Korean J Urol.
2007 Oct;48(10):1050-1057. 10.4111/kju.2007.48.10.1050.
The Significance of Periurethral Fibrosis and the Change of Nitric Oxide Synthase Containing Nerves in the Urethra of Diabetic Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. uroyoon@inha.ac.kr
- 2Yoo Urology Clinic, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Pharmacology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2139738
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2007.48.10.1050
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: We have previously demonstrated that increased urethral resistance was more prominent in diabetic rats than in controls. This may result from a compressive obstruction such as damage of the urethral nerve containing nitric oxide. Another possible cause for urethral obstruction could be a constrictive obstruction such as a periurethral fibrosis. In the present study, we investigated the changes in the expression of nitric oxide synthase(NOS) isoforms(compressive obstruction) and collagen subtypes (constrictive obstruction) in the urethral tissues of non-insulin dependent diabetic rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-six male Sprague-Dawley rats(18 diabetic rats and 18 control rats), bred from birth, were included in this study. Diabetes mellitus was induced by intraperitoneal administration of streptozotocin(90mg/kg) on the second day after birth. Urethral tissues were harvested at 12, 24 and 36 weeks after induction of diabetes and were stained for neuronal NOS(nNOS) and Masson trichrome. We also performed reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction or Western blot analysis to evaluate mRNA or protein expression of NOS isoforms and collagen subtypes in the urethral tissues.
RESULTS
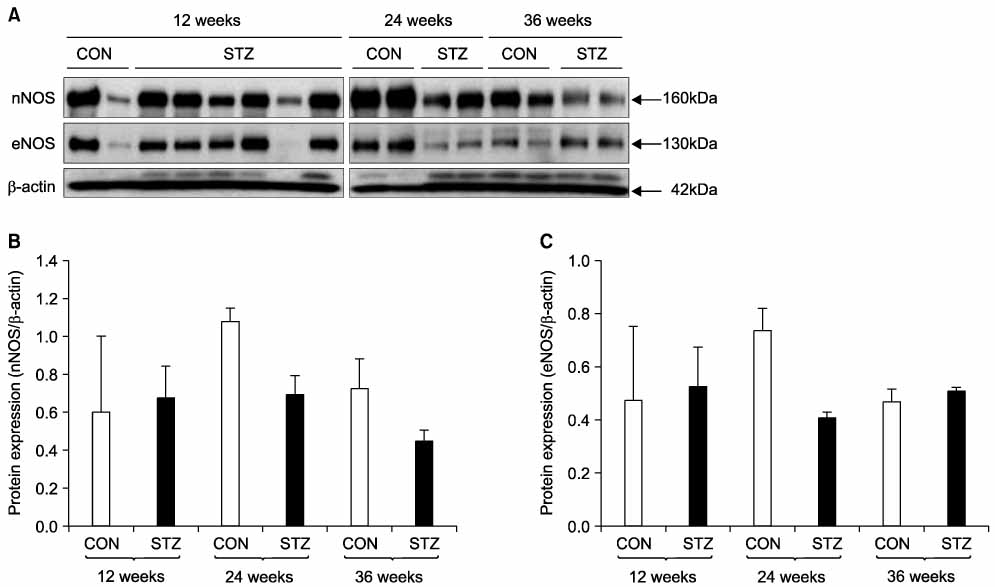
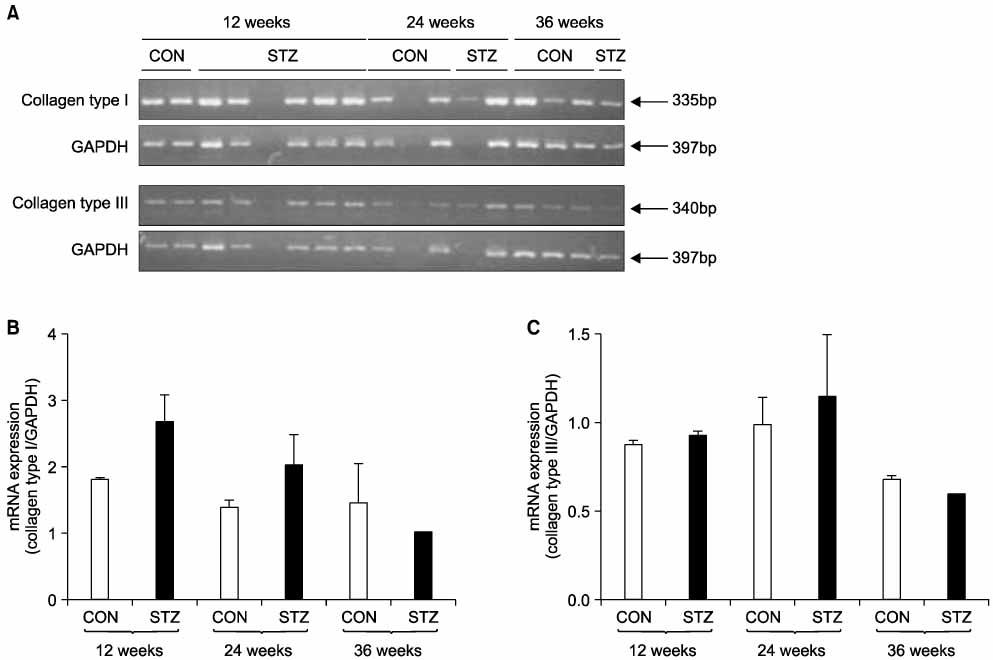
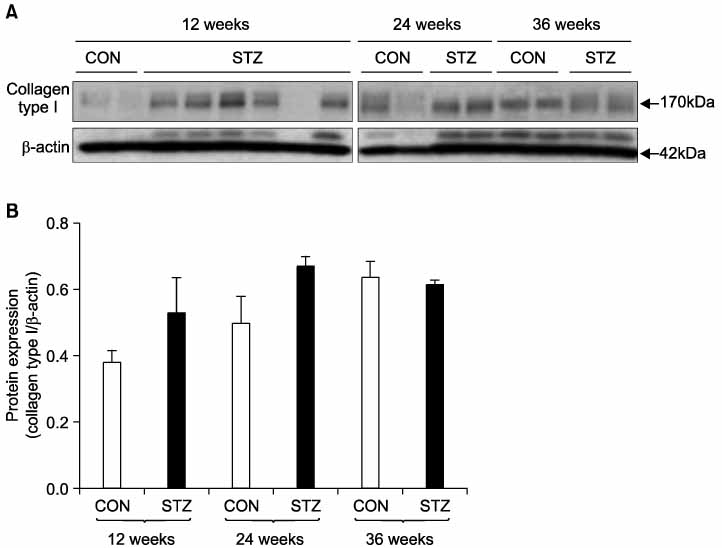
Immunohistochemical staining and Western blot analysis of nNOS revealed that the immunoreactivity and nNOS expression in the urethra was lower in the diabetic rats than in the controls. The Masson trichrome staining showed that there was urethral fibrosis in the diabetic rats. The mRNA or protein expression of collagen subtypes, especially type I collagen, were higher in the diabetic rat urethra than in the controls.
CONCLUSIONS
These data suggest that the increased urethral resistance in diabetic rats may be attributable to a decrease in the urethral nNOS expression and an increase in collagen content. Urethral dysfunction as well as a cystopathy may play an important role in the pathogenesis of diabetes- induced voiding dysfunction. (Korean J Urol 2007;48:1050-1057)
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Blotting, Western
Collagen
Collagen Type I
Diabetes Mellitus
Fibrosis*
Humans
Male
Neurons
Nitric Oxide Synthase*
Nitric Oxide*
Parturition
Protein Isoforms
Rats*
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
RNA, Messenger
Urethra*
Urethral Obstruction
Collagen
Collagen Type I
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase
Protein Isoforms
RNA, Messenger
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim SA, Park WS, Ohrr HC, Kang HY, Lee DH, Yi SW, et al. Prevalence and management status of diabetes mellitus in Korea. Korean J Med. 2005. 68:10–17.2. Bryfogle JW, Bradley RF. The vascular complications of diabetes mellitus: a clinical study. Diabetes. 1957. 6:159–167.3. Vinik AI, Holland MT, Le Bear JM, Liuzze FJ, Stansberry KB, Colen LB. Diabetic neuropathies. Diabetes Care. 1992. 15:1926–1975.4. Frimodt-Moller C. Diabetic cystopathy: epidemiology and related disorders. Ann Intern Med. 1980. 92:318–321.5. Motzkin D. The significance of deficient bladder sensation. J Urol. 1968. 100:445–450.6. Ellenberg M. Development of urinary bladder dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1980. 92:321–323.7. Mumtaz FH, Sullivan ME, Thompson CS, Dashwood MR, Naseem KM, Bruckdorfer KR, et al. Alterations in the nitric oxide synthase binding sites and non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic mediated smooth muscle relaxation in the diabetic rabbit bladder outlet: possible relevance to the pathogenesis of diabetic cystopathy. J Urol. 1999. 162:558–566.8. Derek JG. Pressure-flow studies of micturiation. Urol Clin North Am. 1996. 23:279–297.9. Schafer W. Hinman F, editor. The contribution of the bladder outlet to the relation between pressure and flow rate during micturition. Benign prostatic hypertrophy. 1983. New York: Springer-Verlag;470.10. Eika B, Levin RM, Longhurst PA. Collagen and bladder function in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: effects of insulin and aminoguanidine. J Urol. 1992. 148:167–172.11. Koo HP, Santarosa RP, Buttyan R, Shabsigh R, Olsson CA, Kaplan SA. Early molecular changes associated with streptozotocin-induced diabetic bladder hypertrophy in the rat. Urol Res. 1993. 21:375–381.12. Hellweg R, Hartung HD. Endogenous levels of nerve growth factor (NGF) are altered in experimental diabetes mellitus: a possible role for NGF in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. J Neurosci Res. 1990. 26:258–267.13. Kim JC, Seo SL, Park YH, Hwang TK. Changes of detrusor contractility and growth factors in streptozotocin-induced NIDDM rat. Korean J Urol. 2000. 41:615–621.14. Chung JS, Yoo HS, Lee T. Urethral dysfunction in a non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus rat model. Korean J Urol. 2006. 47:1007–1012.15. Weir GC, Clore ET, Zmachinski CJ, Bonner-Weir S. Islet secretion in a new experimental model for non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1981. 30:590–595.16. Sasaki K, Chancellor MB, Phelan MW, Yokoyama T, Fraser MO, Seki S, et al. Diabetic cystopathy correlates with a long-term decrease in nerve growth factor levels in the bladder and lumbosacral dorsal root Ganglia. J Urol. 2002. 168:1259–1264.17. Low PA, Tuck RR, Dyck PJ, Schmelzer JD, Yao JK. Prevention of some electrophysiologic and biochemical abnormalities with oxygen supplementation in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1984. 81:6894–6898.18. Thrainsdottir S, Malik RA, Dahlin LB, Wiksell P, Eriksson KF, Rosen I, et al. Endoneurial capillary abnormalities presage deterioration of glucose tolerance and accompany peripheral neuropathy in man. Diabetes. 2003. 52:2615–2622.19. Buck AC, Reed PI, Siddiq YK, Chisholm GD, Fraser TR. Bladder dysfunction and neuropathy in diabetes. Diabetologia. 1976. 12:251–258.20. Sima AA, Nathaniel V, Bril V, McEwen TA, Greene DA. Histopathological heterogeneity of neuropathy in insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent diabetes, and demonstration of axo-glial dysjunction in human diabetic neuropathy. J Clin Invest. 1988. 81:349–364.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Expression of NADPH-diaphorase in Corneal Neovascularization of streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rat
- Impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation is mediated by reduced production of nitric oxide in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Distribution of Nitric Oxide Synthase Isoforms in Perioral Exocrine Glands in Rats
- The Effect of Estrogen on Expression of Neuronal and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase and on Histologic Composition in Rat Bladder and Urethra
- Involvement of Fibronectin in the Migration of Macrophage and Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase in the BCG induced Inflammatory Sites in Rat Bladder