Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Jan;48(1):171-179. 10.4143/crt.2014.292.
The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Metformin Treatment on Survival of Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. ohdoyoun@snu.ac.kr
- 2Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2152273
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.292
Abstract
- PURPOSE
A causal relationship between diabetes mellitus (DM) and pancreatic cancer is well established. However, in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer (APC) who receive palliative chemotherapy, the impact of DM on the prognosis of APC is unclear.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively enrolled APC patients who received palliative chemotherapy between 2003 and 2010. The patients were stratified according to the status of DM, in accordance with 2010 DM criteria (American Heart Association/American Diabetes Association). DM at least 2 years' duration prior to diagnosis of APC was defined as remote-onset DM (vs. recent-onset).
RESULTS
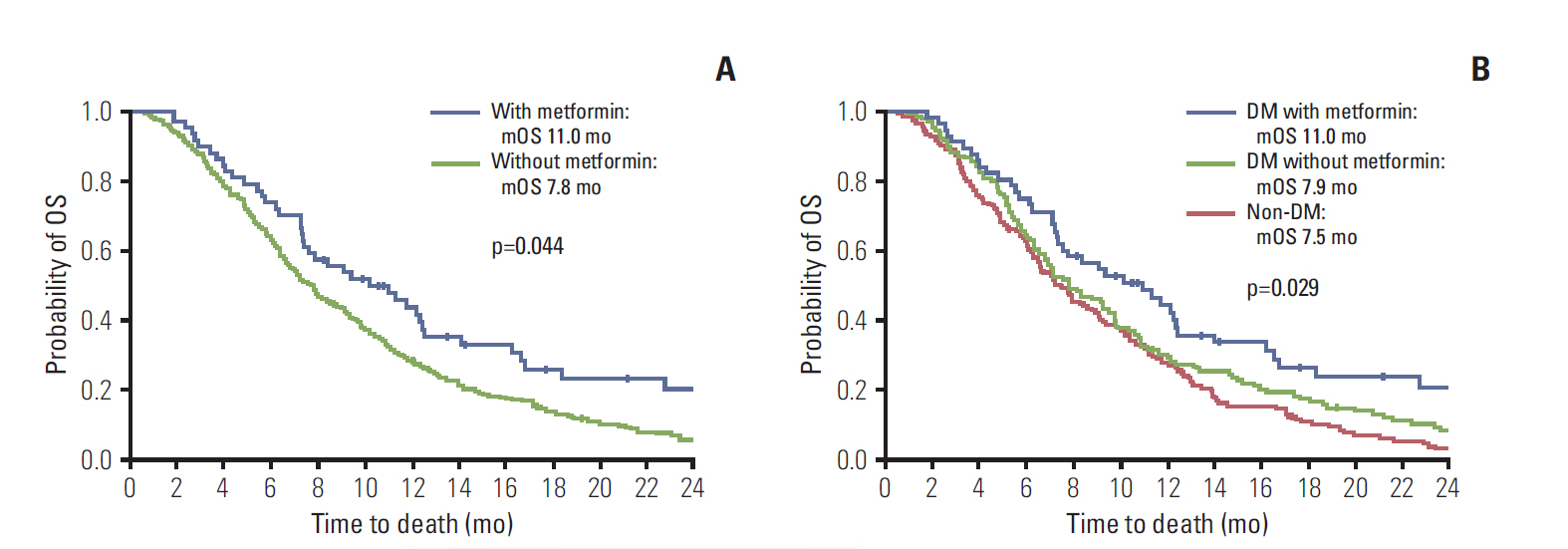
Of the 349 APC patients, 183 (52.4%) had DM. Among the patients with DM, 160 patients had DM at the time of diagnosis of APC (remote-onset, 87; recent-onset, 73) and the remaining 23 patients developed DM during treatment of APC. Ultimately, 73.2% of patients (134/183) with DM received antidiabetic medication, including metformin (56 patients, 41.8%), sulfonylurea (62, 45.5%), and insulin (43, 32.1%). In multivariate analysis, cancer extent (hazard ratio [HR], 1.792; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.313 to 2.445; p < 0.001) showed association with decreased overall survival (OS), whereas a diagnosis of DM (HR, 0.788; 95% CI, 0.615 to 1.009; p=0.059) conferred positive tendency on the OS. Metformin treatment itself conferred better OS in comparison within DM patients (HR 0.693; 95% CI, 0.492 to 0.977; p=0.036) and even in all APC patients (adjusted HR, 0.697; 95% CI, 0.491 to 1.990; p=0.044).
CONCLUSION
For APC patients receiving palliative chemotherapy, metformin treatment is associated with longer OS. Patients with DM tend to survive longer than those without DM.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kris MG, Benowitz SI, Adams S, Diller L, Ganz P, Kahlenberg MS, et al. Clinical cancer advances 2010: annual report on progress against cancer from the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:5327–47.
Article2. Andre T, Balosso J, Louvet C, Gligorov J, Callard P, de Gramont A, et al. Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. General characteristics. Presse Med. 1998; 27:533–6.3. Chiu CC, Huang CC, Chen YC, Chen TJ, Liang Y, Lin SJ, et al. Increased risk of gastrointestinal malignancy in patients with diabetes mellitus and correlations with anti-diabetes drugs: a nationwide population-based study in Taiwan. Intern Med. 2013; 52:939–46.
Article4. Kuuselo R, Savinainen K, Azorsa DO, Basu GD, Karhu R, Tuzmen S, et al. Intersex-like (IXL) is a cell survival regulator in pancreatic cancer with 19q13 amplification. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:1943–9.5. Asano T, Yao Y, Shin S, McCubrey J, Abbruzzese JL, Reddy SA. Insulin receptor substrate is a mediator of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation in quiescent pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:9164–8.
Article6. Pannala R, Leirness JB, Bamlet WR, Basu A, Petersen GM, Chari ST. Prevalence and clinical profile of pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:981–7.
Article7. Huxley R, Ansary-Moghaddam A, Berrington de Gonzalez A, Barzi F, Woodward M. Type-II diabetes and pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis of 36 studies. Br J Cancer. 2005; 92:2076–83.
Article8. Pannala R, Basu A, Petersen GM, Chari ST. New-onset diabetes: a potential clue to the early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:88–95.
Article9. Chari ST, Leibson CL, Rabe KG, Timmons LJ, Ransom J, de Andrade M, et al. Pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus: prevalence and temporal association with diagnosis of cancer. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:95–101.
Article10. Calle EE, Murphy TK, Rodriguez C, Thun MJ, Heath CW Jr. Diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer mortality in a prospective cohort of United States adults. Cancer Causes Control. 1998; 9:403–10.11. Wakasugi H, Funakoshi A, Iguchi H. Clinical observations of pancreatic diabetes caused by pancreatic carcinoma, and survival period. Int J Clin Oncol. 2001; 6:50–4.
Article12. Chu CK, Mazo AE, Goodman M, Egnatashvili V, Sarmiento JM, Staley CA, et al. Preoperative diabetes mellitus and long-term survival after resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:502–13.
Article13. Mizuno S, Nakai Y, Isayama H, Takahara N, Miyabayashi K, Yamamoto K, et al. Diabetes is a useful diagnostic clue to improve the prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 2013; 13:285–9.
Article14. Li D, Yeung SC, Hassan MM, Konopleva M, Abbruzzese JL. Antidiabetic therapies affect risk of pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2009; 137:482–8.
Article15. Sadeghi N, Abbruzzese JL, Yeung SC, Hassan M, Li D. Metformin use is associated with better survival of diabetic patients with pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012; 18:2905.
Article16. Zheng W, McLerran DF, Rolland B, Zhang X, Inoue M, Matsuo K, et al. Association between body-mass index and risk of death in more than 1 million Asians. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:719–29.17. Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG, Sonenberg N, Pollak M. Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:10269–73.
Article18. Quinn BJ, Kitagawa H, Memmott RM, Gills JJ, Dennis PA. Repositioning metformin for cancer prevention and treatment. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 24:469–80.
Article19. Hwang AL, Haynes K, Hwang WT, Yang YX. Metformin and survival in pancreatic cancer: a retrospective cohort study. Pancreas. 2013; 42:1054–9.
Article20. Lee CK, Jung M, Jung I, Heo SJ, Jeong YH, An JY, et al. Cumulative metformin use and its impact on survival in gastric cancer patients after gastrectomy. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015 Jan 8 [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000001086.
Article21. Cui Y, Andersen DK. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2012; 19:F9–F26.
Article22. Hwang A, Narayan V, Yang YX. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. Cancer. 2013; 119:404–10.23. Yuan C, Rubinson DA, Qian ZR, Wu C, Kraft P, Bao Y, et al. Survival among patients with pancreatic cancer and long-standing or recent-onset diabetes mellitus. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:29–35.
Article24. Nakai Y, Isayama H, Sasaki T, Mizuno S, Sasahira N, Kogure H, et al. Clinical outcomes of chemotherapy for diabetic and nondiabetic patients with pancreatic cancer: better prognosis with statin use in diabetic patients. Pancreas. 2013; 42:202–8.25. Sah RP, Nagpal SJ, Mukhopadhyay D, Chari ST. New insights into pancreatic cancer-induced paraneoplastic diabetes. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 10:423–33.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Elevated Hemoglobin A1c Levels Are Associated with Worse Survival in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Patients with Diabetes
- Recent Perspective of Metformin
- The Effect of Metformin on Responses to Chemotherapy and Survival in Stage IV Colorectal Cancer with Diabetes
- Impact of Glycemic Control and Metformin Use on the Recurrence and Progression of Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Metformin Use May Increase Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Diabetic Women: An Analysis of the Korean National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort Database