J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Sep;31(9):1464-1471. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.9.1464.
Impact of Glycemic Control and Metformin Use on the Recurrence and Progression of Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. drjsi@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 2468281
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.9.1464
Abstract
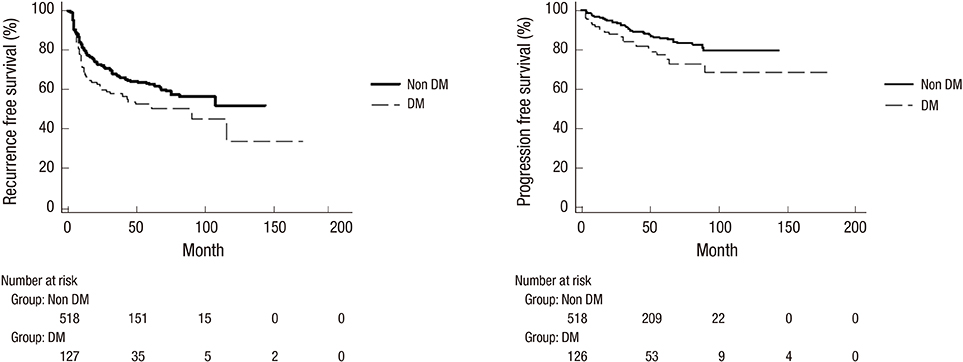
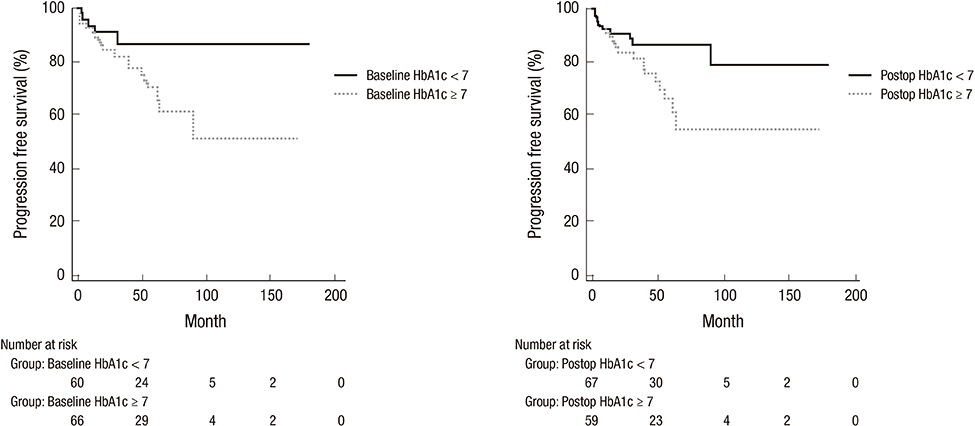
- The purpose of the present study was to determine the potential relationships of glycemic control and use of metformin with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer characteristics. We reviewed data from 645 patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer between January 2004 and May 2015. We analyzed the association of pre and post-operative glycemic control and use of metformin with clinical characteristics of bladder tumors. We also analyzed the association of glycemic control and use of metformin with recurrence-free and progression-free survivals. Diabetes mellitus patients showed decreased recurrence-free survival (hazard ratio 1.42; 95% confidence interval 1.1-1.9; P = 0.021) and progression-free survival (hazard ratio 1.79; 95% confidence interval 1.1-2.8; P = 0.013). Diabetes mellitus patients with a HbA1c ≥ 7.0% demonstrated a higher rate of progression (P = 0.026). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that progression-free survival rate was associated with poor baseline glycemic control (P = 0.026) and post-operative glycemic control (P = 0.025). However, use of metformin had no impact on the recurrence (P = 1.00) and progression (P = 0.282). In conclusion, poor baseline and post-operative glycemic control was related with shorter progression-free survival of patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Use of metformin had no impact on the recurrence and progression. Therefore, tight glycemic control and close follow-up for bladder tumor may be beneficial in patients with poor glycemic control.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/complications/*drug therapy
Disease-Free Survival
Female
Glycated Hemoglobin A/analysis
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Male
Metformin/*therapeutic use
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Recurrence, Local
Neoplasm Staging
Odds Ratio
Proportional Hazards Models
Retrospective Studies
Urinary Bladder Neoplasms/complications/mortality/*pathology/surgery
Glycated Hemoglobin A
Metformin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burger M, Catto JW, Dalbagni G, Grossman HB, Herr H, Karakiewicz P, Kassouf W, Kiemeney LA, La Vecchia C, Shariat S, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2013; 63:234–241.2. van der Heijden AG, Witjes JA. Recurrence, progression, and follow-up in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol Suppl. 2009; 8:556–562.3. Vigneri P, Frasca F, Sciacca L, Pandini G, Vigneri R. Diabetes and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009; 16:1103–1123.4. MacKenzie T, Zens MS, Ferrara A, Schned A, Karagas MR. Diabetes and risk of bladder cancer: evidence from a case-control study in New England. Cancer. 2011; 117:1552–1556.5. Fang H, Yao B, Yan Y, Xu H, Liu Y, Tang H, Zhou J, Cao L, Wang W, Zhang J, et al. Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of bladder cancer: an updated meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013; 15:914–922.6. Larsson SC, Orsini N, Brismar K, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of bladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2006; 49:2819–2823.7. Lin HC, Kachingwe BH, Lin HL, Cheng HW, Uang YS, Wang LH. Effects of metformin dose on cancer risk reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 6-year follow-up study. Pharmacotherapy. 2014; 34:36–45.8. Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 7th ed. West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell;2009.9. Miyamoto H, Miller JS, Fajardo DA, Lee TK, Netto GJ, Epstein JI. Non-invasive papillary urothelial neoplasms: the 2004 WHO/ISUP classification system. Pathol Int. 2010; 60:1–8.10. Larsson SC, Orsini N, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005; 97:1679–1687.11. Larsson SC, Mantzoros CS, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. 2007; 121:856–862.12. Friberg E, Orsini N, Mantzoros CS, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of endometrial cancer: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2007; 50:1365–1374.13. El-Serag HB, Hampel H, Javadi F. The association between diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of epidemiologic evidence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 4:369–380.14. Tripathi A, Folsom AR, Anderson KE; Iowa Women’s Health Study. Risk factors for urinary bladder carcinoma in postmenopausal women. The Iowa Women’s Health Study. Cancer. 2002; 95:2316–2323.15. Coughlin SS, Calle EE, Teras LR, Petrelli J, Thun MJ. Diabetes mellitus as a predictor of cancer mortality in a large cohort of US adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2004; 159:1160–1167.16. Jee SH, Ohrr H, Sull JW, Yun JE, Ji M, Samet JM. Fasting serum glucose level and cancer risk in Korean men and women. JAMA. 2005; 293:194–202.17. Larsson SC, Andersson SO, Johansson JE, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus, body size and bladder cancer risk in a prospective study of Swedish men. Eur J Cancer. 2008; 44:2655–2660.18. Swerdlow AJ, Laing SP, Qiao Z, Slater SD, Burden AC, Botha JL, Waugh NR, Morris AD, Gatling W, Gale EA, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in patients with insulin-treated diabetes: a UK cohort study. Br J Cancer. 2005; 92:2070–2075.19. Zendehdel K, Nyrén O, Ostenson CG, Adami HO, Ekbom A, Ye W. Cancer incidence in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a population-based cohort study in Sweden. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003; 95:1797–1800.20. Zhu Z, Wang X, Shen Z, Lu Y, Zhong S, Xu C. Risk of bladder cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus: an updated meta-analysis of 36 observational studies. BMC Cancer. 2013; 13:310.21. Joo JS, Kim JS, Jung SI, Kang TW, Kwon DD, Choi C, Park KS, Ryu SB. The prognostic significance of elevated serum creatinine for the recurrence and progression in superficial bladder tumors. Korean J Urol. 2007; 48:927–932.22. Macaulay VM. Insulin-like growth factors and cancer. Br J Cancer. 1992; 65:311–320.23. Bach LA, Rechler MM. Insulin-like growth factors and diabetes. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1992; 8:229–257.24. Giovannucci E. Insulin, insulin-like growth factors and colon cancer: a review of the evidence. J Nutr. 2001; 131:3109S–20S.25. Jones JI, Clemmons DR. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev. 1995; 16:3–34.26. Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O’Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet. 2004; 363:1346–1353.27. Zhao H, Grossman HB, Spitz MR, Lerner SP, Zhang K, Wu X. Plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 and binding protein-3, and their association with bladder cancer risk. J Urol. 2003; 169:714–717.28. Siddiqui AA, Spechler SJ, Huerta S, Dredar S, Little BB, Cryer B. Elevated HbA1c is an independent predictor of aggressive clinical behavior in patients with colorectal cancer: a case-control study. Dig Dis Sci. 2008; 53:2486–2494.29. Tai YS, Chen CH, Huang CY, Tai HC, Wang SM, Pu YS. Diabetes mellitus with poor glycemic control increases bladder cancer recurrence risk in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015; 31:307–314.30. Rieken M, Xylinas E, Kluth L, Crivelli JJ, Chrystal J, Faison T, Lotan Y, Karakiewicz PI, Fajkovic H, Babjuk M, et al. Association of diabetes mellitus and metformin use with oncological outcomes of patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2013; 112:1105–1112.31. Gallagher EJ, LeRoith D. Diabetes, cancer, and metformin: connections of metabolism and cell proliferation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011; 1243:54–68.32. Aljada A, Mousa SA. Metformin and neoplasia: implications and indications. Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 133:108–115.33. Inzucchi SE, Lipska KJ, Mayo H, Bailey CJ, McGuire DK. Metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes and kidney disease: a systematic review. JAMA. 2014; 312:2668–2675.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- New therapeutic agents for glycemic control in diabetes mellitus
- Glycemic Control in Diabetic Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy
- Autophagy and urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: A review
- Effects of Simultaneous Transurethral Resection of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- The Effect of Metformin in Obese Pediatric Patients with Type 2 Diabetes