Clin Exp Vaccine Res.
2015 Jan;4(1):99-106. 10.7774/cevr.2015.4.1.99.
In silico analysis for identifying potential vaccine candidates against Staphylococcus aureus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Bacteriology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran.
- 2Applied Microbiology Research Center, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. jafar.amani@gmail.com
- 3Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- KMID: 2049113
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7774/cevr.2015.4.1.99
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most important causes of nosocomial and community-acquired infections. The increasing incidence of multiple antibiotic-resistant S. aureus strains and the emergence of vancomycin resistant S. aureus strains have placed renewed interest on alternative means of prevention and control of infection. S. aureus produces a variety of virulence factors, so a multi-subunit vaccine will be more successful for preventing S. aureus infections than a mono-subunit vaccine.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
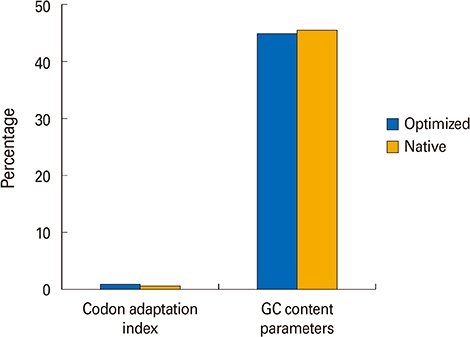
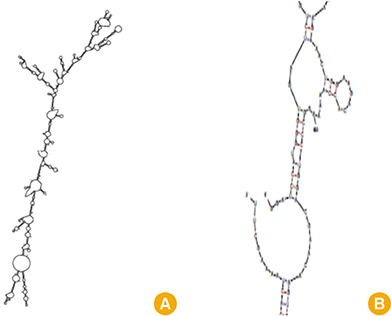
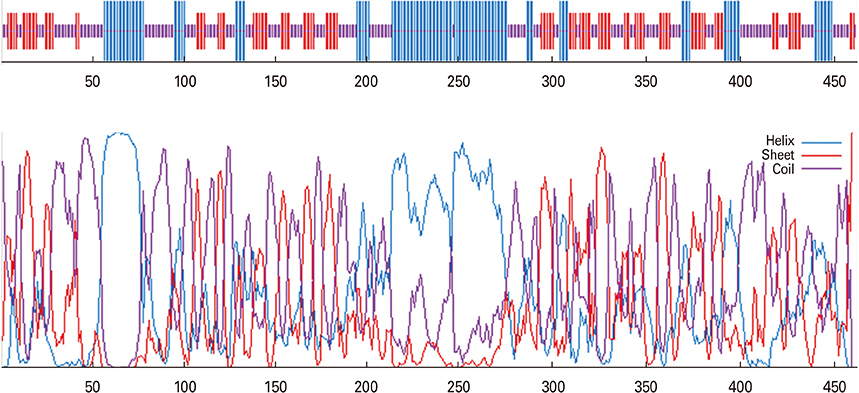
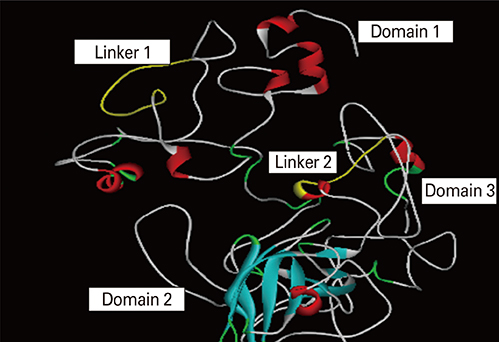
We selected three important virulence factors of S. aureus, clumping factor A (ClfA), iron-regulated surface determinant (IsdB), and gamma hemolysin (Hlg) that are potential candidates for vaccine development. We designed synthetic genes encoding the clfA, isdB, and hlg and used bioinformatics tools to predict structure of the synthetic construct and its stabilities. VaxiJen analysis of the protein showed a high antigenicity. Linear and conformational B-cell epitopes were identified.
RESULTS
The proteins encoded by these genes were useful as vaccine candidates against S. aureus infections.
CONCLUSION
In silico tools are highly suited to study, design, and evaluate vaccine strategies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A potent multivalent vaccine for modulation of immune system in atherosclerosis: an in silico approach
Ahmad Karkhah, Jafar Amani
Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2016;5(1):50-59. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2016.5.1.50.
Reference
-
1. Spellberg B, Daum R. Development of a vaccine against Staphylococcus aureus. Semin Immunopathol. 2012; 34:335–348.
Article2. Stranger-Jones YK, Bae T, Schneewind O. Vaccine assembly from surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:16942–16947.3. Adhikari RP, Karauzum H, Sarwar J, et al. Novel structurally designed vaccine for S. aureus alpha-hemolysin: protection against bacteremia and pneumonia. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e38567.4. Hall AE, Domanski PJ, Patel PR, et al. Characterization of a protective monoclonal antibody recognizing Staphylococcus aureus MSCRAMM protein clumping factor A. Infect Immun. 2003; 71:6864–6870.
Article5. Ganesh VK, Rivera JJ, Smeds E, et al. A structural model of the Staphylococcus aureus ClfA-fibrinogen interaction opens new avenues for the design of anti-staphylococcal therapeutics. PLoS Pathog. 2008; 4:e1000226.
Article6. Hartford OM, Wann ER, Hook M, Foster TJ. Identification of residues in the Staphylococcus aureus fibrinogen-binding MSCRAMM clumping factor A (ClfA) that are important for ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:2466–2473.
Article7. Kuklin NA, Clark DJ, Secore S, et al. A novel Staphylococcus aureus vaccine: iron surface determinant B induces rapid antibody responses in rhesus macaques and specific increased survival in a murine S. aureus sepsis model. Infect Immun. 2006; 74:2215–2223.
Article8. Schaffer AC, Lee JC. Vaccination and passive immunisation against Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008; 32:Suppl 1. S71–S78.
Article9. Brown M, Kowalski R, Zorman J, et al. Selection and characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus iron-regulated surface determinant B with functional activity in vitro and in vivo. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009; 16:1095–1104.
Article10. Gouaux E, Hobaugh M, Song L. Alpha-hemolysin, gamma-hemolysin, and leukocidin from Staphylococcus aureus: distant in sequence but similar in structure. Protein Sci. 1997; 6:2631–2635.
Article11. Verkaik NJ, Dauwalder O, Antri K, et al. Immunogenicity of toxins during Staphylococcus aureus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2010; 50:61–68.
Article12. Prevost G, Cribier B, Couppie P, et al. Panton-valentine leucocidin and gamma-hemolysin from Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 49775 are encoded by distinct genetic loci and have different biological activities. Infect Immun. 1995; 63:4121–4129.
Article13. Nazarian S, Mousavi Gargari SL, Rasooli I, Amani J, Bagheri S, Alerasool M. An in silico chimeric multi subunit vaccine targeting virulence factors of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) with its bacterial inbuilt adjuvant. J Microbiol Methods. 2012; 90:36–45.
Article14. Grote A, Hiller K, Scheer M, et al. JCat: a novel tool to adapt codon usage of a target gene to its potential expression host. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005; 33:W526–W531.
Article15. Doytchinova IA, Flower DR. VaxiJen: a server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007; 8:4.
Article16. Zuker M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003; 31:3406–3415.
Article17. Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, et al. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol Biol. 1999; 112:531–552.
Article18. Sen TZ, Jernigan RL, Garnier J, Kloczkowski A. GOR V server for protein secondary structure prediction. Bioinformatics. 2005; 21:2787–2788.
Article19. Zhang Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008; 9:40.
Article20. El-Manzalawy Y, Dobbs D, Honavar V. Predicting flexible length linear B-cell epitopes. Comput Syst Bioinformatics Conf. 2008; 7:121–132.
Article21. Kringelum JV, Lundegaard C, Lund O, Nielsen M. Reliable B cell epitope predictions: impacts of method development and improved benchmarking. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012; 8:e1002829.
Article22. Schaffer AC, Lee JC. Staphylococcal vaccines and immunotherapies. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2009; 23:153–171.
Article23. Amani J, Mousavi SL, Rafati S, Salmanian AH. In silico analysis of chimeric espA, eae and tir fragments of Escherichia coli O157:H7 for oral immunogenic applications. Theor Biol Med Model. 2009; 6:28.
Article24. Gaspar P, Moura G, Santos MA, Oliveira JL. mRNA secondary structure optimization using a correlated stem-loop prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013; 41:e73.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Panton-Valentine Leukocidin Positive Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus: A Case Report of Two Pediatric Patients with Thrombotic Complications
- Emergence of Superbacteria, Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
- In silico analysis of an envelope domain III-based multivalent fusion protein as a potential dengue vaccine candidate
- A statistical analysis of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
- Toxic-Shock Syndrome Toxin in Staphylococcus aureus