Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2010 Dec;14(6):359-364. 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.6.359.
Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist BD1047 Reduces Allodynia and Spinal ERK Phosphorylation Following Chronic Compression of Dorsal Root Ganglion in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Institute for Medical Science, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju 561-180, Korea.
- 2Department of Pharmacology, Institute for Medical Science, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju 561-180, Korea. 1972y@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2071706
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.6.359
Abstract
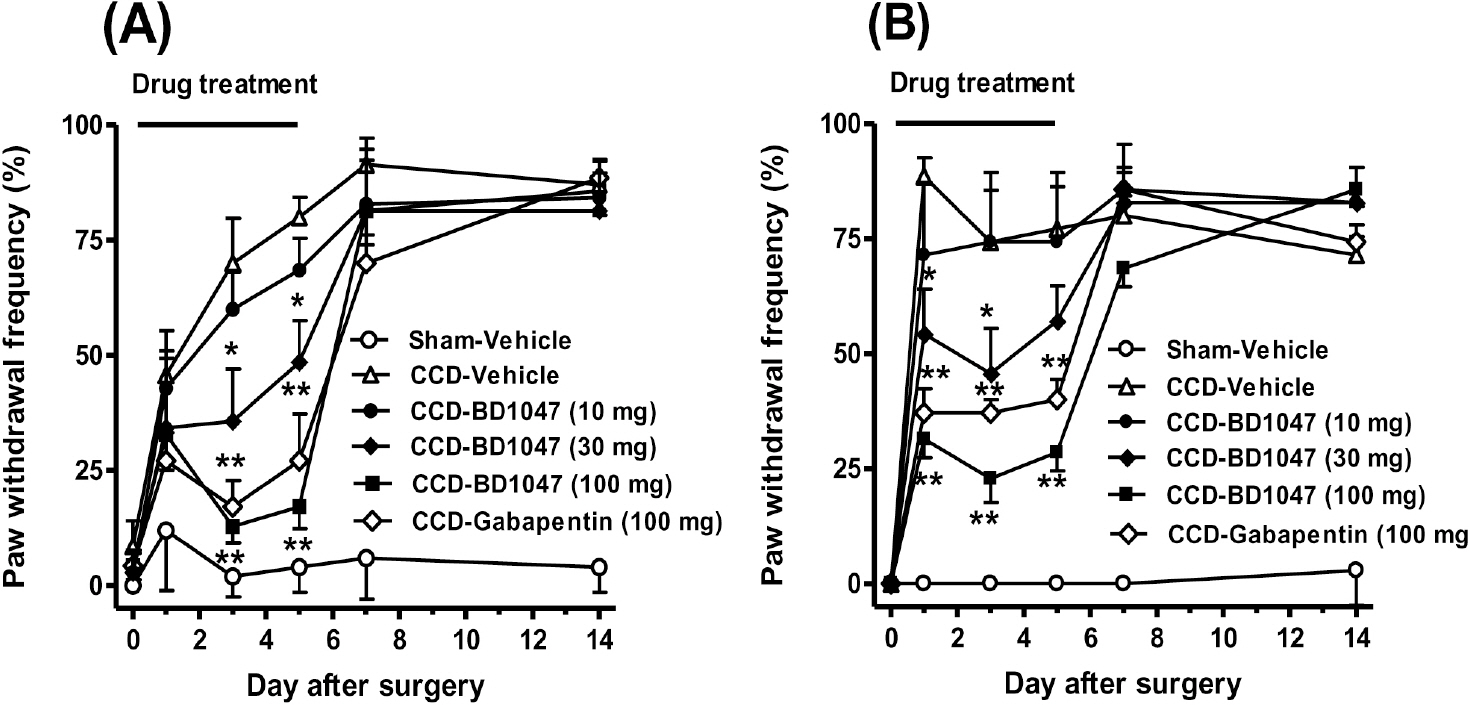
- Many therapeutic roles have been proposed for sigma-1 receptor (Sig-1R), but the involvement of Sig-1R in neuropathic pain has currently not been well explored. The present study aimed to evaluate the anti-nociceptive effect of Sig-1R antagonist (BD1047) in a rat model of chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion (CCD), which is a model of human foraminal stenosis and radicular pain. When stainless steel rods were inserted into the intervertebral foramen of lumbar vertebrae 4 and 5, the CCD developed reliable mechanical (from 3 day) and cold allodynia (from 1 day) as compared with the sham operation group. The spinal expressions of Sig-1R and phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (pERK) were significantly increased from day 3 to day 14 after CCD surgery, as is consistent with the manifestation of allodynia. The BD 1047 (10, 30, 100 mg/kg) administered on postoperative days 0~5 dose-dependently suppressed both the induction of allodynia and the elevation of the spinal pERK expression in a manner comparable with that of gabapentin (100 mg/kg). At 7 days post-CCD surgery, BD1047 (10, 30, 100 mg/kg) administration also produced anti-nociceptive effects on the mechanical and cold allodynia similar with those of gabapentin (100 mg/kg). Therefore, this data suggested that Sig-1R may play an important role in both the development and maintenance of CCD-induced neuropathy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Amines
Animals
Cold Temperature
Constriction, Pathologic
Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acids
Ethylenediamines
gamma-Aminobutyric Acid
Ganglia, Spinal
Humans
Hyperalgesia
Lumbar Vertebrae
Neuralgia
Phosphorylation
Phosphotransferases
Rats
Receptors, sigma
Salicylamides
Spinal Nerve Roots
Stainless Steel
Amines
Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acids
Ethylenediamines
Phosphotransferases
Receptors, sigma
Salicylamides
Stainless Steel
gamma-Aminobutyric Acid
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Antinociceptive Effect of
Cyperi rhizoma andCorydalis tuber Extracts on Neuropathic Pain in Rats
Jae-Gyun Choi, Suk-Yun Kang, Jae-Min Kim, Dae-Hyun Roh, Seo-Yeon Yoon, Jin Bong Park, Jang-Hern Lee, Hyun-Woo Kim
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;16(6):387-392. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.6.387.
Reference
-
References
1. Maurice T, Su TP. The pharmacology of sigma-1 receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 2009; 124:195–206.
Article2. Cendan CM, Pujalte JM, Portillo-Salido E, Montoliu L, Baeyens JM. Formalin-induced pain is reduced in sigma(1) receptor knockout mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005; 511:73–74.3. Kim HW, Kwon YB, Roh DH, Yoon SY, Han HJ, Kim KW, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. Intrathecal treatment with sigma1 receptor antagonists reduces formalin-induced phosphorylation of NMDA receptor subunit 1 and the second phase of formalin test in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 2006; 148:490–498.4. Kim HW, Roh DH, Yoon SY, Seo HS, Kwon YB, Han HJ, Kim KW, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. Activation of the spinal sigma-1 receptor enhances NMDA-induced pain via PKC- and PKA-dependent phosphorylation of the NR1 subunit in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 2008; 154:1125–1134.
Article5. Yoon SY, Roh DH, Seo HS, Kang SY, Han HJ, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. Intrathecal injection of the neurosteroid, DHEAS, produces mechanical allodynia in mice: involvement of spinal sigma-1 and GABA receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2009; 157:666–673.6. Kibaly C, Meyer L, Patte-Mensah C, Mensah-Nyagan AG. Biochemical and functional evidence for the control of pain mechanisms by dehydroepiandrosterone endogenously synthesized in the spinal cord. FASEB J. 2008; 22:93–104.
Article7. de la Puente B, Nadal X, Portillo-Salido E, Sanchez-Arroyos R, Ovalle S, Palacios G, Muro A, Romero L, Entrena JM, Baeyens JM, Lopez-Garcia JA, Maldonado R, Zamanillo D, Vela JM. Sigma-1 receptors regulate activity-induced spinal sensitization and neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. Pain. 2009; 145:294–303.8. Roh DH, Kim HW, Yoon SY, Seo HS, Kwon YB, Kim KW, Han HJ, Beitz AJ, Na HS, Lee JH. Intrathecal injection of the sigma(1) receptor antagonist BD1047 blocks both mechanical allodynia and increases in spinal NR1 expression during the induction phase of rodent neuropathic pain. Anesthesiology. 2008; 109:879–889.9. Huang ZJ, Song XJ. Differing alterations of sodium currents in small dorsal root ganglion neurons after ganglion compression and peripheral nerve injury. Mol Pain. 2008; 4:20.
Article10. Ji RR, Gereau RW 4th, Malcangio M, Strichartz GR. MAP kinase and pain. Brain Res Rev. 2009; 60:135–148.
Article11. Ma W, Quirion R. Partial sciatic nerve ligation induces increase in the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in astrocytes in the lumbar spinal dorsal horn and the gracile nucleus. Pain. 2002; 99:175–184.
Article12. Ma C, LaMotte RH. Multiple sites for generation of ectopic spontaneous activity in neurons of the chronically compressed dorsal root ganglion. J Neurosci. 2007; 27:14059–14068.
Article13. Coderre TJ, Kumar N, Lefebvre CD, Yu JS. Evidence that gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain by inhibiting the spinal release of glutamate. J Neurochem. 2005; 94:1131–1139.
Article14. Werner MF, Kassuya CA, Ferreira J, Zampronio AR, Calixto JB, Rae GA. Peripheral kinin B(1) and B(2) receptor-operated mechanisms are implicated in neuropathic nociception induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2007; 53:48–57.
Article15. Zhuang ZY, Gerner P, Woolf CJ, Ji RR. ERK is sequentially activated in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes by spinal nerve ligation and contributes to mechanical allodynia in this neuropathic pain model. Pain. 2005; 114:149–159.
Article16. Ma W, Quirion R. The ERK/MAPK pathway, as a target for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2005; 9:699–713.
Article17. Dubrovsky BO. Steroids, neuroactive steroids and neurosteroids in psychopathology. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2005; 29:169–192.
Article18. Schaeffer V, Meyer L, Patte-Mensah C, Eckert A, Mensah-Nyagan AG. Sciatic nerve injury induces apoptosis of dorsal root ganglion satellite glial cells and selectively modifies neurosteroidogenesis in sensory neurons. Glia. 2010; 58:169–180.
Article19. Roh DH, Kim HW, Yoon SY, Seo HS, Kwon YB, Kim KW, Han HJ, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. Intrathecal administration of sigma-1 receptor agonists facilitates nociception: involvement of a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. J Neurosci Res. 2008; 86:3644–3654.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Antinociceptive Effect of Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist, BD1047, in a Capsaicin Induced Headache Model in Rats
- Role of Sigma Receptor and Neurosteroids in Pain Sensation
- Spinal and Peripheral GABA-A and B Receptor Agonists for the Alleviation of Mechanical Hypersensitivity following Compressive Nerve Injury in the Rat
- The Intracisternal Administration of MEK Inhibitor Attenuates Mechanical and Cold Allodynia in a Rat Model of Compression of the Trigeminal Ganglion
- Change in the Expression of p75 Neurotrophin Receptor and TRPV1 in the Spinal Cord and Dorsal Root Ganglion after an Injury to the Spinal Nerves in Rats