Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2009 Dec;13(6):425-429. 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.6.425.
The Antinociceptive Effect of Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist, BD1047, in a Capsaicin Induced Headache Model in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 561-180, Korea. keewon222@gmail.com
- 2Department of Laboratory Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 561-180, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, College of Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 561-180, Korea.
- KMID: 2285376
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.6.425
Abstract
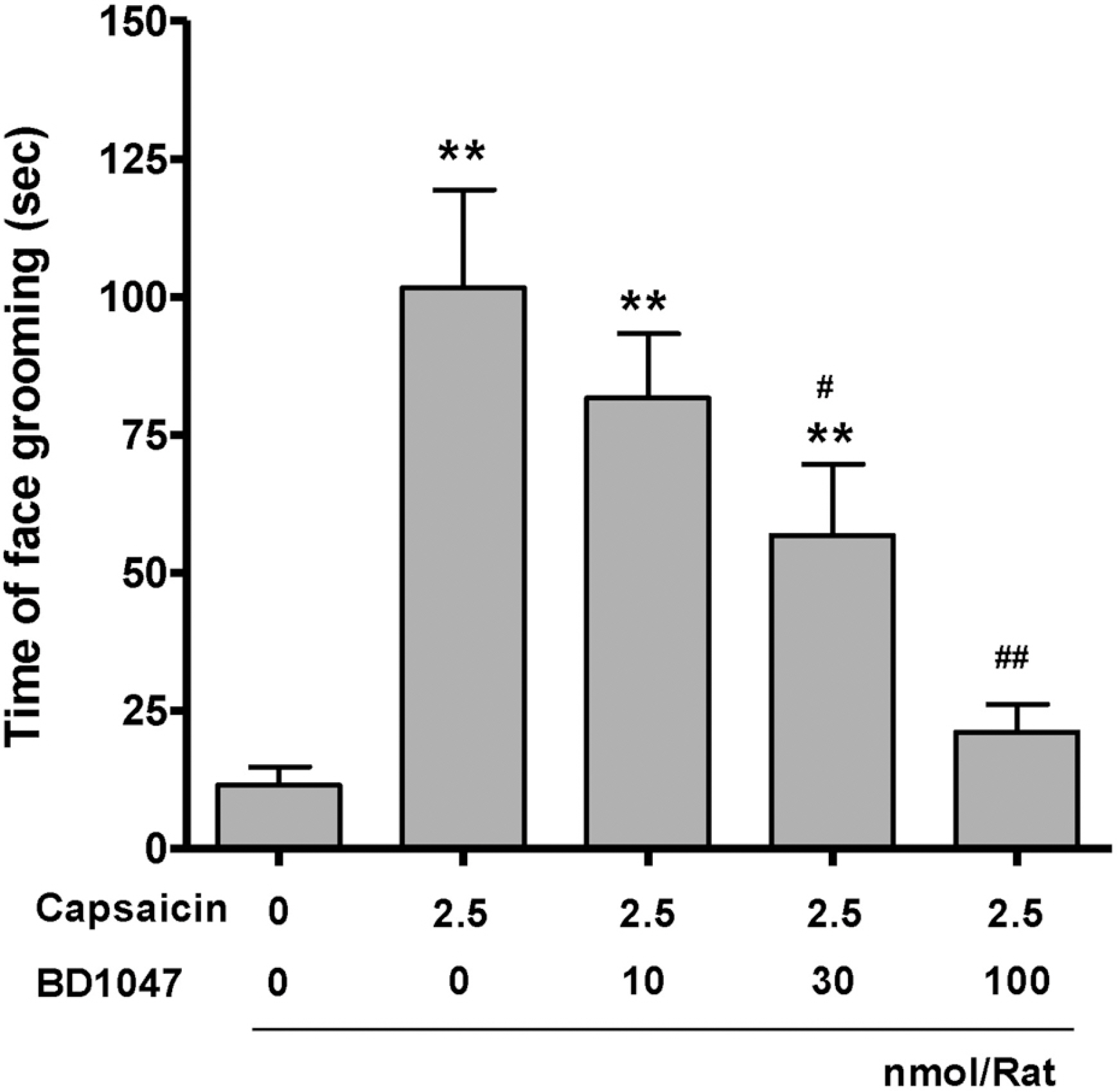
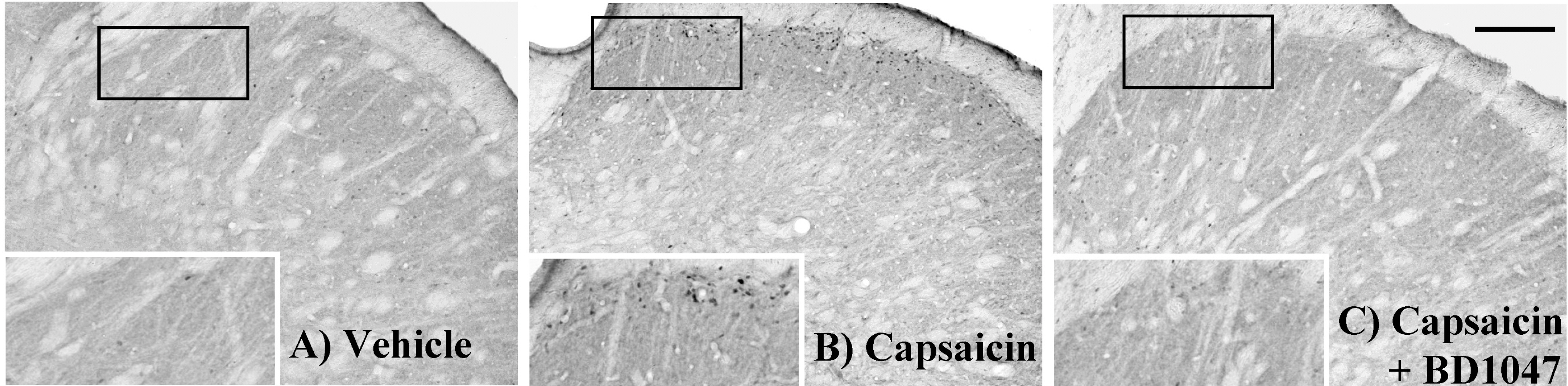
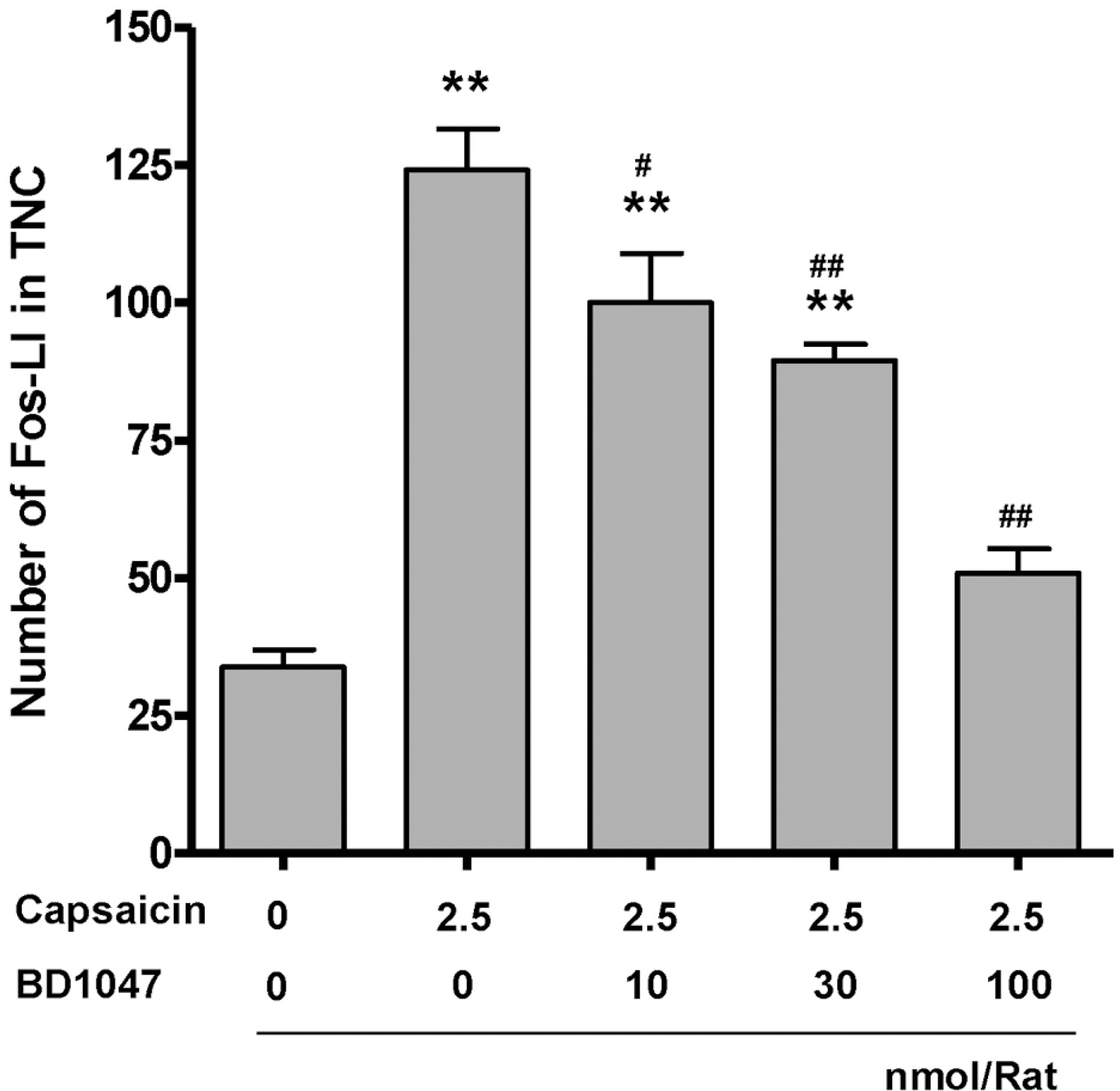
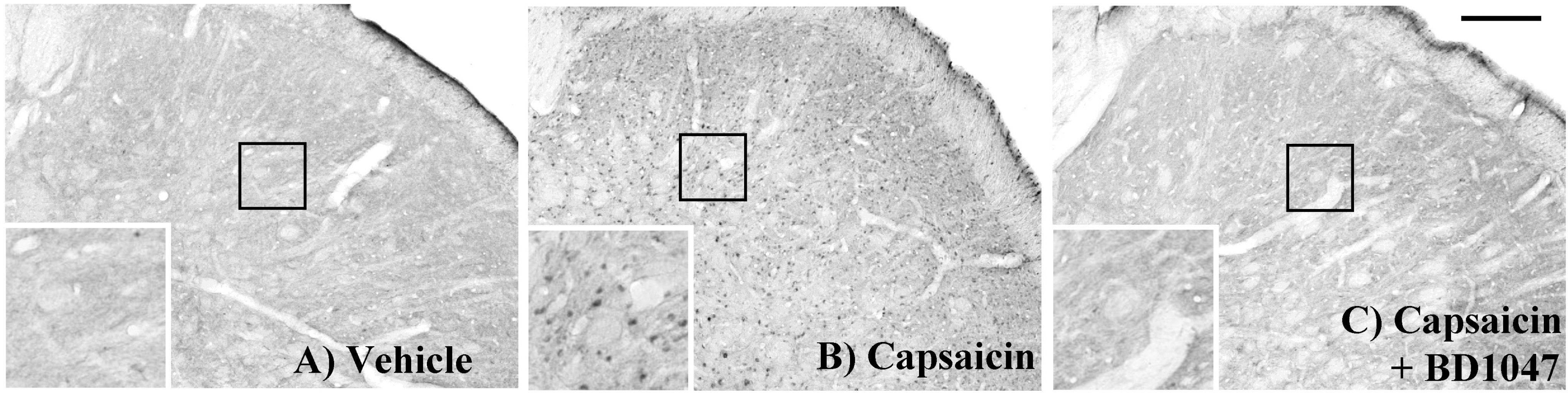
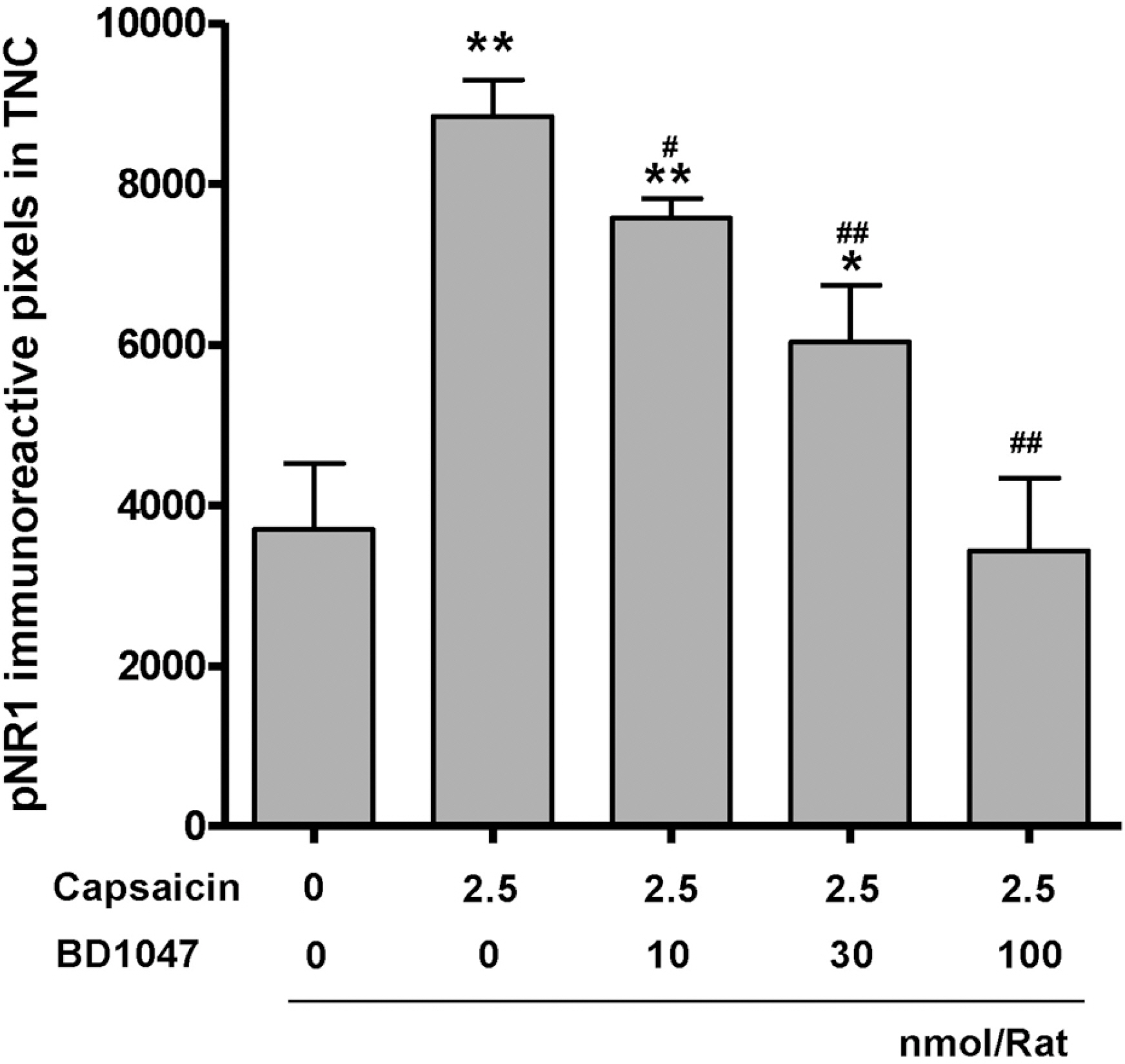
- Intracranial headaches, including migraines, are mediated by nociceptive activation of the trigeminal nucleus caudalis (TNC), but the precise mechanisms are poorly understood. We previously demonstrated that selective blockage of spinal sigma-1 receptors (Sig-1R) produces a prominent antinociceptive effect in several types of pain models. This study evaluates whether the Sig-1R antagonist (BD1047) has an antinociceptive effect on capsaicin (a potent C-fiber activator) induced headache models in rats. Intracisternal infusion of capsaicin evoked pain behavior (face grooming), which was significantly attenuated by BD1047 pretreatment. BD1047 consistently reduced capsaicin-induced Fos-like immunoreactivity (Fos-LI), a neuronal activator, in the TNC in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, capsaicin-induced phosphorylation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 1 was reversed by BD1047 pretreatment in the TNC. These results indicate that the Sig-1R antagonist has an inhibitory effect on nociceptive activation of the TNC in the capsaicin-induced headache animal model.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Role of Sigma Receptor and Neurosteroids in Pain Sensation
Jang-Hern Lee
Hanyang Med Rev. 2011;31(2):123-133. doi: 10.7599/hmr.2011.31.2.123.Antinociceptive Effect of
Cyperi rhizoma andCorydalis tuber Extracts on Neuropathic Pain in Rats
Jae-Gyun Choi, Suk-Yun Kang, Jae-Min Kim, Dae-Hyun Roh, Seo-Yeon Yoon, Jin Bong Park, Jang-Hern Lee, Hyun-Woo Kim
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;16(6):387-392. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.6.387.
Reference
-
References
Bermack J., Lavoie N., Dryver E., Debonnel G. Effects of sigma ligands on NMDA receptor function in the bulbectomy model of depression: a behavioural study in the rat. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 5:53–62. 2002.
ArticleCendán CM., Pujalte JM., Portillo-Salido E., Baeyens JM. Formalin-induced pain is reduced in sigma (1) receptor knockout mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 511:73–74. 2005.Entrena JM., Cobos EJ., Nieto FR., Cendán CM., Baeyens JM., Del Pozo E. Antagonism by haloperidol and its metabolites of mechanical hypersensitivity induced by intraplantar capsaicin in mice: role of sigma-1 receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 205:21–33. 2009.
ArticleGoadsby PJ., Edvinsson L. The trigeminovascular system and migraine: studies characterizing cerebrovascular and neuropeptide changes seen in humans and cats. Ann Neurol. 33:48–56. 1993.
ArticleGuitart X., Codony X., Monroy X. Sigma receptors: biology and therapeutic potential. Psychopharmacology. 174:301–319. 2004.
ArticleKemper RH., Spoelstra MB., Meijler WJ., Ter Horst GJ. Lipo-polysaccharide-induced hyperalgesia of intracranial capsaicin sensitive afferents in conscious rats. Pain. 78:181–190. 1998.
ArticleKim HW., Kwon YB., Roh DH., Yoon SY., Han HJ., Kim KW., Beitz AJ., Lee JH. Intrathecal treatment with sigma1 receptor antagonists reduces formalin-induced phosphorylation of NMDA receptor subunit 1 and the second phase of formalin test in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 148:490–498. 2006.Kim HW., Roh DH., Yoon SY., Seo HS., Kwon YB., Han HJ., Kim KW., Beitz AJ., Lee JH. Activation of the spinal sigma-1 receptor enhances NMDA-induced pain via PKC- and PKA-dependent phosphorylation of the NR1 subunit in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 154:1125–1134. 2008.
ArticleKwon YB., Lee JD., Lee HJ., Han HJ., Mar WC., Kang SK., Beitz AJ., Lee JH. Bee venom injection into an acupuncture point reduces arthritis associated edema and nociceptive responses. Pain. 90:271–280. 2001.
ArticleLipton SA. Pathologically-activated therapeutics for neuroprotection: Mechanism of NMDA receptor block by memantine and S-nitrosylation. Curr Drug Targets. 8:621–632. 2007.
ArticleManeepak M., Grand SL., Srikiatkhachorn A. Serotonin depletion increases nociception-evoked trigeminal NMDA receptor phosphorylation. Headache. 49:375–382. 2009.
ArticleMitsikostas DD., Sanchez del Rio M. Receptor systems mediating c-fos expression within trigeminal nucleus caudalis in animal models of migraine. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 35:20–35. 2001.
ArticleNuwayhid SJ., Werling LL. Sigma1 receptor agonist-mediated regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate-stimulated [3H]dopamine release is dependent upon protein kinase C. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 304:364–369. 2003.Oshinsky ML., Luo J. Neurochemistry of trigeminal activation in an animal model of migraine. Headache. 46(Suppl 1):S39–S44. 2006.
ArticleOtahara N., Ikeda T., Sakoda S., Shiba R., Nishimori T. Involvement of NMDA receptors in Zif/268 expression in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis following formalin injection into the rat whisker pad. Brain Res Bull. 62:63–70. 2003.
ArticlePark BR., Doh NY., Kim MS., Chun SW., Lee MY., Lee SH. Correlation between electrical activity of type I neuron and c-Fos expression in the medial vestibular nuclei following unilateral labyrinthectomy in rats. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 1:505–513. 1997.Roh DH., Kim HW., Yoon SY., Seo HS., Kwon YB., Kim KW., Han HJ., Beitz AJ., Na HS., Lee JH. Intrathecal injection of the sigma(1) receptor antagonist BD1047 blocks both mechanical allodynia and increases in spinal NR1 expression during the induction phase of rodent neuropathic pain. Anesthesiology. 109:879–889. 2008.Spengos K., Theleritis C., Paparrigopoulos T. Memantine and NMDA antagonism for chronic migraine: a potentially novel therapeutic approach? Headache. 48:284–286. 2008.
ArticleTer Horst GJ., Meijler WJ., Korf J., Kemper RH. Trigeminal nociception-induced cerebral Fos expression in the conscious rat. Cephalalgia. 21:963–975. 2001.
ArticleYagasaki Y., Numakawa T., Kumamaru E., Hayashi T., Su TP., Kunugi H. Chronic antidepressants potentiate via sigma-1 receptors the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced signaling for glutamate release. J Biol Chem. 281:12941–12949. 2006.
ArticleYao D., Sessle BJ. Nitroglycerin facilitates calcitonin gene-related peptide-induced behavior. Neuroreport. 19:1307–1311. 2008.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Protective effects of sigma 1 receptor agonist PRE084 on 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid–induced experimental colitis in mice
- Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist BD1047 Reduces Allodynia and Spinal ERK Phosphorylation Following Chronic Compression of Dorsal Root Ganglion in Rats
- Effects of Haloperidol on [Ca2+]i Change in HIT T-15 Insulinoma Cells
- The role of spinal adrenergic receptors on the antinociception of ginsenosides in a rat postoperative pain model
- The morphometric study of the effect of capsaicin on the spinal ganglion cells in neonatal rats