J Korean Surg Soc.
2011 Feb;80(2):157-160. 10.4174/jkss.2011.80.2.157.
Acute Hepatic Failure Associated with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Induced by Carbamazepine Treatment in a Patient with Transverse Myelitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine and the Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea. sunhyung@chol.com
- 2Department of Neurology, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine and the Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2117125
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.80.2.157
Abstract
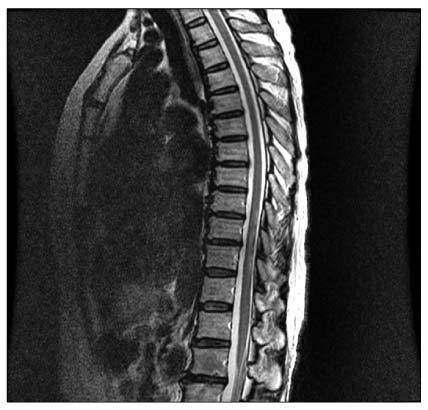
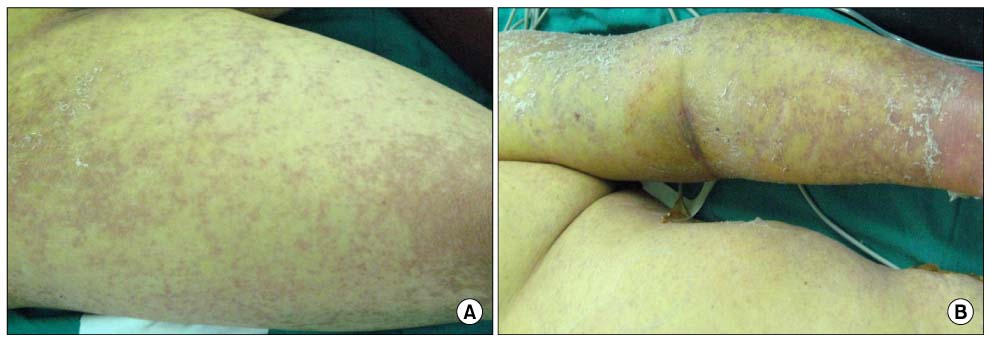
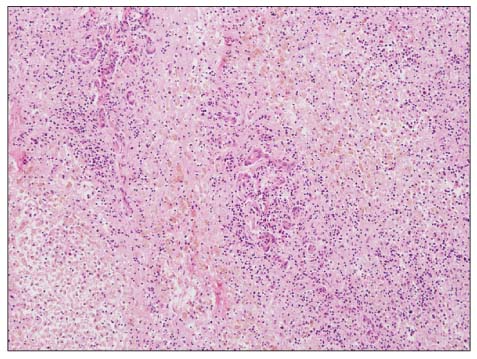
- Carbamazepine-induced liver injury is less common, but the consequences of the side effects can be very serious leading to death or a need for liver transplantation. We report a case of a 60-year-old female transverse myelitis patient with fulminant hepatic failure and Stevens-Johnson syndrome induced by carbamazepine who successfully underwent deceased donor liver transplantation. The patient, a 60-year-old female, was admitted to our service due to acute liver insufficiency and a drowsy mental state attributable to carbamazepine. She had been treated with carbamazepine to control transverse myelitis. Fifty days after the use of carbamazepine, she developed jaundice, erythematous papules and bullae, and decreased consciousness. The diagnosis of Stevens-Johnson syndrome was considered. She underwent deceased donor liver transplantation. She was discharged with normal graft functions 5 months after transplantation. Thus, liver transplantation can be a feasible therapy for patients with carbamazepine-induced hepatic failure associated with Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berman M, Feldman S, Alter M, Zilber N, Kahana E. Acute transverse myelitis: incidence and etiologic considerations. Neurology. 1981. 31:966–971.2. Jeffery DR, Mandler RN, Davis LE. Transverse myelitis. Retrospective analysis of 33 cases, with differentiation of cases associated with multiple sclerosis and parainfectious events. Arch Neurol. 1993. 50:532–535.3. Ross DS, Swain R. Acute atraumatic quadriparesis in a college football player. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998. 30:1663–1665.4. Defresne P, Meyer L, Tardieu M, Scalais E, Nuttin C, De Bont B, et al. Efficacy of high dose steroid therapy in children with severe acute transverse myelitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001. 71:272–274.5. Kalita J, Misra UK. Is methyl prednisolone useful in acute transverse myelitis? Spinal Cord. 2001. 39:471–476.6. Lahat E, Pillar G, Ravid S, Barzilai A, Etzioni A, Shahar E. Rapid recovery from transverse myelopathy in children treated with methylprednisolone. Pediatr Neurol. 1998. 19:279–282.7. Çelik Y, Tabak F, Mert A, Çelik AD, Aktuğlu Y. Transverse myelitis caused by Varicella. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2001. 103:260–261.8. Tennis P, Stern RS. Risk of serious cutaneous disorders after initiation of use of phenytoin, carbamazepine, or sodium valproate: a record linkage study. Neurology. 1997. 49:542–546.9. Roujeau JC, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Rzany B, Stern RS, Anderson T, et al. Medication use and the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. N Engl J Med. 1995. 333:1600–1607.10. Paquet P, Pierard GE, Quatresooz P. Novel treatment for drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome). Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005. 136:205–216.11. Patterson R, Tripathi A. Stevens-Johnson syndrome: Getting ready for the year 2000 and beyond. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1999. 83:339–340.12. Straussberg R, Harel L, Ben-Amitai D, Cohen D, Amir J. Carbamazepine-Induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome treated with IV steroids and IVIG. Pediatr Neurol. 2000. 22:231–233.13. Lee DM, Jeon HS, Yoo WH. Transverse myelitis in a patient with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Yonsei Medical Journal. 2003. 44:323–327.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in a Hypoxic Brain Injury Patient Treated with Carbamazepine
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Induced by Carbamazepine Treatment in a Patient Who Previously Had Carbamazepine Induced Pruritus: A Case Report
- A case of Stevens-Johnson syndrome caused by oxcarbazepine
- Five Cases of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome May Be Associated with Methazolamide Treatment
- Clinical Study of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome