiency causes familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 5 and impairs cytotoxic granule exocytosis in patient NK cells. J Clin Invest. 119:3765–73. DOI: 10.1172/JCI40732. PMID: 19884660. PMCID: PMC2786810.
Article17. Pagel J, Beutel K, Lehmberg K, et al. 2012; Distinct mutations in STXBP2 are associated with variable clinical presentations in patients with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 5 (FHL5). Blood. 119:6016–24. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-398958. PMID: 22451424.
Article18. Baothman A, Almalki H, Abumelha K, Alshegifi A, Baashar A. 2019; Type 5 familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a seven-year-old girl post second bone marrow transplantation with failure to thrive: STXBP2 novel mutation. Cureus. 11:e6246. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.6246. PMID: 31807395. PMCID: PMC6881083.
Article19. Zur Stadt U, Beutel K, Kolberg S, et al. 2006; Mutation spectrum in children with primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: molecular and functional analyses of PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, and RAB27A. Hum Mutat. 27:62–8. DOI: 10.1002/humu.20274. PMID: 16278825.20. El-Mouzan MI, Al-Salloum AA, Al-Herbish AS, Qurachi MM, Al-Omar AA. 2007; Regional variations in the prevalence of consanguinity in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 28:1881–4. DOI: 10.4103/0256-4947.51726. PMID: 18500181. PMCID: PMC6074430.21. Muralitharan S, Wali YA, Dennison D, et al. 2007; Novel spectrum of perforin gene mutations in familial hemophagocytic lympho-histiocytosis in ethnic Omani patients. Am J Hematol. 82:1099–102. DOI: 10.1002/ajh.21009. PMID: 17674359.
Article22. Zhizhuo H, Junmei X, Yuelin S, et al. 2012; Screening the PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, SH2D1A, XIAP, and ITK gene mutations in Chinese children with Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 58:410–4. DOI: 10.1002/pbc.23216. PMID: 21674762.
Article23. Yoon HS, Kim HJ, Yoo KH, et al. 2010; UNC13D is the predominant causative gene with recurrent splicing mutations in Korean patients with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Haematologica. 95:622–6. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.016949. PMID: 20015888. PMCID: PMC2857192.
Article24. Balta G, Okur H, Unal S, et al. 2010; Assessment of clinical and laboratory presentations of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis patients with homozygous W374X mutation. Leuk Res. 34:1012–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2010.02.002. PMID: 20197201.
Article25. Cetica V, Sieni E, Pende D, et al. 2016; Genetic predisposition to hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: report on 500 patients from the Italian registry. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 137:188–96. e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.06.048. PMID: 26342526. PMCID: PMC4699615.
Article26. Kaufman KM, Linghu B, Szustakowski JD, et al. 2014; Whole-exome sequencing reveals overlap between macrophage activation syndrome in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:3486–95. DOI: 10.1002/art.38793. PMID: 25047945. PMCID: PMC4321811.
Article27. Zhang K, Chandrakasan S, Chapman H, et al. 2014; Synergistic defects of different molecules in the cytotoxic pathway lead to clinical familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood. 124:1331–4. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-573105. PMID: 24916509. PMCID: PMC4141517.
Article28. Gholam C, Grigoriadou S, Gilmour KC, Gaspar HB. 2011; Familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: advances in the genetic basis, diagnosis and management. Clin Exp Immunol. 163:271–83. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04302.x. PMID: 21303357. PMCID: PMC3048610.
Article29. Chinn IK, Eckstein OS, Peckham-Gregory EC, et al. 2018; Genetic and mechanistic diversity in pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood. 132:89–100. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-11-814244. PMID: 29632024. PMCID: PMC6034641.
Article30. Meeths M, Bryceson YT, Rudd E, et al. 2010; Clinical presentation of Griscelli syndrome type 2 and spectrum of RAB27A mutations. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 54:563–72. DOI: 10.1002/pbc.22357. PMID: 19953648.
Article31. Rudd E, Göransdotter Ericson K, Zheng C, et al. 2006; Spectrum and clinical implications of syntaxin 11 gene mutations in familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: association with disease-free remissions and haematopoietic malignancies. J Med Genet. 43:e14. DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2005.035253. PMID: 16582076. PMCID: PMC2563216.
Article32. Gurgey A, Aytac S, Balta G, Oguz KK, Gumruk F. 2008; Central nervous system involvement in Turkish children with primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Child Neurol. 23:1293–9. DOI: 10.1177/0883073808319073. PMID: 18984839.
Article33. Stepp SE, Dufourcq-Lagelouse R, Le Deist F, et al. 1999; Perforin gene defects in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Science. 286:1957–9. DOI: 10.1126/science.286.5446.1957. PMID: 10583959.
Article34. Trizzino A, zur Stadt U, Ueda I, et al. 2008; Genotype-phenotype study of familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis due to perforin mutations. J Med Genet. 45:15–21. DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2007.052670. PMID: 17873118.35. Gadoury-Levesque V, Dong L, Su R, et al. 2020; Frequency and spectrum of disease-causing variants in 1892 patients with suspected genetic HLH disorders. Blood Adv. 4:2578–94. DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001605. PMID: 32542393. PMCID: PMC7322966.
Article36. Aguilar C, Lenoir C, Lambert N, et al. 2014; Characterization of Crohn disease in X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-deficient male patients and female symptomatic carriers. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 134:1131–41. e9. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.04.031. PMID: 24942515.
Article37. Jordan MB, Allen CE, Weitzman S, Filipovich AH, McClain KL. 2011; How I treat hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood. 118:4041–52. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-278127. PMID: 21828139. PMCID: PMC3204727.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults: Overview, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- Current status of the diagnosis and treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults
- Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
- Multiple Ecthyma Gangrenosum in a Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Patient
- Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis