Chonnam Med J.
2011 Aug;47(2):116-121. 10.4068/cmj.2011.47.2.116.
Effects of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on the Expression of TGF-beta1, PKC alpha/betaII, and NF-kappaB in High-Glucose-Stimulated Glomerular Epithelial Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Mechanical Systems Engineering, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Physiology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. nhk111@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2048795
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2011.47.2.116
Abstract
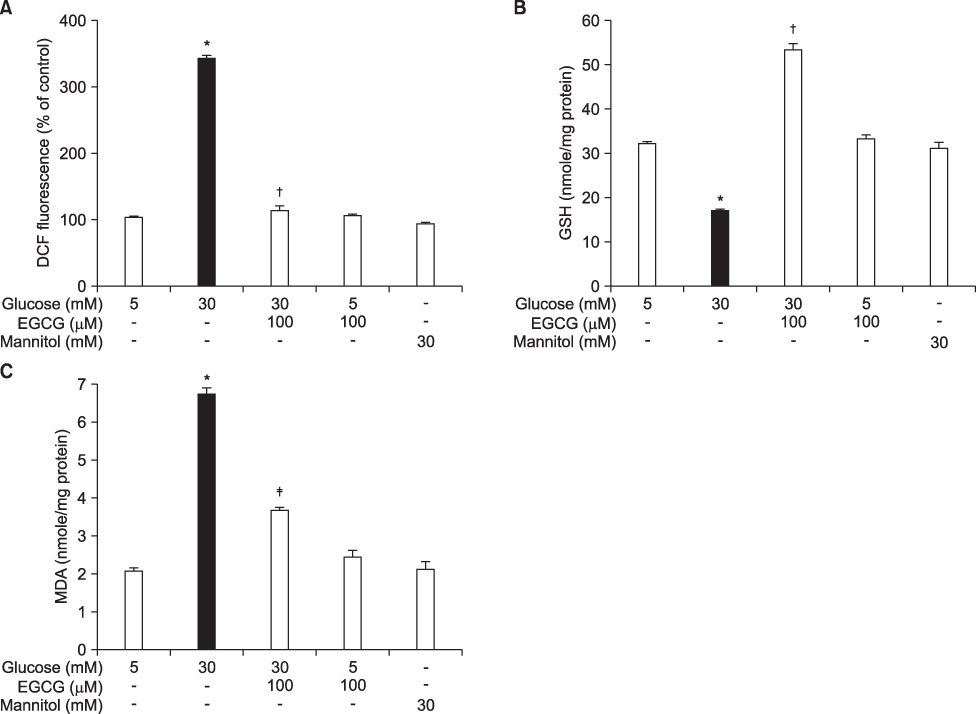
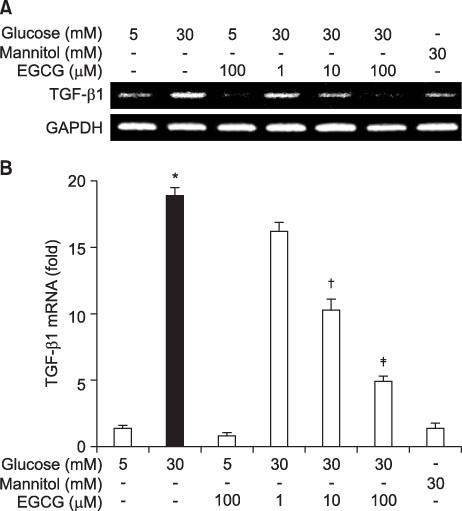
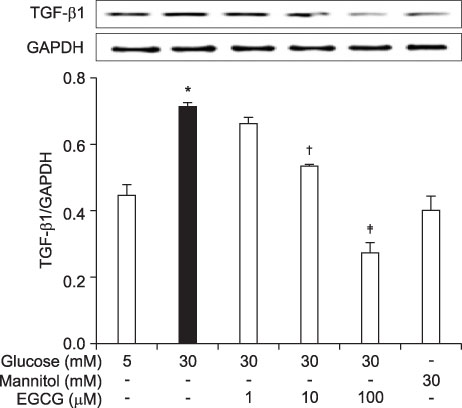
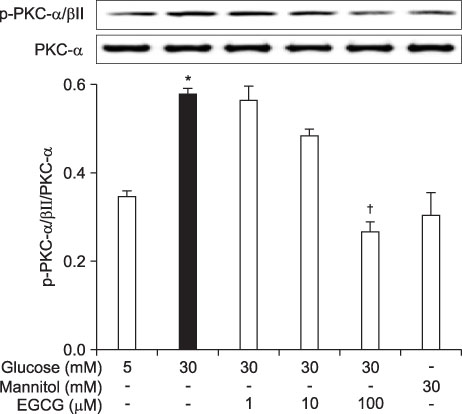
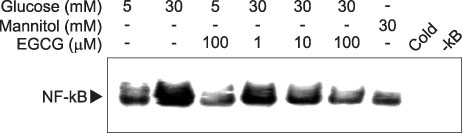
- Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is the most potent antioxidant polyphenol in green tea. In the present study, we investigated whether EGCG plays a role in the expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1), protein kinase C (PKC) alpha/betaII, and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) in glomerular epithelial cells (GECs) against high-glucose injury. Treatment with high glucose (30 mM) increased reactive oxygen species (ROS)/lipid peroxidation (LPO) and decreased glutathione (GSH) in GECs. Pretreatment with 100 microM EGCG attenuated the increase in ROS/LPO and restored the levels of GSH, whereas ROS, LPO, and GSH levels were not affected by treatment with 30 mM mannitol as an osmotic control. Interestingly, high-glucose treatment affected 3 separate signal transduction pathways in GECs. It increased the expression of TGF-beta1, PKC alpha/betaII, and NF-kappaB in GECs, respectively. EGCG (1, 10, 100 microM) pretreatment significantly decreased the expression of TGF-beta1 induced by high glucose in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, EGCG (100 microM) inhibited the phosphorylation of PKC alpha/betaII caused by glucose at 30 mM. Moreover, EGCG (1, 10, 100 microM) pretreatment significantly decreased the transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB induced by high glucose in a dose-dependent manner. These data suggest that EGCG could be a useful factor in modulating the injury to GECs caused by high glucose.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pavenstädt H, Kriz W, Kretzler M. Cell biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol Rev. 2003. 83:253–307.
Article2. Riser BL, Varani J, Cortes P, Yee J, Dame M, Sharba AK. Cyclic stretching of mesangial cells up-regulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and leukocyte adherence: a possible new mechanism for glomerulosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 2001. 158:11–17.
Article3. Jain S, De Petris L, Hoshi M, Akilesh S, Chatterjee R, Liapis H. Expression profiles of podocytes exposed to high glucose reveal new insights into early diabetic glomerulopathy. Lab Invest. 2011. 91:488–498.
Article4. Noh H, Ha H. Reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. 170:102–112.
Article5. Stanton RC. Oxidative stress and diabetic kidney disease. Curr Diab Rep. 2011. 11:330–336.
Article6. Hawkins CL, Davies MJ. Generation and propagation of radical reactions on proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. 1504:196–219.
Article7. Yu BP. Cellular defenses against damage from reactive oxygen species. Physiol Rev. 1994. 74:139–162.
Article8. Lan HY, Chung AC. Transforming growth factor-β and Smads. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. 170:75–82.
Article9. Gopalakrishna R, Chen ZH, Gundimeda U. Modifications of cysteine-rich regions in protein kinase C induced by oxidant tumor promoters and enzyme-specific inhibitors. Methods Enzymol. 1995. 252:132–146.10. Barnes PJ, Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 1997. 336:1066–1071.
Article11. Yokozawa T, Nakagawa T, Oya T, Okubo T, Juneja LR. Green tea polyphenols and dietary fibre protect against kidney damage in rats with diabetic nephropathy. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005. 57:773–780.
Article12. Sutherland BA, Shaw OM, Clarkson AN, Jackson DN, Sammut IA, Appleton I. Neuroprotective effects of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate following hypoxia-ischemia-induced brain damage: novel mechanisms of action. FASEB J. 2005. 19:258–260.13. Yamabe N, Yokozawa T, Oya T, Kim M. Therapeutic potential of (-)-epigallocatechin 3-O-gallate on renal damage in diabetic nephropathy model rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006. 319:228–236.
Article14. Fornoni A, Li H, Foschi A, Striker GE, Striker LJ. Hepatocyte growth factor, but not insulin-like growth factor I, protects podocytes against cyclosporin A-induced apoptosis. Am J Pathol. 2001. 158:275–280.
Article15. Kasinath BS, Maaba MR, Schwartz MM, Lewis EJ. Demonstration and characterization of C3 receptors on rat glomerular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1986. 30:852–861.
Article16. Pugliese F, Singh AK, Kasinath BS, Kreisberg JI, Lewis EJ. Glomerular epithelial cell, polyanion neutralization is associated with enhanced prostanoid production. Kidney Int. 1987. 32:57–61.
Article17. Ellman GL. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959. 82:70–77.
Article18. Buege JA, Aust SD. Lactoperoxidase-catalyzed lipid peroxidation of microsomal and artificial membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976. 444:192–201.
Article19. Adhikary L, Chow F, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Stambe C, Dowling J, Atkins RC, et al. Abnormal p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling in human and experimental diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia. 2004. 47:1210–1222.
Article20. Stambe C, Atkins RC, Tesch GH, Masaki T, Schreiner GF, Nikolic-Paterson DJ. The role of p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. 15:370–379.
Article21. Hong SW, Isono M, Chen S, Iglesias-De La Cruz MC, Han DC, Ziyadeh FN. Increased glomerular and tubular expression of transforming growth factor-beta1, its type II receptor, and activation of the Smad signaling pathway in the db/db mouse. Am J Pathol. 2001. 158:1653–1663.22. Sharma K, Ziyadeh FN. Hyperglycemia and diabetic kidney disease. The case for transforming growth factor-beta as a key mediator. Diabetes. 1995. 44:1139–1146.
Article23. Wolf G, Sharma K, Chen Y, Ericksen M, Ziyadeh FN. High glucose-induced proliferation in mesangial cells is reversed by autocrine TGF-beta. Kidney Int. 1992. 42:647–656.
Article24. Inoki K, Haneda M, Ishida T, Mori H, Maeda S, Koya D, et al. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases as downstream effectors of transforming growth factor-beta in mesangial cells. Kidney Int Suppl. 2000. 77:S76–S80.25. Schiffer M, von Gersdorff G, Bitzer M, Susztak K, Böttinger EP. Smad proteins and transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Kidney Int Suppl. 2000. 77:S45–S52.26. Kouroedov A, Eto M, Joch H, Volpe M, Lüscher TF, Cosentino F. Selective inhibition of protein kinase Cbeta2 prevents acute effects of high glucose on vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human endothelial cells. Circulation. 2004. 110:91–96.
Article27. Chu S, Bohlen HG. High concentration of glucose inhibits glomerular endothelial eNOS through a PKC mechanism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004. 287:F384–F392.
Article28. Park JY, Takahara N, Gabriele A, Chou E, Naruse K, Suzuma K, et al. Induction of endothelin-1 expression by glucose: an effect of protein kinase C activation. Diabetes. 2000. 49:1239–1248.
Article29. Bowie A, O'Neill LA. Oxidative stress and nuclear factor-kappaB activation: a reassessment of the evidence in the light of recent discoveries. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. 59:13–23.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Suppresses Galactose-alpha1,4-galactose-beta1,4-glucose Ceramide Expression in TNF-alpha Stimulated Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells Through Inhibition of MAPKs and NF-kappa B
- Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Inhibits the Expression of Adhesion Molecules by Blocking Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling in Intestinal Epithelial Cells
- Inhibitory Effect of Delphinidin on Extracellular Matrix Production via the MAPK/NF-kappaB Pathway in Nasal Polyp-Derived Fibroblasts
- Nuclear Factor-kappa B Activation and Chemokine Genes Expression in HT-29 Intestinal Epithelial Cells in Response to Clostridium difficile Toxin A Stimulation
- Role of protein kinases on NF- kappaB activation and cell death in bovine cerebral endothelial cells