Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2009 Oct;13(5):343-348. 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.5.343.
Ser1778 of 53BP1 Plays a Role in DNA Double-strand Break Repairs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, DNA Repair Research Center, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju 501-759, Korea. shsfkys@chosun.ac.kr
- 2Department of Life Science, College of Natural Science, Chung-Ang University, Seoul 156-756, Korea.
- 3Division of Influenza and Respiratory Viruses, Center for Infectious Disease, National Institute of Health, Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Seoul 122-701, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju 501-717, Korea.
- KMID: 1982566
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.5.343
Abstract
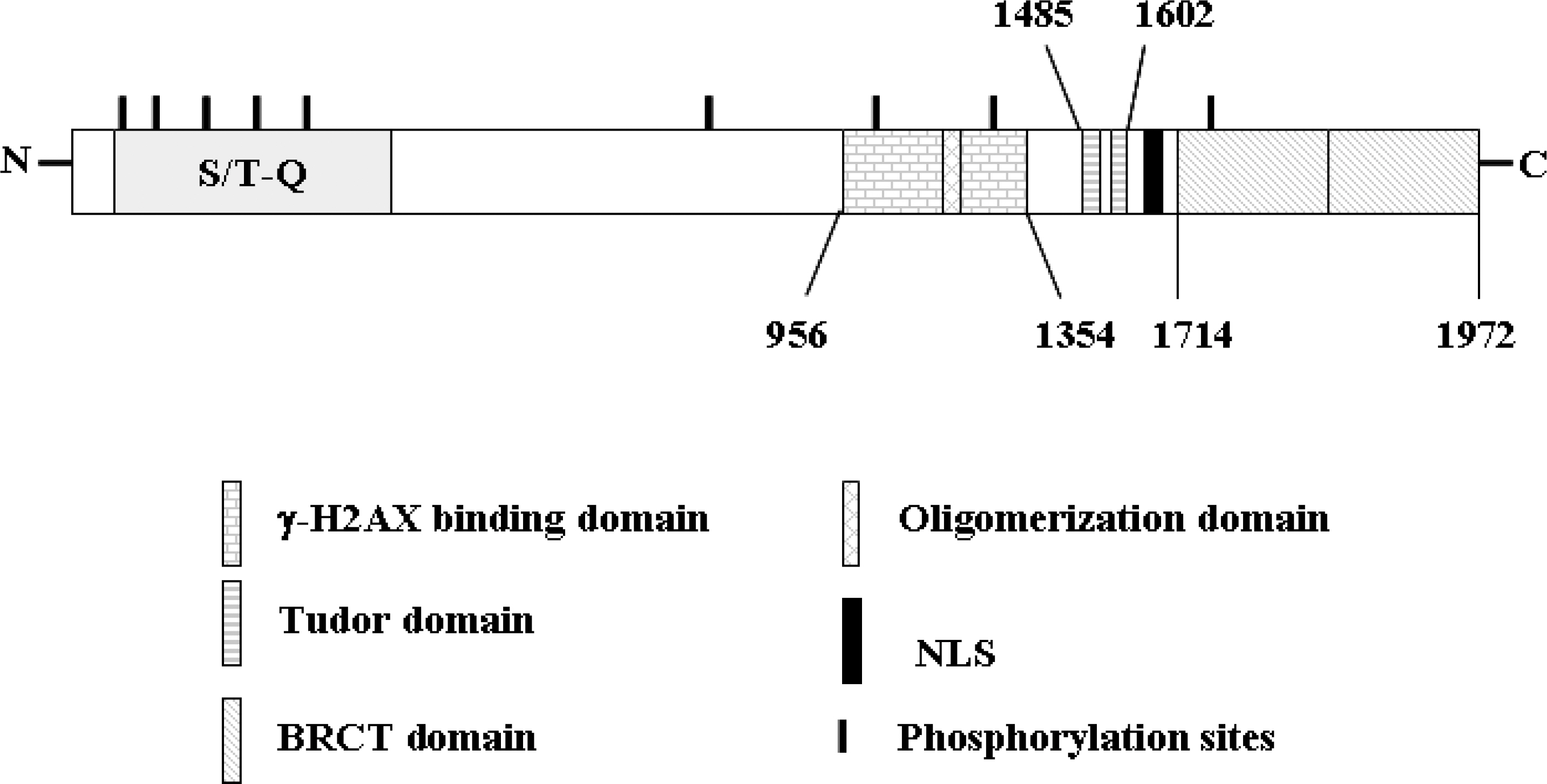
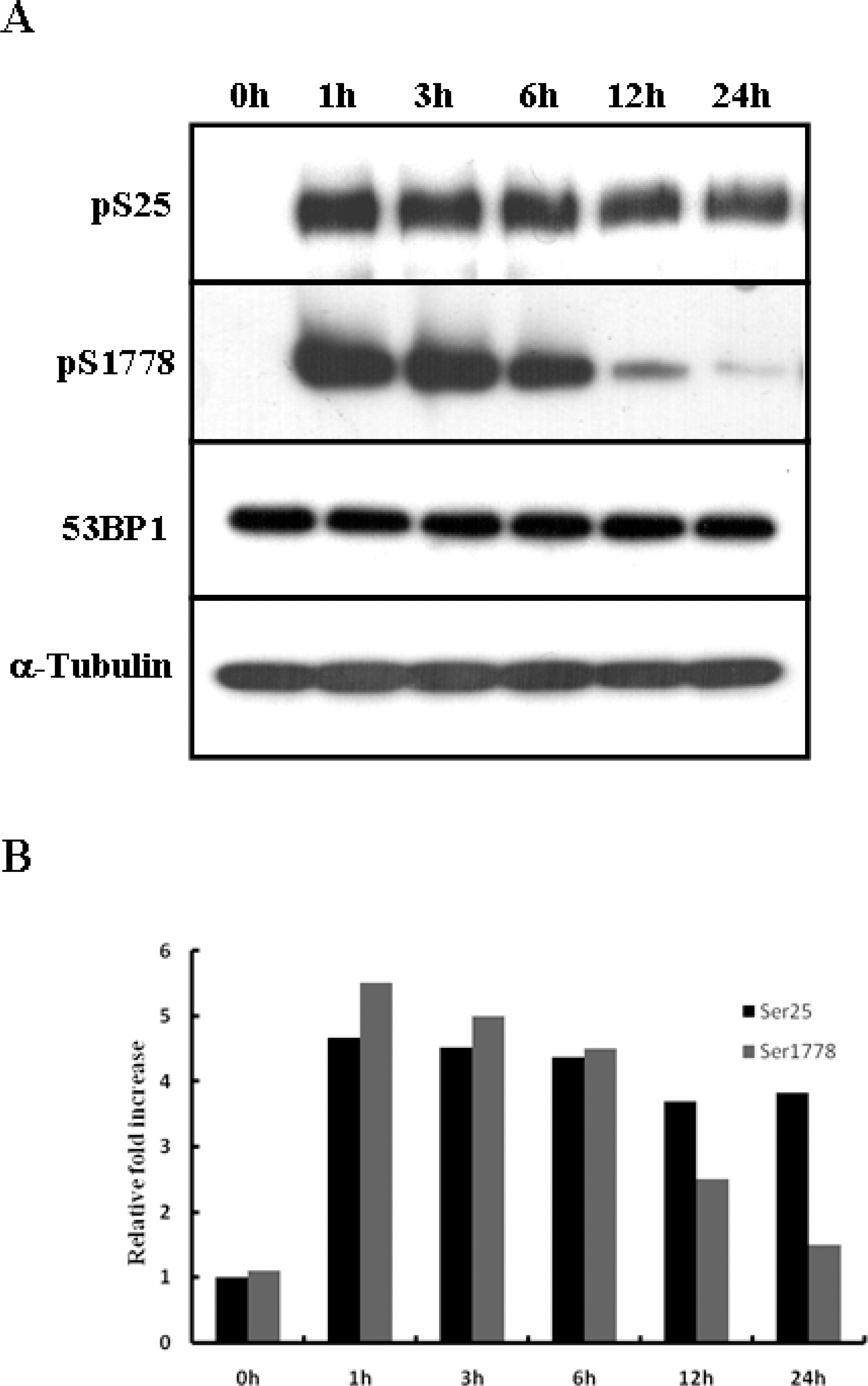
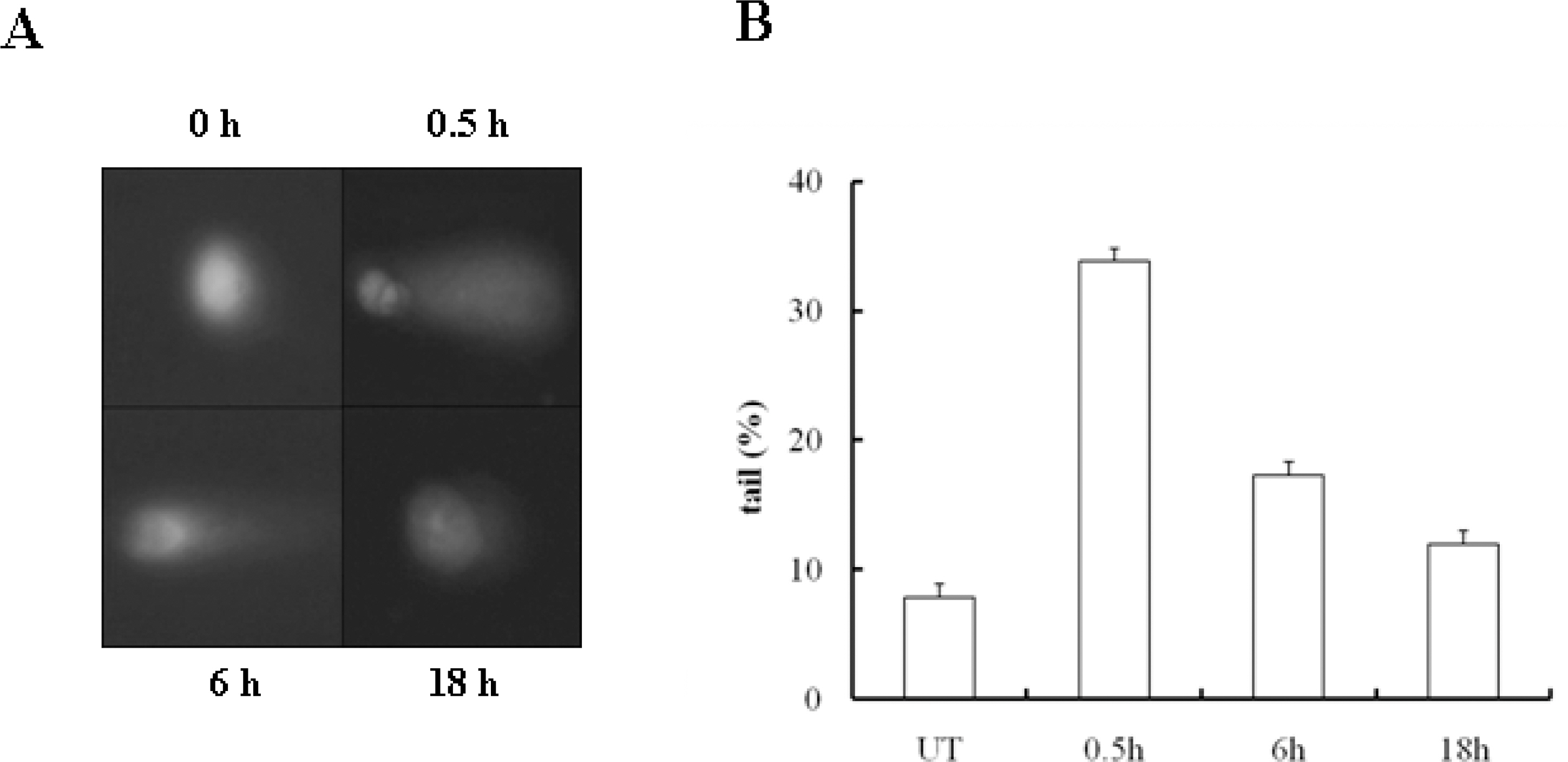
- 53BP1 is an important genome stability regulator, which protects cells against double-strand breaks. Following DNA damage, 53BP1 is rapidly recruited to sites of DNA breakage, along with other DNA damage response proteins, including gamma-H2AX, MDC1, and BRCA1. The recruitment of 53BP1 requires a tandem Tudor fold which associates with methylated histones H3 and H4. It has already been determined that the majority of DNA damage response proteins are phosphorylated by ATM and/or ATR after DNA damage, and then recruited to the break sites. 53BP1 is also phosphorylated at several sites, like other proteins after DNA damage, but this phosphorylation is not critically relevant to recruitment or repair processes. In this study, we evaluated the functions of phosphor-53BP1 and the role of the BRCT domain of 53BP1 in DNA repair. From our data, we were able to detect differences in the phosphorylation patterns in Ser25 and Ser1778 of 53BP1 after neocarzinostatin-induced DNA damage. Furthermore, the foci formation patterns in both phosphorylation sites of 53BP1 also evidenced sizeable differences following DNA damage. From our results, we concluded that each phosphoryaltion site of 53BP1 performs different roles, and Ser1778 is more important than Ser25 in the process of DNA repair.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
Anderson L., Henderson C., Adachi Y. Phosphorylation and rapid relocalization of 53BP1 to nuclear foci upon DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol. 21:1719–1729. 2001.
ArticleBakkenist CJ., Kastan MB. Initiating cellular stress responses. Cell. 118:9–17. 2004.
ArticleBork P., Hofmann K., Bucher P., Neuwald AF., Altschul SF., Koonin EV. A superfamily of conserved domains in DNA damage-responsive cell cycle checkpoint proteins. Faseb J. 11:68–76. 1997.Botuyan MV., Lee J., Ward IM., Kim JE., Thompson JR., Chen J., Mer G. Structural basis for the methylation state-specific recognition of histone H4-K20 by 53BP1 and Crb2 in DNA repair. Cell. 127:1361–1373. 2006.
ArticleBurma S., Chen BP., Murphy M., Kurimasa A., Chen DJ. ATM phosphorylates histone H2AX in response to DNA double-strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 276:42462–42467. 2001.
ArticleChowdhury D., Keogh MC., Ishii H., Peterson CL., Buratowski S., Lieberman J. gamma-H2AX dephosphorylation by protein phosphatase 2A facilitates DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cell. 20:801–809. 2005.Difilippantonio S., Gapud E., Wong N., Huang CY., Mahowald G., Chen HT., Kruhlak MJ., Callen E., Livak F., Nussenzweig MC., Sleckman BP., Nussenzweig A. 53BP1 facilitates long-range DNA end-joining during V(D)J recombination. Nature. 456:529–533. 2008.
ArticleDiTullio RA., Mochan TA., Venere M., Bartkova J., Sehested M., Bartek J., Halazonetis TD. 53BP1 functions in an ATM-dependent checkpoint pathway that is constitutively activated in human cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 4:998–1002. 2002.
ArticleDulic A., Bates PA., Zhang X., Martin SR., Freemont PS., Lindahl T., Barnes DE. BRCT domain interactions in the heterodimeric DNA repair protein XRCC1-DNA ligase III. Biochemistry. 40:5906–5913. 2001.
ArticleHuyen Y., Zgheib O., Ditullio RA., Gorgoulis VG., Zacharatos P., Petty TJ., Sheston EA., Mellert HS., Stavridi ES., Halazonetis TD. Methylated lysine 79 of histone H3 targets 53BP1 to DNA double-strand breaks. Nature. 432:406–411. 2004.
ArticleIwabuchi K., Li B., Massa HF., Trask BJ., Date T., Fields S. Stimulation of p53-mediated transcriptional activation by the p53-binding proteins, 53BP1 and 53BP2. J Biol Chem. 273:26061–26068. 1998.
ArticleJeggo PA., Lobrich M. DNA double-strand breaks: their cellular and clinical impact? Oncogene. 26:7717–7719. 2007.
ArticleJowsey P., Morrice NA., Hastie CJ., McLauchlan H., Toth R., Rouse J. Characterisation of the sites of DNA damage-induced 53BP1 phosphorylation catalysed by ATM and ATR. DNA Repair (Amst). 6:1536–1544. 2007.
ArticleKang Y., Lee JH., Hoan NN., Sohn HM., Chang IY., You HJ. Protein phosphatase 5 regulates the function of 53BP1 after neocarzinostatin-induced DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 284:9845–9853. 2009.
ArticleKim ST., Lim DS., Canman CE., Kastan MB. Substrate specificities and identification of putative substrates of ATM kinase family members. J Biol Chem. 274:37538–37543. 1999.
ArticleLee H., Kwak HJ., Cho IT., Park SH., Lee CH. S1219 residue of 53BP1 is phosphorylated by ATM kinase upon DNA damage and required for proper execution of DNA damage response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 378:32–36. 2009.
ArticleManke IA., Lowery DM., Nguyen A., Yaffe MB. BRCT repeats as phosphopeptide-binding modules involved in protein targeting. Science. 302:636–639. 2003.
ArticleMorales JC., Xia Z., Lu T., Aldrich MB., Wang B., Rosales C., Kellems RE., Hittelman WN., Elledge SJ., Carpenter PB. Role for the BRCA1 C-terminal repeats (BRCT) protein 53BP1 in maintaining genomic stability. J Biol Chem. 278:14971–14977. 2003.
ArticleNakamura A., Sedelnikova OA., Redon C., Pilch DR., Sinogeeva NI., Shroff R., Lichten M., Bonner WM. Techniques for gamma-H2AX detection. Methods Enzymol. 409:236–250. 2006.Rappold I., Iwabuchi K., Date T., Chen J. Tumor suppressor p53 binding protein 1 (53BP1) is involved in DNA damage-signaling pathways. J Cell Biol. 153:613–620. 2001.
ArticleSchultz LB., Chehab NH., Malikzay A., Halazonetis TD. p53 binding protein 1 (53BP1) is an early participant in the cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks. J Cell Biol. 151:1381–1390. 2000.
ArticleShiloh Y. ATM and related protein kinases: safeguarding genome integrity. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:155–168. 2003.
ArticleSilverman J., Takai H., Buonomo SB., Eisenhaber F., de Lange T. Human Rif1, ortholog of a yeast telomeric protein, is regulated by ATM and 53BP1 and functions in the S-phase checkpoint. Genes Dev. 18:2108–2119. 2004.
ArticleStiff T., O'Driscoll M., Rief N., Iwabuchi K., Lobrich M., Jeggo PA. ATM and DNA-PK function redundantly to phosphorylate H2AX after exposure to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 64:2390–2396. 2004.
ArticleTraven A., Heierhorst J. SQ/TQ cluster domains: concentrated ATM/ATR kinase phosphorylation site regions in DNA-damage-response proteins. Bioessays. 27:397–407. 2005.
ArticleWang B., Matsuoka S., Carpenter PB., Elledge SJ. 53BP1, a mediator of the DNA damage checkpoint. Science. 298:1435–1438. 2002.
ArticleWard I., Kim JE., Minn K., Chini CC., Mer G., Chen J. The tandem BRCT domain of 53BP1 is not required for its repair function. J Biol Chem. 281:38472–38477. 2006.
ArticleWard IM., Chen J. Histone H2AX is phosphorylated in an ATR-dependent manner in response to replicational stress. J Biol Chem. 276:47759–47762. 2001.
ArticleWard IM., Minn K., van Deursen J., Chen J. p53 Binding protein 53BP1 is required for DNA damage responses and tumor suppression in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 23:2556–2563. 2003.
ArticleWard IM., Reina-San-Martin B., Olaru A., Minn K., Tamada K., Lau JS., Cascalho M., Chen L., Nussenzweig A., Livak F., Nussenzweig MC., Chen J. 53BP1 is required for class switch recombination. J Cell Biol. 165:459–464. 2004.
ArticleYu X., Chini CC., He M., Mer G., Chen J. The BRCT domain is a phospho-protein binding domain. Science. 302:639–642. 2003.
ArticleZgheib O., Pataky K., Brugger J., Halazonetis TD. An oligomerized 53BP1 tudor domain suffices for recognition of DNA double-strand breaks. Mol Cell Biol. 29:1050–1058. 2009.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Double Strand Break of DNA in Gastric Adenoma and Adenocarcinoma
- Aberrant DNA Double-strand Break Repair Threads in Breast Carcinoma: Orchestrating Genomic Insult Survival
- DNA Double Strand Breaks in Gastric Epithelium with Helicobacter pylori Infection
- Analysis of Tensile Strength of Double Helix Wires
- Evaluation of DNA Double Strand Breaks in Human and Mouse Lymphocyte Following gamma-Irradiation