Cancer Res Treat.
2004 Oct;36(5):330-337.
Dexamethasone Inhibits TRAIL- and Anti-cancer Drugs-induced Cell Death in A549 Cells through Inducing NF-kappaB-independent cIAP2 Expression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. kyleemd@dankook.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
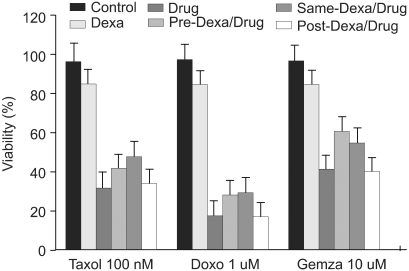
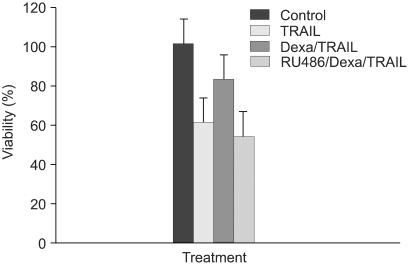
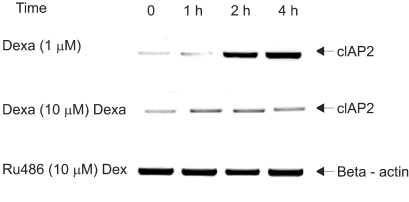
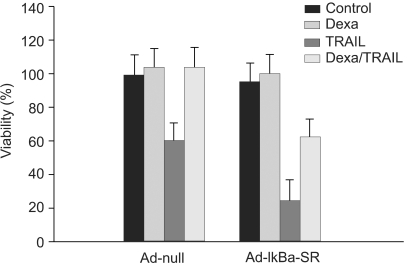
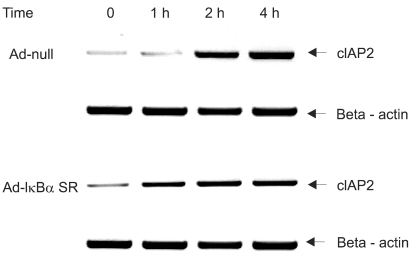
We have examined that dexamethasone inhibits apoptotic cell death of A549 lung epithelial cells through TRAIL and anti-cancer drugs. The purpose of the study is to determine the roles of GR, cIAP and NF- kappaB in this mechanism. MATERIALS AND METHODS: In the A549 lung epithelial cell line, TRAIL, taxol, doxorubicine & gemcitabine were used to investigate cell toxicity. Cells were pretreated 12 hours in advance with dexamethasone. RU486 was pretreated 30 minutes before dexamethasone. Crystal violet assay was used for cell toxicity tests. Apoptosis assay was performed by taking morphologic surveys with fluorescent microscopy after double staining with Hoechst 33342 & propium iodide. RT-PCR was used to investigate the gene expression of cIAP1 & cIAP2 by dexamethasone. Ad-IkappaBalpha-SR transduction study was used for the role of NF-kappaB. RESULTS: TRAIL and anti-cancer drug-induced apoptosis was partially suppressed in A549 cells pretreated with dexamethasone. The inhibitory effect on cell death disappeared in A549 cells pretreated with RU486. Using RT-PCR, changes of cIAP1 and cIAP2 genes manifestation in A549 cells subsequent to pretreatment with dexamethasone were examined. The results showed an increase in cIAP2 expression during a course of time which was suppressed by RU486 pretreatment. Induction of cIAP2 expression changes by dexamethasone was uniquely observed despite the blockade of NF-kappa by Ad-IkappaB alpha-SR transduction. CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that dexametha sone inhibits TRAIL- and anti-cancer drug-induced apoptosis in A549 cells by inducing cIAP2 gene expression through a GR-mediated, NF-kappa-independent pathway.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McKay LI, Cidlowski JA. Molecular control of immune/inflammatory responses: interactions between nuclear factor-κB and steroid/receptor-signaling pathways. Endocr Rev. 1999; 20:435–459. PMID: 10453354.2. Bamberger CM, Schulte HM, Chrousos GP. Molecular determinants of glucocorticoid receptor function and tissue sensitivity to glucocorticoids. Endocr Rev. 1996; 17:245–261. PMID: 8771358.
Article3. Barnes PJ. Anti-inflammatory actions of glucocorticoids: molecular mechanisms. Clin Sci. 1998; 94:557–572. PMID: 9854452.
Article4. Schwiebert LM, Beck LA, Stellato C, Bickel CA, Bochner BS, Schleimer RP, Schwiebert LA. Glucocorticosteroid inhibition of cytokine production: relevance to antiallergic actions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996; 97:143–152. PMID: 8568145.
Article5. Van der Burg B, Okret S, Liden J, Wissink S, Van der Saag PT, Gustafsson JA. Nuclear factor-kappa-B repression in anti-inflammation and immunosuppression by glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1997; 8:152–157. PMID: 18406801.6. Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL, Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV, Boldin MP. Tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999; 17:331–367. PMID: 10358762.
Article7. Hakem R, Hakem A, Duncan GS, Henderson JT, Woo M, Soengas MS, Elia A, de la Pompa JL, Kagi D, Khoo W, Potter J, Yoshida R, Kaufman SA, Lowe SW, Penninger JM, Mak TW. Differential requirement for caspase 9 in apoptotic pathways in vivo. Cell. 1998; 94:339–352. PMID: 9708736.
Article8. Tolosa E, Ashwell JD. Thymus-derived glucocorticoids and the regulation of antigen-specific T-cell development. Neuroimmunomodulation. 1999; 6:90–96. PMID: 9876239.
Article9. Chae HJ, Chae SW, Kang JS, Bang BG, Cho SB, Park RK, So HS, Kim YK, Kim HM, Kim HR. Dexamethasone suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis in osteoblasts: possible role for ceramide. Endocrinology. 2000; 141:2904–2913. PMID: 10919278.10. Liston P, Roy N, Tamai K, Lefebvre C, Baird S, Cherton-Horvat G, Farahani R, McLean M, Ikeda JE, MacKenzie A, Korneluk RG. Suppression of apoptosis in mammalian cells by NAIP and a related family of IAP genes. Nature. 1996; 379:349–353. PMID: 8552191.
Article11. Hay BA, Wassarman DA, Rubin GM. Drosophila homologs of baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis proteins function to block cell death. Cell. 1995; 83:1253–1262. PMID: 8548811.
Article12. Aota K, Azuma M, Tamatani T, Yamashita T, Ashida Y, Sato M. Stable inhibition of NF-kappa B in salivary gland cells does not enhance sensitivity to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis due to upregulation of TRAF-1 expression. Exp Cell Res. 2002; 276:111–119. PMID: 11978013.13. Craxton A, Shu G, Graves JD, Saklatvala J, Krebs EG, Clark EA. p38 MAPK is required for CD40-induced gene expression and proliferation in B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1998; 161:3225–3236. PMID: 9759836.14. Hong SY, Yoon WH, Park JH, Kang SG, Ahn JH, Lee TH. Involvement of two NF-kappa B binding elements in tumor necrosis factor alpha -, CD40-, and epstein-barr virus latent membrane protein 1-mediated induction of the cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 gene. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:18022–18028. PMID: 10751398.15. Webster JC, Huber RM, Hanson RL, Collier PM, Haws TF, Mills JK, Burn TC, Allegretto EA. Dexamethasone and tumor necrosis factor-alpha act together to induce the cellular inhibitor of apoptosis-2 gene and prevent apoptosis in a variety of cell types. Endocrinology. 2002; 143:3866–3874. PMID: 12239098.16. Fisher DE. Apoptosis in cancer therapy: crossing the threshold. Cell. 1994; 78:539–542. PMID: 8069905.
Article17. Griffith T, Lynch DH. TRAIL: a molecule with multiple receptors and control mechanisms. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998; 10:559–563. PMID: 9794836.
Article18. Park C, Yoon KH, Lee YJ, Kim YK, Choi YC, Shin JH, Cho JH, Park R. 5-FU Induces Apoptosis of Fas (+), HepG2 Cells Via Activation of Fas-mediated Caspase and Mitochondria Dysfunction. Cancer Res Treat. 2002; 34:128–138.
Article19. Cohen L, Henzel WJ, Baeuerle PA. IKAP is a scaffold protein of the IkappaB kinase complex. Nature. 1998; 395:292–296. PMID: 9751059.20. Birnbaum MJ, Clem RJ, Miller LK. An apoptosis-inhibiting gene from a nuclear polyhedrosis virus encoding a polypeptide with Cys/His sequence motifs. J Virol. 1994; 68:2521–2528. PMID: 8139034.
Article21. Wen LP, Wen LP, Madani K, Fahrni JA, Duncan SR, Rosen GD. Dexamethasone inhibits lung epithelial cell apoptosis induced by IFN-gamma and Fas. Am J Physiol. 1997; 273:L921–L929. PMID: 9374718.22. Costas M, Trapp T, Pereda MP, Sauer J, Rupprecht R, Nahmod VE, Reul JM, Holsboer F, Arzt E. Molecular and functional evidence for in vitro cytokine enhancement of human and murine target cell sensitivity to glucocorticoids. TNF-alpha priming increases glucocorticoid inhibition of TNF-alpha-induced cytotoxicity/apoptosis. J Clin Invest. 1996; 98:1409–1416. PMID: 8823306.
Article23. Nissen RM, Yamamoto KR. The glucocorticoid receptor inhibits NF-κB by interfering with serine-2 phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:2314–2329. PMID: 10995388.
Article24. Auphan N, Didonato JA, Rosette C, Helmberg A, Karin M. Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: Inhibition of NFkappaB activity through induction of IκB synthesis. Science. 1995; 270:2314–2329.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- NF-kappaB Activation and cIAP Expression in Radiation-induced Cell Death of A549 Lung Cancer Cells
- Inhibiting NF-kappaB Activation by Triptolide Enhances TRAIL-induced Cell Death in Lung Cancer Cells
- The Proteasome Inhibitor MG132 Sensitizes Lung Cancer Cells to TRAIL-induced Apoptosis by Inhibiting NF-kappaB Activation
- TRAIL-induced cell death and caspase-8 activation are inhibited by cisplatin but not carboplatin
- Human hepatocellular carcinoma cells resist to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, and the resistance is abolished by cisplatin