Korean J Urol.
2009 Jan;50(1):33-38. 10.4111/kju.2009.50.1.33.
The Clinical Significance of Serum and Urine Cytokines in Patients with Acute Uncomplicated Pyelonephritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kthlmk@hanafos.com
- KMID: 2140111
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2009.50.1.33
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: In this prospective study, we evaluated the clinical significance of inflammatory cytokines in women with acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis undergoing antimicrobial therapy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyzed 26 female patients diagnosed with acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis between September 2007 and March 2008. Body temperature, white blood cell (WBC) counts, serum C-reactive protein (CRP), and serum and urine interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 were measured before and 12 hours, 24 hours, and 4 days after the intravenous administration of empirical ciprofloxacin.
RESULTS
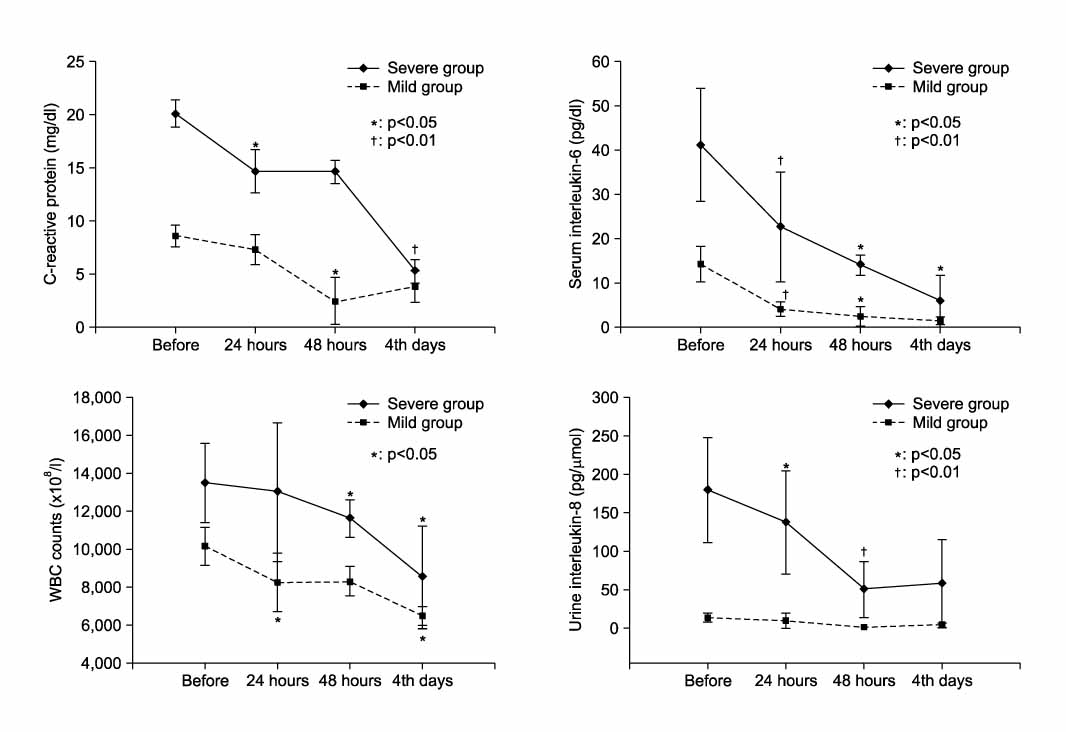
Initial serum CRP levels were correlated with initial serum IL-6 and initial urine IL-8 levels. Twenty-four hours after the start of antibiotic treatment, the CRP level and urine IL-8 level continued to be high, whereas serum IL-6 levels decreased significantly (26.1+/-32.4 vs 9.9+/-23.5pg/dl, p<0.01). When we divided the patients into mild (CRP<15mg/dl, n=14) and severe (CRP> or =15mg/dl, n=12) groups according to initial CRP levels, the serum IL-6 level decreased significantly in both the mild (14.2+/-4.0 vs 4.0+/-1.7pg/dl, p<0.01) and the severe (41.1+/-12.7 vs. 22.7+/-16.4pg/dl, p<0.01) groups within 24 hours, whereas CRP and urine IL-8 levels did not change significantly in either group.
CONCLUSIONS
Clinically, initial serum IL-6 and urine IL-8 levels were increased according to disease severity. Moreover, the serum IL-6 level decreased rapidly after antibiotic treatment within 24 hours. Serum IL-6 levels are a better indicator of the severity of disease and the therapeutic effect of empirical parenteral antibiotic use in patients with acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis than were either CRP or WBC counts.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Foxman B, Klemstine KL, Brown PD. Acute pyelonephritis in US hospitals in 1997: hospitalization and in-hospital mortality. Ann Epidemiol. 2003. 13:144–150.2. Ki M, Park T, Choi B, Foxman B. The epidemiology of acute pyelonephritis in South Korea, 1997-1999. Am J Epidemiol. 2004. 160:985–993.3. Nicolle LE, Friesen D, Harding GK, Roos LL. Hospitalization for acute pyelonephritis in Manitoba, Canada, during the period from 1989 to 1992; impact of diabetes, pregnancy, and aboriginal origin. Clin Infect Dis. 1996. 22:1051–1056.4. Nicolle LE. Uncomplicated urinary tract infection in adults including uncomplicated pyelonephritis. Urol Clin North Am. 2008. 35:1–12.5. Warren JW, Abrutyn E, Hebel JR, Johnson JR, Schaeffer AJ, Stamm WE. Guidelines for antimicrobial treatment of uncomplicated acute bacterial cystitis and acute pyelonephritis in women. Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA). Clin Infect Dis. 1999. 29:745–758.6. Chung H, Kim TW, Lee CH, Kim HS. The clinical significance of serum C-reactive protein in patients with acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis. Korean J Urol. 2005. 46:476–480.7. Bang SH, Chang IH, Han JH, Ahn SH. C-reactive protein is a useful marker to predict the severity and early response of acute pyelonephritis in women. Korean J Urol. 2007. 48:1143–1148.8. Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM. C-reactive protein: a critical update. J Clin Invest. 2003. 111:1805–1812.9. Horcajada JP, Velasco M, Filella X, Alvarez L, De Lazzari E, Marin JL, et al. Evaluation of inflammatory and renal-injury markers in women treated with antibiotics for acute pyelonephritis caused by Escherichia coli. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004. 11:142–146.10. Gurgoze MK, Akarsu S, Yilmaz E, Godekmerdan A, Akca Z, Ciftci I, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines and procalcitonin in children with acute pyelonephritis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005. 20:1445–1448.11. Kassir K, Vargas-Shiraishi O, Zaldivar F, Berman M, Singh J, Arrieta A. Cytokine profiles of pediatric patients treated with antibiotics for pyelonephritis: potential therapeutic impact. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001. 8:1060–1063.12. Fischer C, Gill C, Forrester MG, Nakamura R. Quantitation of "acute-phase proteins" postoperatively. Value in detection and monitoring of complications. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976. 66:840–846.13. Sheu JN, Chen MC, Lue KH, Cheng SL, Lee IC, Chen SM, et al. Serum and urine levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in children with acute pyelonephritis. Cytokine. 2006. 36:276–282.14. Svanborg C, Hedlund M, Connell H, Agace W, Duan RD, Nilsson A, et al. Bacterial adherence and mucosal cytokine responses. Receptors and transmembrane signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996. 797:177–190.15. Galanakis E, Bitsori M, Dimitriou H, Giannakopoulou C, Karkavitsas NS, Kalmanti M. Urine interleukin-8 as a marker of vesicoureteral reflux in infants. Pediatrics. 2006. 117:e863–e867.16. Unkila-Kallio L, Kallio MJ, Eskola J, Peltola H. Serum C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and white blood cell count in acute hematogenous osteomyelitis of children. Pediatrics. 1994. 93:59–62.17. Bach D, van den Berg-Segers A, Hubner A, van Breukelen G, Cesana M, Pletan Y. Rufloxacin once daily versus ciprofloxacin twice daily in the treatment of patients with acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis. J Urol. 1995. 154:19–24.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Significance of Serum C-reactive Protein in Patients with Acute Uncomplicated Pyelonephritis
- Usefulness of Blood Cultures in Acute Pyelonephritis
- Clinical Observation of Acute Bacterial Pyelonephritis
- The Assessment of Carfecillin in Acute Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection
- Serum alkaline phosphatase and γ-glutamyl transferase in acute pyelonephritis