J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Apr;27(4):343-349. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.4.343.
Potential Association of DCBLD2 Polymorphisms with Fall Rates of FEV1 by Aspirin Provocation in Korean Asthmatics
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Life Science, Sogang University, Seoul, Korea. hdshin@sogang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Genetic Epidemiology, SNP Genetics Inc., Seoul, Korea.
- 3Genome Research Center for Allergy and Respiratory Diseases, Division of Allergy and Respiratory Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- 5Department of Allergy, Chonnam National University Medical School and Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2157892
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.4.343
Abstract
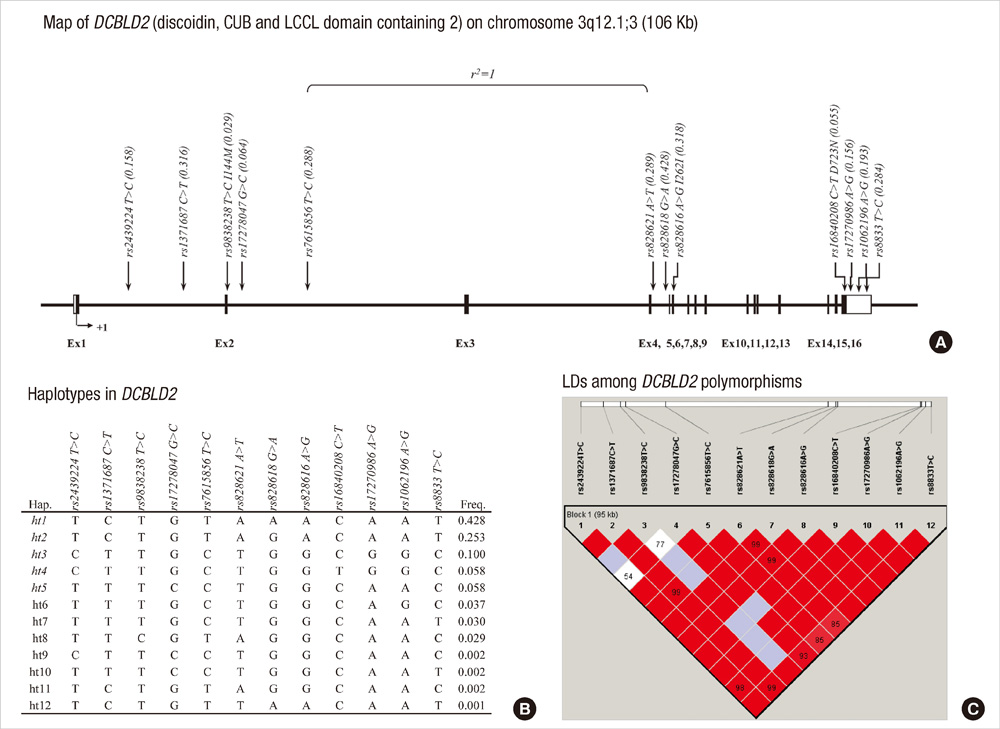
- Aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD) is a clinical syndrome characterized by chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis and aspirin hypersensitivity. The aspirin-induced bronchospasm is mediated by mast cell and eosinophilic inflammation. Recently, it has been reported that the expression of discoidin, CUB and LCCL domain-containing protein 2 (DCBLD2) is up-regulated in lung cancers and is regulated by transcription factor AP-2 alpha (TFAP2A), a component of activator protein-2 (AP-2) that is known to regulate IL-8 production in human lung fibroblasts and epithelial cells. To investigate the associations between AERD and DCBLD2 polymorphisms, 12 common variants were genotyped in 163 AERD subjects and 429 aspirin tolerant asthma (ATA) controls. Among these variants, seven SNPs (rs1371687, rs7615856, rs828621, rs828618, rs828616, rs1062196, and rs8833) and one haplotype (DCBLD2-ht1) show associations with susceptibility to AERD. In further analysis, this study reveals significant associations between the SNPs or haplotypes and the percentage of forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) decline following aspirin challenge using multiple linear regression analysis. Furthermore, a non-synonymous SNP rs16840208 (Asp723Asn) shows a strong association with FEV1 decline in AERD patients. Although further studies for the non-synonymous Asp723Asn variation are needed, our findings suggest that DCBLD2 could be related to FEV1-related phenotypes in asthmatics.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Alleles
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Aspirin/*adverse effects
Asthma, Aspirin-Induced/etiology/*genetics
Female
Forced Expiratory Volume/drug effects/genetics
Gene Frequency
Genetic Predisposition to Disease
Genotype
Haplotypes
Humans
Male
Membrane Proteins/*genetics
Middle Aged
*Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Regression Analysis
Republic of Korea
Risk Factors
Young Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. Szczeklik A. Aspirin-induced asthma: a tribute to John Vane as a source of inspiration. Pharmacol Rep. 2010. 62:526–529.2. Lee RU, Stevenson DD. Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease: evaluation and management. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011. 3:3–10.3. Katial RK, Strand M, Prasertsuntarasai T, Leung R, Zheng W, Alam R. The effect of aspirin desensitization on novel biomarkers in aspirin-exacerbated respiratory diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 126:738–744.4. Park JS, Chang HS, Park CS, Lee JH, Lee YM, Choi JH, Park HS, Kim LH, Park BL, Choi YH, Shin HD. Association analysis of cysteinyl-leukotriene receptor 2 (CYSLTR2) polymorphisms with aspirin intolerance in asthmatics. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2005. 15:483–492.5. Kim JH, Park BL, Cheong HS, Bae JS, Park JS, Jang AS, Uh ST, Choi JS, Kim YH, Kim MK, Choi IS, Cho SH, Choi BW, Park CS, Shin HD. Genome-wide and follow-up studies identify CEP68 gene variants associated with risk of aspirin-intolerant asthma. PLoS One. 2010. 5:e13818.6. Koshikawa K, Osada H, Kozaki K, Konishi H, Masuda A, Tatematsu Y, Mitsudomi T, Nakao A, Takahashi T. Significant up-regulation of a novel gene, CLCP1, in a highly metastatic lung cancer subline as well as in lung cancers in vivo. Oncogene. 2002. 21:2822–2828.7. Orso F, Corà D, Ubezio B, Provero P, Caselle M, Taverna D. Identification of functional TFAP2A and SP1 binding sites in new TFAP2A-modulated genes. BMC Genomics. 2010. 11:355.8. Orso F, Penna E, Cimino D, Astanina E, Maione F, Valdembri D, Giraudo E, Serini G, Sismondi P, De Bortoli M, Taverna D. AP-2alpha and AP-2gamma regulate tumor progression via specific genetic programs. FASEB J. 2008. 22:2702–2714.9. Kim M, Lee KT, Jang HR, Kim JH, Noh SM, Song KS, Cho JS, Jeong HY, Kim SY, Yoo HS, Kim YS. Epigenetic down-regulation and suppressive role of DCBLD2 in gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Mol Cancer Res. 2008. 6:222–230.10. Sadeghi MM, Esmailzadeh L, Zhang J, Guo X, Asadi A, Krassilnikova S, Fassaei HR, Luo G, Al-Lamki RS, Takahashi T, Tellides G, Bender JR, Rodriguez ER. ESDN is a marker of vascular remodeling and regulator of cell proliferation in graft arteriosclerosis. Am J Transplant. 2007. 7:2098–2105.11. Lee HS, Myers A, Kim J. Vascular endothelial growth factor drives autocrine epithelial cell proliferation and survival in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009. 180:1056–1067.12. Kim BS, Park SM, Uhm TG, Kang JH, Park JS, Jang AS, Uh ST, Kim MK, Choi IS, Cho SH, Hong CS, Lee YW, Lee JY, Choi BW, Park HS, Park BL, Shin HD, Chung IY, Park CS. Effect of single nucleotide polymorphisms within the interleukin-4 promoter on aspirin intolerance in asthmatics and interleukin-4 promoter activity. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2010. 20:748–758.13. Nizankowska-Mogilnicka E, Bochenek G, Mastalerz L, Swierczyńska M, Picado C, Scadding G, Kowalski ML, Setkowicz M, Ring J, Brockow K, Bachert C, Wöhrl S, Dahlén B, Szczeklik A. EAACI/GA2LEN guideline: aspirin provocation tests for diagnosis of aspirin hypersensitivity. Allergy. 2007. 62:1111–1118.14. Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005. 21:263–265.15. Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P. A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. 68:978–989.16. Guo X, Nie L, Esmailzadeh L, Zhang J, Bender JR, Sadeghi MM. Endothelial and smooth muscle-derived neuropilin-like protein regulates platelet-derived growth factor signaling in human vascular smooth muscle cells by modulating receptor ubiquitination. J Biol Chem. 2009. 284:29376–29382.17. Klatt AR, Zech D, Kühn G, Paul-Klausch B, Klinger G, Renno JH, Schmidt J, Malchau G, Wielckens K. Discoidin domain receptor 2 mediates the collagen II-dependent release of interleukin-6 in primary human chondrocytes. J Pathol. 2009. 218:241–247.18. Matsuyama W, Wang L, Farrar WL, Faure M, Yoshimura T. Activation of discoidin domain receptor 1 isoform b with collagen up-regulates chemokine production in human macrophages: role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappa B. J Immunol. 2004. 172:2332–2340.19. Kobuke K, Furukawa Y, Sugai M, Tanigaki K, Ohashi N, Matsumori A, Sasayama S, Honjo T, Tashiro K. ESDN, a novel neuropilin-like membrane protein cloned from vascular cells with the longest secretory signal sequence among eukaryotes, is up-regulated after vascular injury. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:34105–34114.20. Shi HZ, Qin XJ. CD4CD25 regulatory T lymphocytes in allergy and asthma. Allergy. 2005. 60:986–995.21. Hofford JM, Milakofsky L, Pell S, Fish JE, Peters SP, Pollice M, Vogel WH. Levels of amino acids and related compounds in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of asthmatic patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. 155:432–435.22. Laitinen T, Polvi A, Rydman P, Vendelin J, Pulkkinen V, Salmikangas P, Makela S, Rehn M, Pirskanen A, Rautanen A, Zucchelli M, Gullstén H, Leino M, Alenius H, Petäys T, Haahtela T, Laitinen A, Laprise C, Hudson TJ, Laitinen LA, Kere J. Characterization of a common susceptibility locus for asthma-related traits. Science. 2004. 304:300–304.23. Reinscheid RK, Xu YL, Okamura N, Zeng J, Chung S, Pai R, Wang Z, Civelli O. Pharmacological characterization of human and murine neuropeptide s receptor variants. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. 315:1338–1345.24. Brinster RL, Allen JM, Behringer RR, Gelinas RE, Palmiter RD. Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988. 85:836–840.25. Pagani F, Baralle FE. Genomic variants in exons and introns: identifying the splicing spoilers. Nat Rev Genet. 2004. 5:389–396.26. Kim JH, Cheong HS, Park BL, Bae JS, Jung S, Yoon SH, Park JS, Jang AS, Park SW, Uh ST, Kim YH, Hwang HK, Park CS, Shin HD. A new association between polymorphisms of the SLC6A7 gene in the chromosome 5q31-32 region and asthma. J Hum Genet. 2010. 55:358–365.27. Pasaje CF, Kim JH, Park BL, Cheong HS, Chun JY, Park TJ, Lee JS, Kim Y, Bae JS, Park JS, Yoon SH, Uh ST, Choi JS, Kim YH, Kim MK, Choi IS, Cho SH, Choi BW, Park CS, Shin HD. Association of SLC6A12 variants with aspirin-intolerant asthma in a Korean population. Ann Hum Genet. 2010. 74:326–334.28. Kim JH, Cha JY, Cheong HS, Park JS, Jang AS, Uh ST, Kim MK, Choi IS, Cho SH, Park BL, Bae JS, Park CS, Shin HD. KIF3A, a cilia structural gene on chromosome 5q31, and its polymorphisms show an association with aspirin hypersensitivity in asthma. J Clin Immunol. 2011. 31:112–121.29. Lee JS, Kim JH, Bae JS, Kim JY, Park TJ, Pasaje CF, Park BL, Cheong HS, Uh ST, Park JS, Jang AS, Kim MK, Choi IS, Park CS, Shin HD. Association of CACNG6 polymorphisms with aspirin-intolerance asthmatics in a Korean population. BMC Med Genet. 2010. 11:138.30. Kim JY, Kim JH, Park TJ, Bae JS, Lee JS, Pasaje CF, Park BL, Cheong HS, Park JS, Park SW, Uh ST, Kim MK, Choi IS, Cho SH, Choi BW, Park CS, Shin HD. Positive association between aspirin-intolerant asthma and genetic polymorphisms of FSIP1: a case-case study. BMC Pulm Med. 2010. 10:34.31. Tantisira KG, Drazen JM. Genetics and pharmacogenetics of the leukotriene pathway. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. 124:422–427.32. Seo KW, Lee SJ, Kim CE, Yun MR, Park HM, Yun JW, Bae SS, Kim CD. Participation of 5-lipoxygenase-derived LTB(4) in 4-hydroxynonenal-enhanced MMP-2 production in vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 2010. 208:56–61.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence of aspirin sensitivity among asthmatic patients with mild to moderate severity and its clinical characteristics
- Asthmatics Without Rhinitis Have More Fixed Airway Obstruction Than Those With Concurrent Rhinitis
- Polymorphisms of ATF6B Are Potentially Associated With FEV1 Decline by Aspirin Provocation in Asthmatics
- Oral provocation tests with aspirin and food additives in asthmatic patients
- Prevalence of Subclinical Aspirin-Intolerant Asthma in Patients with Nasal Polyposis and Chronic Rhinosinusitis