Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2014 Jun;19(2):108-112. 10.6065/apem.2014.19.2.108.
A Korean boy with 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development caused by SOX9 duplication
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jmko@snu.ac.kr
- 2Research Coordination Center for Rare Diseases, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1803864
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2014.19.2.108
Abstract
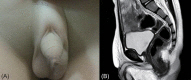
- The 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development (DSD), also known as 46,XX male syndrome, is a rare form of DSD and clinical phenotype shows complete sex reversal from female to male. The sex-determining region Y (SRY) gene can be identified in most 46,XX testicular DSD patients; however, approximately 20% of patients with 46,XX testicular DSD are SRY-negative. The SRY-box 9 (SOX9) gene has several important functions during testis development and differentiation in males, and overexpression of SOX9 leads to the male development of 46,XX gonads in the absence of SRY. In addition, SOX9 duplication has been found to be a rare cause of 46,XX testicular DSD in humans. Here, we report a 4.2-year-old SRY-negative 46,XX boy with complete sex reversal caused by SOX9 duplication for the first time in Korea. He showed normal external and internal male genitalia except for small testes. Fluorescence in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analyses failed to detect the presence of SRY, and SOX9 intragenic mutation was not identified by direct sequencing analysis. Therefore, we performed real-time PCR analyses with specific primer pairs, and duplication of the SOX9 gene was revealed. Although SRY-negative 46,XX testicular DSD is a rare condition, an effort to make an accurate diagnosis is important for the provision of proper genetic counseling and for guiding patients in their long-term management.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boucekkine C, Toublanc JE, Abbas N, Chaabouni S, Ouahid S, Semrouni M, et al. Clinical and anatomical spectrum in XX sex reversed patients: relationship to the presence of Y specific DNA-sequences. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1994; 40:733–742. PMID: 8033363.
Article2. Zenteno JC, Lopez M, Vera C, Mendez JP, Kofman-Alfaro S. Two SRY-negative XX male brothers without genital ambiguity. Hum Genet. 1997; 100:606–610. PMID: 9341880.3. Ono M, Harley VR. Disorders of sex development: new genes, new concepts. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013; 9:79–91. PMID: 23296159.
Article4. Huang B, Wang S, Ning Y, Lamb AN, Bartley J. Autosomal XX sex reversal caused by duplication of SOX9. Am J Med Genet. 1999; 87:349–353. PMID: 10588843.5. Cox JJ, Willatt L, Homfray T, Woods CG. A SOX9 duplication and familial 46,XX developmental testicular disorder. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:91–93. PMID: 21208124.
Article6. Vetro A, Ciccone R, Giorda R, Patricelli MG, Della Mina E, Forlino A, et al. XX males SRY negative: a confirmed cause of infertility. J Med Genet. 2011; 48:710–712. PMID: 21653197.
Article7. Benko S, Gordon CT, Mallet D, Sreenivasan R, Thauvin-Robinet C, Brendehaug A, et al. Disruption of a long distance regulatory region upstream of SOX9 in isolated disorders of sex development. J Med Genet. 2011; 48:825–830. PMID: 22051515.
Article8. Seeherunvong T, Ukarapong S, McElreavey K, Berkovitz GD, Perera EM. Duplication of SOX9 is not a common cause of 46,XX testicular or 46,XX ovotesticular DSD. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 25:121–123. PMID: 22570960.
Article9. Lee JW, Hong CH, Kim HR, Sin JB. A case of SRY negative 46, XX male syndrome with deletion on long arm of X chromosome. Korean J Perinatol. 2006; 17:353–358.10. Moalem S, Babul-Hirji R, Stavropolous DJ, Wherrett D, Bagli DJ, Thomas P, et al. XX male sex reversal with genital abnormalities associated with a de novo SOX3 gene duplication. Am J Med Genet A. 2012; 158A:1759–1764. PMID: 22678921.11. De la chapelle A, Hortling H, Niemi M, Wennstroem J. XX chromosomes in a human male. First case. Acta Med Scand. 1964; 175(Suppl 412):25–28. PMID: 14154995.12. Lee PA, Houk CP, Ahmed SF, Hughes IA. International Consensus Conference on Intersex organized by the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society and the European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology. Consensus statement on management of intersex disorders. International Consensus Conference on Intersex. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:e488–e500. PMID: 16882788.13. de la Chapelle A. Analytic review: nature and origin of males with XX sex chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1972; 24:71–105. PMID: 4622299.14. De Santa Barbara P, Bonneaud N, Boizet B, Desclozeaux M, Moniot B, Sudbeck P, et al. Direct interaction of SRY-related protein SOX9 and steroidogenic factor 1 regulates transcription of the human anti-Mullerian hormone gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1998; 18:6653–6665. PMID: 9774680.
Article15. Ergun-Longmire B, Vinci G, Alonso L, Matthew S, Tansil S, Lin-Su K, et al. Clinical, hormonal and cytogenetic evaluation of 46,XX males and review of the literature. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 18:739–748. PMID: 16200839.
Article16. Maciel-Guerra AT, de Mello MP, Coeli FB, Ribeiro ML, Miranda ML, Marques-de-Faria AP, et al. XX Maleness and XX true hermaphroditism in SRY-negative monozygotic twins: additional evidence for a common origin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:339–343. PMID: 18056774.
Article17. de la Chapelle A, Hastbacka J, Korhonen T, Maenpaa J. The etiology of XX sex reversal. Reprod Nutr Dev. 1990; (Suppl 1):39s–49s. PMID: 1976312.
Article18. Sinclair AH, Berta P, Palmer MS, Hawkins JR, Griffiths BL, Smith MJ, et al. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990; 346:240–244. PMID: 1695712.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The rare case of 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development carrying a heterozygous p.Arg92Trp variant in NR5A1
- A case of XX male syndrome
- Three cases of rare SRY-negative 46,XX testicular disorder of sexual development with complete masculinization and a review of the literature
- A case of SRY Negative 46, XX Male Syndrome with Deletion on Long Arm of X Chromosome
- XX-Male Syndrome: A Case Report