J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2013 Apr;51(2):82-89. 10.4047/jkap.2013.51.2.82.
Combined effects of rhBMP-2 and rhVEGF coated onto implants on osseointegration: pilot study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea. jeonyc@paran.com
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, Institute for Clinical Dental Research, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2045110
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2013.51.2.82
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The present study is aimed to evaluate the combined effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 (rhBMP-2) and recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor (rhVEGF) coated onto anodized implants on osseointeration.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
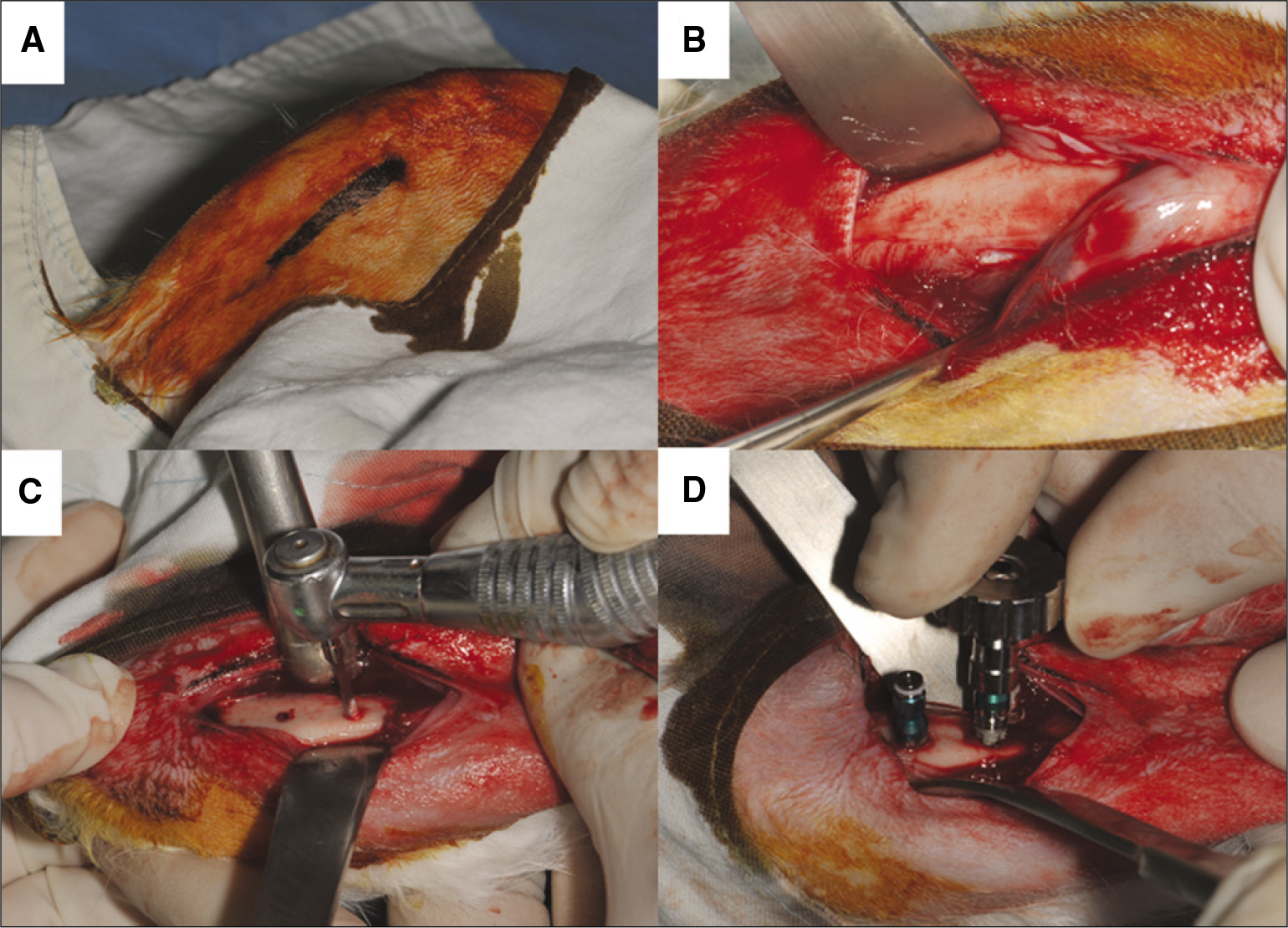
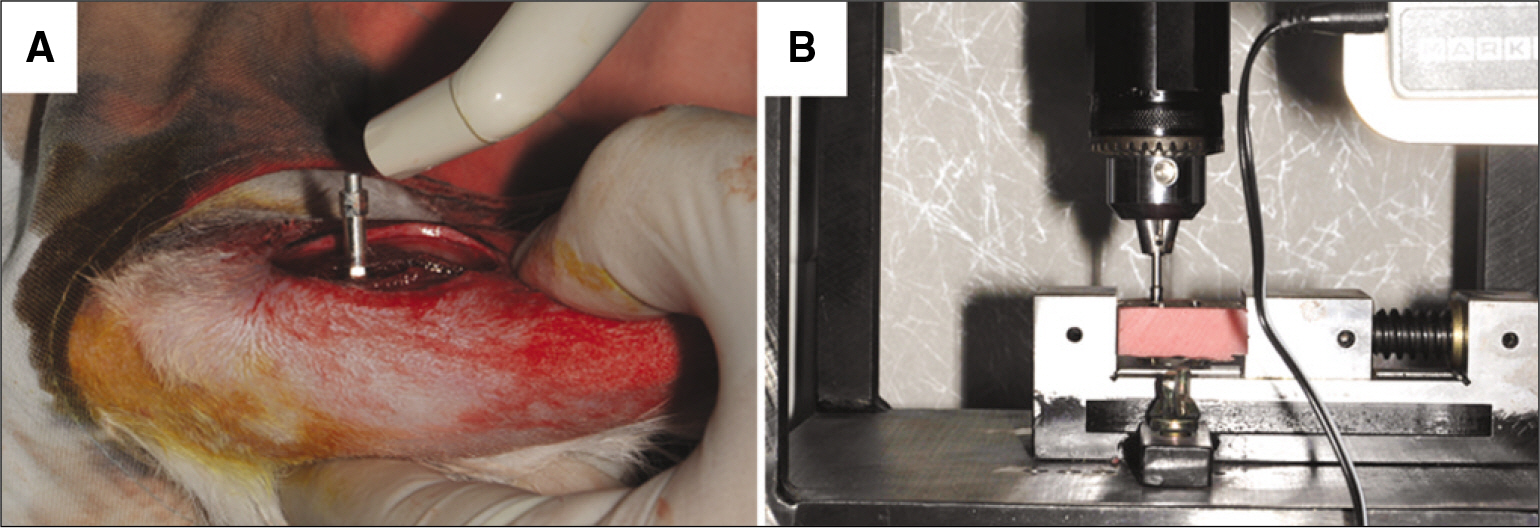
Six New Zealand white rabbit were used in this study. Each animal received 4 implants that were either coated with rhBMP-2 and rhVEGF (Study group) or anodized implant (Control group) in both tibia. This was performed using a randomized split-mouth design. A total 24 implants were used. The implant stability quotient (ISQ) value using resonance frequency analyser and removal torque (RTQ) measurement were investigated at 2 and 8 weeks. The t-test was used for statistical analysis (alpha=.05).
RESULTS
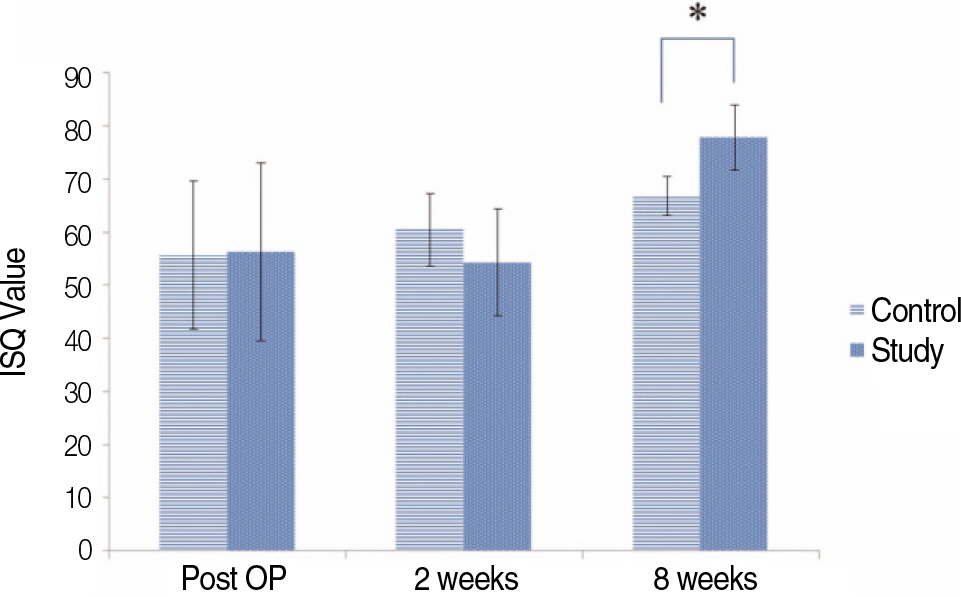
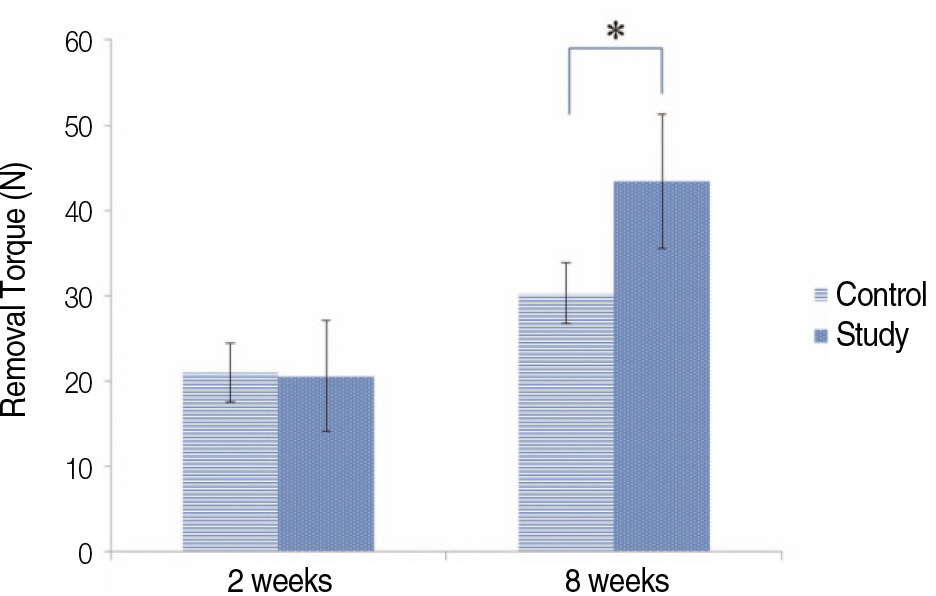
Control and study group showed good osseointegration at 8 weeks. The ISQ and RTQ values of study group were significant compared with the control group at 8 weeks (P<.05). However, No statistical significance was observed at 2 weeks (P>.05).
CONCLUSION
It was concluded that rhBMP-2 with rhVEGF coated onto anodized implants can induce better osseointegration at late healing period.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of immobilization of the recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 (rhBMP-2) on anodized implants coated with heparin for improving alveolar ridge augmentation in beagle dogs: Radiographic observations
So-Hyoun Lee, Jae-Young Jo, Mi-Jung Yun, Young-Chan Jeon, Jung-Bo Huh, Chang-Mo Jeong
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2013;51(4):307-314. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2013.51.4.307.
Reference
-
1.Retzepi M., Lewis MP., Donos N. Effect of diabetes and metabolic control on de novo bone formation following guided bone regeneration. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010. 21:71–9.
Article2.Sykaras N., Woody RD., Lacopino AM., Triplett RG., Nunn ME. Osseointegration of dental implants complexed with rhBMP-2: a comparative histomorphometric and radiographic evaluation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004. 19:667–78.3.Sumner DR., Turner TM., Urban RM., Turek T., Seeherman H., Wozney JM. Locally delivered rhBMP-2 enhances boneingrowth and gap healing in a canine model. J Orthop Res. 2004. 22:58–65.4.Becker J., Kirsch A., Schwarz F., Chatzinikolaidou M., Rothamel D., Lekovic V., Laub M., Jennissen HP. Bone apposition to titanium implants biocoated with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2). A pilot study in dogs. Clin Oral Investig. 2006. 10:217–24.
Article5.Huh JB., Ryu JJ., Kim JE., Kim DW., Kim SJ., Park YB., Kim YS., Lee SY., Lee JY., Shin SW. Effects of anodized implants coated with Escherichia coli-derived recombinant Human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on osseointegration in rabbits. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011. 8:62–8.6.Huh JB., Kim SE., Kim HE., Kang SS., Choi KH., Jeong CM., Lee JY., Shin SW. Effects of anodized implants coated with Escherichia coli-derived rhBMP-2 in beagle dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012. 41:1577–84.
Article7.Huh JB., Park CK., Kim SE., Shim KM., Choi KH., Kim SJ., Shim JS., Shin SW. Alveolar ridge augmentation using anodized implants coated with Escherichia coli-derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011. 112:42–9.
Article8.Stenport VF., Johansson C., Heo SJ., Aspenberg P., Albrektsson T. Titanium implants and BMP-7 in bone: an experimental model in the rabbit. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2003. 14:247–54.9.Schliephake H., Aref A., Scharnweber D., Bierbaum S., Roessler S., Sewing A. Effect of immobilized bone morphogenic protein 2 coating of titanium implants on peri-implant bone formation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005. 16:563–9.
Article10.Park J., Lutz R., Felszeghy E., Wiltfang J., Nkenke E., Neukam FW., Schlegel KA. The effect on bone regeneration of a liposomal vector to deliver BMP-2 gene to bone grafts in peri-implant bone de-fects. Biomaterials. 2007. 28:2772–82.
Article11.Stadlinger B., Pilling E., Huhle M., Mai R., Bierbaum S., Scharnweber D., Kuhlisch E., Loukota R., Eckelt U. Evaluation of osseointegration of dental implants coated with collagen, chondroitin sulphate and BMP-4: an animal study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008. 37:54–9.
Article12.Kim SE., Yun YP., Lee JY., Shim JS., Park K., Huh JB. Co-delivery of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-BB) and bone morphogenic protein (BMP-2) coated onto heparinized titanium for improving osteoblast function and osteointegration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013 Jan 3.
Article13.Huh JB., Lee JY., Lee KL., Kim SE., Yun MJ., Shim JS., Shim JS., Shin SW. Effects of the immobilization of heparin and rhPDGF-BB to titanium surfaces for the enhancement of osteoblastic functions and anti-inflammation. J Adv Prosthodont. 2011. 3:152–60.
Article14.Ferrara N., Gerber HP., LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003. 9:669–76.
Article15.Senger DR., Van de Water L., Brown LF., Nagy JA., Yeo KT., Yeo TK., Berse B., Jackman RW., Dvorak AM., Dvorak HF. Vascular permeability factor (VPF, VEGF) in tumor biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1993. 12:303–24.
Article16.Zelzer E., Olsen BR. Multiple roles of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in skeletal development, growth, and repair. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2005. 65:169–87.
Article17.Harper J., Klagsbrun M. Cartilage to bone-angiogenesis leads the way. Nat Med. 1999. 5:617–8.
Article18.Rabie AB., Shum L., Chayanupatkul A. VEGF and bone formation in the glenoid fossa during forward mandibular positioning. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002. 122:202–9.
Article19.Deckers MM., Karperien M., van der Bent C., Yamashita T., Papapoulos SE., Lo¨wik CW. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factors and their receptors during osteoblast differentiation. Endocrinology. 2000. 141:1667–74.
Article20.Peng H., Wright V., Usas A., Gearhart B., Shen HC., Cummins J., Huard J. Synergistic enhancement of bone formation and healing by stem cell-expressed VEGF and bone morphogenetic protein-4. J Clin Invest. 2002. 110:751–9.
Article21.Patel ZS., Young S., Tabata Y., Jansen JA., Wong ME., Mikos AG. Dual delivery of an angiogenic and an osteogenic growth factor for bone regeneration in a critical size defect model. Bone. 2008. 43:931–40.
Article22.Byrne AM., Bouchier-Hayes DJ., Harmey JH. Angiogenic and cell survival functions of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). J Cell Mol Med. 2005. 9:777–94.
Article23.Wang DS., Miura M., Demura H., Sato K. Anabolic effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on osteoblasts are enhanced by vascular endothelial growth factor produced by osteoblasts and by growth factors produced by endothelial cells. Endocrinology. 1997. 138:2953–62.
Article24.Mayr-Wohlfart U., Waltenberger J., Hausser H., Kessler S., Gu¨nther KP., Dehio C., Puhl W., Brenner RE. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates chemotactic migration of primary human osteoblasts. Bone. 2002. 30:472–7.
Article25.Hall J., Sorensen RG., Wozney JM., Wikesjo¨ UM. Bone formation at rhBMP-2-coated titanium implants in the rat ectopic model. J Clin Periodontol. 2007. 34:444–51.
Article26.Wikesjo¨ UM., Qahash M., Polimeni G., Susin C., Shanaman RH., Rohrer MD., Wozney JM., Hall J. Alveolar ridge augmentation using implants coated with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: histologic observations. J Clin Periodontol. 2008. 35:1001–10.27.Samee M., Kasugai S., Kondo H., Ohya K., Shimokawa H., Kuroda S. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) transfection to human periosteal cells enhances osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008. 108:18–31.
Article28.Huang YC., Kaigler D., Rice KG., Krebsbach PH., Mooney DJ. Combined angiogenic and osteogenic factor delivery enhances bone marrow stromal cell-driven bone regeneration. J Bone Miner Res. 2005. 20:848–57.
Article29.Kanczler JM., Ginty PJ., White L., Clarke NM., Howdle SM., Shakesheff KM., Oreffo RO. The effect of the delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor and bone morphogenic protein-2 to os-teoprogenitor cell populations on bone formation. Biomaterials. 2010. 31:1242–50.
Article30.Li G., Corsi-Payne K., Zheng B., Usas A., Peng H., Huard J. The dose of growth factors influences the synergistic effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on bone morphogenetic protein 4-induced ectopic bone formation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009. 15:2123–33.
Article31.Ramazanoglu M., Lutz R., Ergun C., von Wilmowsky C., Nkenke E., Schlegel KA. The effect of combined delivery of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 and recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor 165 from biomimetic calcium-phosphate-coated implants on osseointegration. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011. 22:1433–9.
Article32.Buser D., Broggini N., Wieland M., Schenk RK., Denzer AJ., Cochran DL., Hoffmann B., Lussi A., Steinemann SG. Enhanced bone apposition to a chemically modified SLA titanium surface. J Dent Res. 2004. 83:529–33.
Article33.Le Guehennec L., Goyenvalle E., Lopez-Heredia MA., Weiss P., Amouriq Y., Layrolle P. Histomorphometric analysis of the os-seointegration of four different implant surfaces in the femoral epiphyses of rabbits. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008. 19:1103–10.
Article34.Stadlinger B., Pilling E., Huhle M., Mai R., Bierbaum S., Bernhardt R., Scharnweber D., Kuhlisch E., Hempel U., Eckelt U. Influence of extracellular matrix coatings on implant stability and os-seointegration: an animal study. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2007. 83:222–31.
Article35.Lioubavina-Hack N., Lang NP., Karring T. Significance of primary stability for osseointegration of dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:244–50.
Article36.Liu Y., de Groot K., Hunziker EB. BMP-2 liberated from biomimetic implant coatings induces and sustains direct ossification in an ectopic rat model. Bone. 2005. 36:745–57.
Article37.Luo T., Zhang W., Shi B., Cheng X., Zhang Y. Enhanced bone regeneration around dental implant with bone morphogenetic protein 2 gene and vascular endothelial growth factor protein de- livery. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012. 23:467–73.38.Schmid J., Wallkamm B., Ha¨mmerle CH., Gogolewski S., Lang NP. The significance of angiogenesis in guided bone regeneration. A case report of a rabbit experiment. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997. 8:244–8.
Article39.Sojo K., Sawaki Y., Hattori H., Mizutani H., Ueda M. Immunohistochemical study of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and bone morphogenetic protein-2, -4 (BMP-2, -4) on lengthened rat femurs. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2005. 33:238–45.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Teh Effect of Hydroxyapatite Coating on the Mechanical Strengths and Histologic Profiles of Porous Titanium Implants in Dogs
- A comparative experimental study of bone ingrowth and osseointegration in hydroxyapatite-coated vs. porous-coated implants
- Effect of rhPMP-2 coated implants on alveolar ridge augmentation in dogs
- Reducing Healing Period with DDM/rhBMP-2 Grafting for Early Loading in Dental Implant Surgery
- Bone formation around rhBMP-2-coated implants in rabbit sinuses with or without absorbable collagen sponge grafting