Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2012 Jul;4(4):199-205. 10.4168/aair.2012.4.4.199.
WDR46 is a Genetic Risk Factor for Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease in a Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Life Science, Sogang University, Seoul, Korea. hdshin@sogang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Genetic Epidemiology, SNP Genetics Inc., Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Allergy and Respiratory Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Allergy and Respiratory Medicine & Genome Research Center for Allergy and Respiratory Diseases, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. schalr@schbc.ac.kr
- KMID: 1970708
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2012.4.4.199
Abstract
- PURPOSE
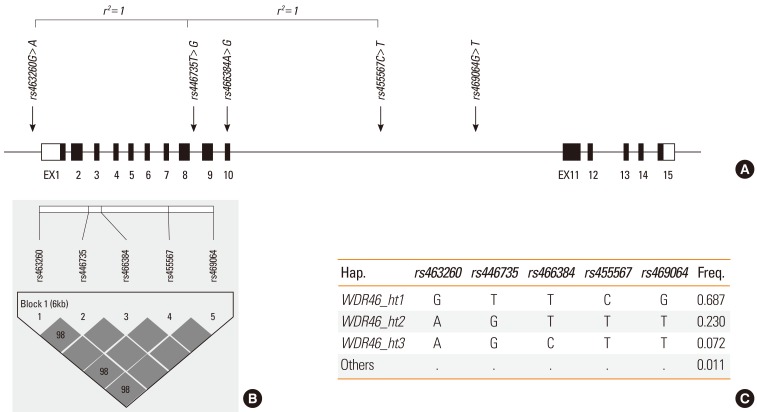
The human WD repeat-containing protein 46 (WDR46; also known as C6orf11), located at the disease-relevant centromere side of the class II major histocompatibility complex region, is hypothesized to be associated with risk of aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD) as well as a decline in forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1), an important diagnostic marker of asthma.
METHODS
To investigate the association between WDR46 and AERD, five single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were genotyped in 93 AERD cases and 96 aspirin-tolerant asthma controls of Korean ethnicity. Three major haplotypes were inferred from pairwise comparison of the SNPs, and one was included in the association analysis. Differences in the frequency distribution of WDR46 SNPs and haplotype were analyzed using logistic and regression models via various modes of genetic inheritance.
RESULTS
Depending on the genetic model, the logistic and regression analyses revealed significant associations between rs463260, rs446735, rs455567, rs469064, and WDR46_ht2 and the risk of AERD (P=0.007-0.04, Pcorr=0.01-0.04) and FEV1 decline after aspirin provocation (P=0.006-0.03, Pcorr=0.01-0.03). Furthermore, functional analysis in silico showed that the G>A allele of rs463260 located in the 5' untranslated region potentially matched a nucleotide sequence within an upstream open reading frame of WDR46.
CONCLUSIONS
These findings show for the first time that WDR46 is an important genetic marker of aspirin-induced airway inflammation and may be useful for formulating new disease-management strategies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
5' Untranslated Regions
Alleles
Aspirin
Asthma
Base Sequence
Centromere
Computer Simulation
Forced Expiratory Volume
Genetic Markers
Haplotypes
Humans
Inflammation
Major Histocompatibility Complex
Models, Genetic
Open Reading Frames
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Risk Factors
5' Untranslated Regions
Aspirin
Genetic Markers
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee RU, Stevenson DD. Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease: evaluation and management. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011; 3:3–10. PMID: 21217919.
Article2. Bennett A. The importance of COX-2 inhibition for aspirin induced asthma. Thorax. 2000; 55(Suppl 2):S54–S56. PMID: 10992560.
Article3. Choi JH, Lee KW, Oh HB, Lee KJ, Suh YJ, Park CS, Park HS. HLA association in aspirin-intolerant asthma: DPB1*0301 as a strong marker in a Korean population. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:562–564. PMID: 15007363.4. Pasaje CF, Kim JH, Park BL, Cheong HS, Chun JY, Park TJ, Lee JS, Kim Y, Bae JS, Park JS, Yoon SH, Uh ST, Choi JS, Kim YH, Kim MK, Choi IS, Cho SH, Choi BW, Park CS, Shin HD. Association of SLC6A12 variants with aspirin-intolerant asthma in a Korean population. Ann Hum Genet. 2010; 74:326–334. PMID: 20597903.
Article5. Pasaje CF, Kim JH, Park BL, Cheong HS, Kim MK, Choi IS, Cho SH, Hong CS, Lee YW, Lee JY, Koh IS, Park TJ, Lee JS, Kim Y, Bae JS, Park CS, Shin HD. A possible association of EMID2 polymorphisms with aspirin hypersensitivity in asthma. Immunogenetics. 2011; 63:13–21. PMID: 21086123.
Article6. Pasaje CF, Bae JS, Park BL, Jang AS, Uh ST, Kim MK, Koh IS, Kim JH, Park TJ, Lee JS, Kim Y, Park CS, Shin HD. Association analysis of DTD1 gene variations with aspirin-intolerance in asthmatics. Int J Mol Med. 2011; 28:129–137. PMID: 21479357.7. Pasaje CF, Bae JS, Park BL, Cheong HS, Jang AS, Uh ST, Kim MK, Koh IS, Kim JH, Park TJ, Lee JS, Kim Y, Park CS, Shin HD. Association analysis of C6 genetic variations and aspirin hypersensitivity in Korean asthmatic patients. Hum Immunol. 2011; 72:973–978. PMID: 21704099.
Article8. Rosenberg SA, Tong-On P, Li Y, Riley JP, El-Gamil M, Parkhurst MR, Robbins PF. Identification of BING-4 cancer antigen translated from an alternative open reading frame of a gene in the extended MHC class II region using lymphocytes from a patient with a durable complete regression following immunotherapy. J Immunol. 2002; 168:2402–2407. PMID: 11859131.
Article9. Herberg JA, Beck S, Trowsdale J. TAPASIN, DAXX, RGL2, HKE2 and four new genes (BING 1, 3 to 5) form a dense cluster at the centromeric end of the MHC. J Mol Biol. 1998; 277:839–857. PMID: 9545376.10. Johnson EN, Druey KM. Heterotrimeric G protein signaling: role in asthma and allergic inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002; 109:592–602. PMID: 11941304.
Article11. Akahoshi M, Obara K, Hirota T, Matsuda A, Hasegawa K, Takahashi N, Shimizu M, Nakashima K, Cheng L, Doi S, Fujiwara H, Miyatake A, Fujita K, Higashi N, Taniguchi M, Enomoto T, Mao XQ, Nakashima H, Adra CN, Nakamura Y, Tamari M, Shirakawa T. Functional promoter polymorphism in the TBX21 gene associated with aspirin-induced asthma. Hum Genet. 2005; 117:16–26. PMID: 15806396.
Article12. Varga EM, Jacobson MR, Masuyama K, Rak S, Till SJ, Darby Y, Hamid Q, Lund V, Scadding GK, Durham SR. Inflammatory cell populations and cytokine mRNA expression in the nasal mucosa in aspirin-sensitive rhinitis. Eur Respir J. 1999; 14:610–615. PMID: 10543283.
Article13. Kim BS, Park SM, Uhm TG, Kang JH, Park JS, Jang AS, Uh ST, Kim MK, Choi IS, Cho SH, Hong CS, Lee YW, Lee JY, Choi BW, Park HS, Park BL, Shin HD, Chung IY, Park CS. Effect of single nucleotide polymorphisms within the interleukin-4 promoter on aspirin intolerance in asthmatics and interleukin-4 promoter activity. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2010; 20:748–758. PMID: 20921925.
Article14. Nizankowska-Mogilnicka E, Bochenek G, Mastalerz L, Swierczyńska M, Picado C, Scadding G, Kowalski ML, Setkowicz M, Ring J, Brockow K, Bachert C, Wöhrl S, Dahlén B, Szczeklik A. EAACI/GA2LEN guideline: aspirin provocation tests for diagnosis of aspirin hypersensitivity. Allergy. 2007; 62:1111–1118. PMID: 17521312.
Article15. Livak KJ. Allelic discrimination using fluorogenic probes and the 5' nuclease assay. Genet Anal. 1999; 14:143–149. PMID: 10084106.
Article16. Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005; 21:263–265. PMID: 15297300.
Article17. Menashe I, Rosenberg PS, Chen BE. PGA: power calculator for case-control genetic association analyses. BMC Genet. 2008; 9:36. PMID: 18477402.
Article18. Nyholt DR. A simple correction for multiple testing for single-nucleotide polymorphisms in linkage disequilibrium with each other. Am J Hum Genet. 2004; 74:765–769. PMID: 14997420.
Article19. Grillo G, Turi A, Licciulli F, Mignone F, Liuni S, Banfi S, Gennarino VA, Horner DS, Pavesi G, Picardi E, Pesole G. UTRdb and UTRsite (RELEASE 2010): a collection of sequences and regulatory motifs of the untranslated regions of eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010; 38:D75–D80. PMID: 19880380.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Update on the Management of Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease
- Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease: Evaluation and Management
- Association Analysis of TEC Polymorphisms with Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease in a Korean Population
- Update on Recent Advances in the Management of Aspirin Exacerbated Respiratory Disease
- Unraveling the Genetic Basis of Aspirin Hypersensitivity in Asthma Beyond Arachidonate Pathways