J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Feb;24(1):62-68. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.62.
Gene-to-Gene Interaction between Sodium Channel-Related Genes in Determining the Risk of Antiepileptic Drug Resistance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. mkkim@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- KMID: 1794408
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.62
Abstract
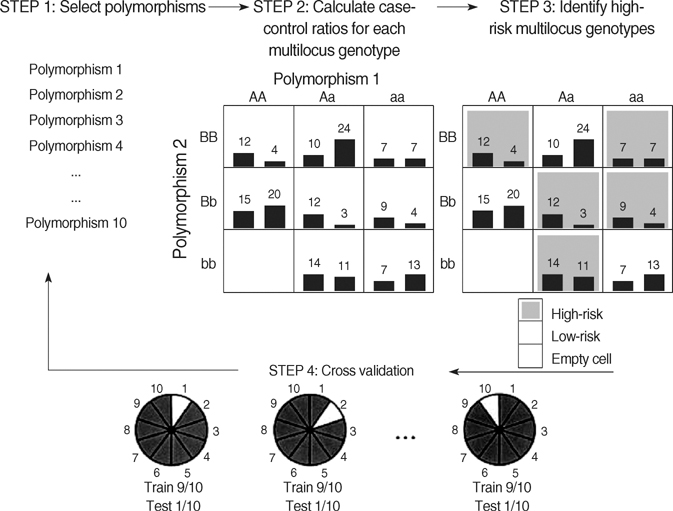
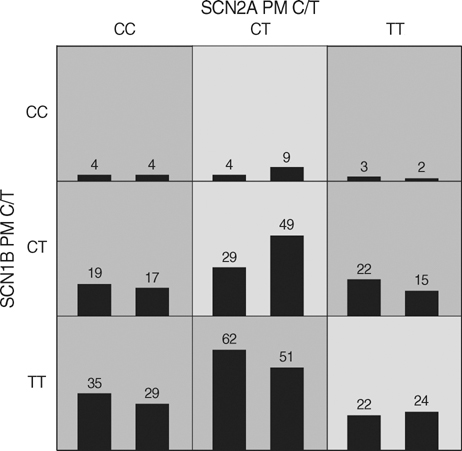
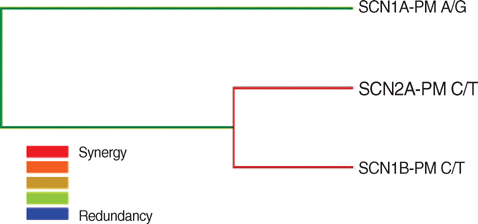
- The pathogenesis of antiepileptic drug (AED) resistance is multifactorial. However, most candidate gene association studies typically assess the effects of candidate genes independently of each other, which is partly because of the limitations of the parametric-statistical methods for detecting the gene-to-gene interactions. A total of 200 patients with drug-resistant epilepsy and 200 patients with drug-responsive epilepsy were genotyped for 3 representative the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the voltage-gated sodium channel genes (SCN1A, SCN1B, and SCN2A) by polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing analysis. Besides the typical parametric statistical method, a new statistical method (multifactor dimensionality reduction [MDR]) was used to determine whether gene-to-gene interactions increase the risk of AED resistance. None of the individual genotypes or alleles tested in the present study showed a significant association with AED resistance, regardless of their theoretical functional value. With the MDR method, of three possible 2-locus genotype combinations, the combination of SCN2A-PM with SCN1B-PM was the best model for predicting susceptibility to AED resistance, with a p value of 0.0547. MDR, as an analysis paradigm for investigating multi-locus effects in complex disorders, may be a useful statistical method for determining the role of gene-to-gene interactions in the pathogenesis of AED resistance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kwan P, Brodie MJ. Early identification of refractory epilepsy. N Engl J Med. 2000. 342:314–319.
Article2. Kwan P, Brodie MJ. Refractory epilepsy: a progressive, intractable but preventable condition? Seizure. 2002. 11:77–84.
Article3. Regesta G, Tanganelli P. Clinical aspects and biological bases of drug-resistant epilepsies. Epilepsy Res. 1999. 34:109–122.
Article4. Traub RD, Borck C, Colling SB, Jefferys JG. On the structure of ictal events in vitro. Epilepsia. 1996. 37:879–891.
Article5. Armijo JA, Shushtarian M, Valdizan EM, Cuadrado A, de las Cuevas I, Adin J. Ion channels and epilepsy. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. 11:1975–2003.
Article6. Meldrum BS, Rogawski MA. Molecular targets for antiepileptic drug development. Neurotherapeutics. 2007. 4:18–61.
Article7. Hirose S, Mitsudome A, Okada M, Kaneko S. Epilepsy Genetic Study Group, Japan. Genetics of idiopathic epilepsies. Epilepsia. 2005. 46:Suppl 1. 38–43.8. Gibson G. Epistasis and pleiotropy as natural properties of transcriptional regulation. Theor Popul Biol. 1996. 49:58–89.
Article9. Williams SM, Ritchie MD, Phillips JA 3rd, Dawson E, Prince M, Dzhura E, Willis A, Semenya A, Summar M, White BC, Addy JH, Kpodonu J, Wong LJ, Felder RA, Jose PA, Moore JH. Multilocus analysis of hypertension: a hierarchical approach. Hum Hered. 2004. 57:28–38.
Article10. Ritchie MD, Hahn LW, Roodi N, Bailey LR, Dupont WD, Parl FF, Moore JH. Multifactor-dimensionality reduction reveals high-order interactions among estrogen-metabolism genes in sporadic breast cancer. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. 69:138–147.
Article11. Templeton AR. Wade M, Brodie B, Wolf J, editors. Epistasis and complex trait. Epistasis and evolutionary process. Oxford: Oxford University Press;213–231.12. McNamara JO. Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Gilman AG, editors. Drugs effective in the therapy of the epilepsies. Goodmann & Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 2001. 10th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill;521–547.13. Kwok PY, Carlson C, Yager TD, Ankener W, Nickerson DA. Comparative analysis of human DNA variations by fluorescence-based sequencing of PCR products. Genomics. 1994. 23:138–144.
Article14. Evans WE, McLeod HL. Pharmacogenomics-drug disposition, drug targets, and side effects. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:538–549.15. Mann MW, Pons G. Various pharmacogenetic aspects of antiepileptic drug therapy: a review. CNS Drugs. 2007. 21:143–164.16. Depondt C. The potential of pharmacogenetics in the treatment of epilepsy. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2006. 10:57–65.
Article17. Siddiqui A, Kerb R, Weale ME, Brinkmann U, Smith A, Goldstein DB, Wood NW, Sisodiya SM. Association of multidrug resistance in epilepsy with a polymorphism in the drug-transporter gene ABCB1. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:1442–1448.18. Kim YO, Kim MK, Woo YJ, Lee MC, Kim JH, Park KW, Kim EY, Roh YI, Kim CJ. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the multidrug resistance 1 gene in Korean epileptics. Seizure. 2006. 15:67–72.
Article19. Meisler MH, Kearney JA. Sodium channel mutations in epilepsy and other neurological disorders. J Clin Invest. 2005. 115:2010–2017.
Article20. Kullmann DM, Hanna MG. Neurological disorders caused by inherited ion-channel mutations. Lancet Neurol. 2002. 1:157–166.
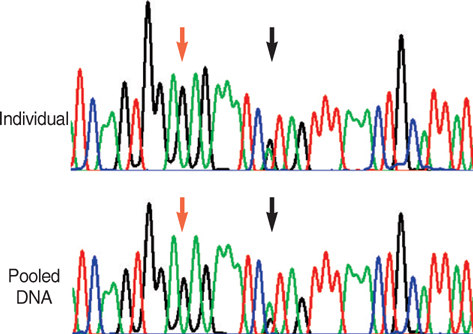
Article21. Bang-Ce Y, Peng Z, Bincheng Y, Songyang L. Estimation of relative allele frequencies of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in different populations by microarray hybridization of pooled DNA. Anal Biochem. 2004. 333:72–78.
Article22. Germer S, Holland MJ, Higuchi R. High-throughput SNP allele-frequency determination in pooled DNA samples by kinetic PCR. Genome Res. 2000. 10:258–266.
Article23. Fakhrai-Rad H, Zheng J, Willis TD, Wong K, Suyenaga K, Moorhead M, Eberle J, Thorstenson YR, Jones T, Davis RW, Namsaraev E, Faham M. SNP discovery in pooled samples with mismatch repair detection. Genome Res. 2004. 14:1404–1412.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Identification of Genes Related to Fungicide Resistance in Fusarium fujikuroi
- Molecular biologic mechanism of drug resistance in cancer chemotherapy
- Expression of Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein(MRP), c-myc and c-fos in L1210 Cells
- Multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) and multidrug resistance (MDR1) gene expression in osteosarcoma and their prognostic significance
- Publicly Available Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Genes Possibly Susceptible to Antiepileptic Drug Resistance in Healthy Koreans