The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Score-Based System Predicts Short Term Mortality Better Than the Current Child-Turcotte-Pugh Score-Based Allocation System during Waiting for Deceased Liver Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kwleegs@gmail.com
- KMID: 1793027
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1207
Abstract
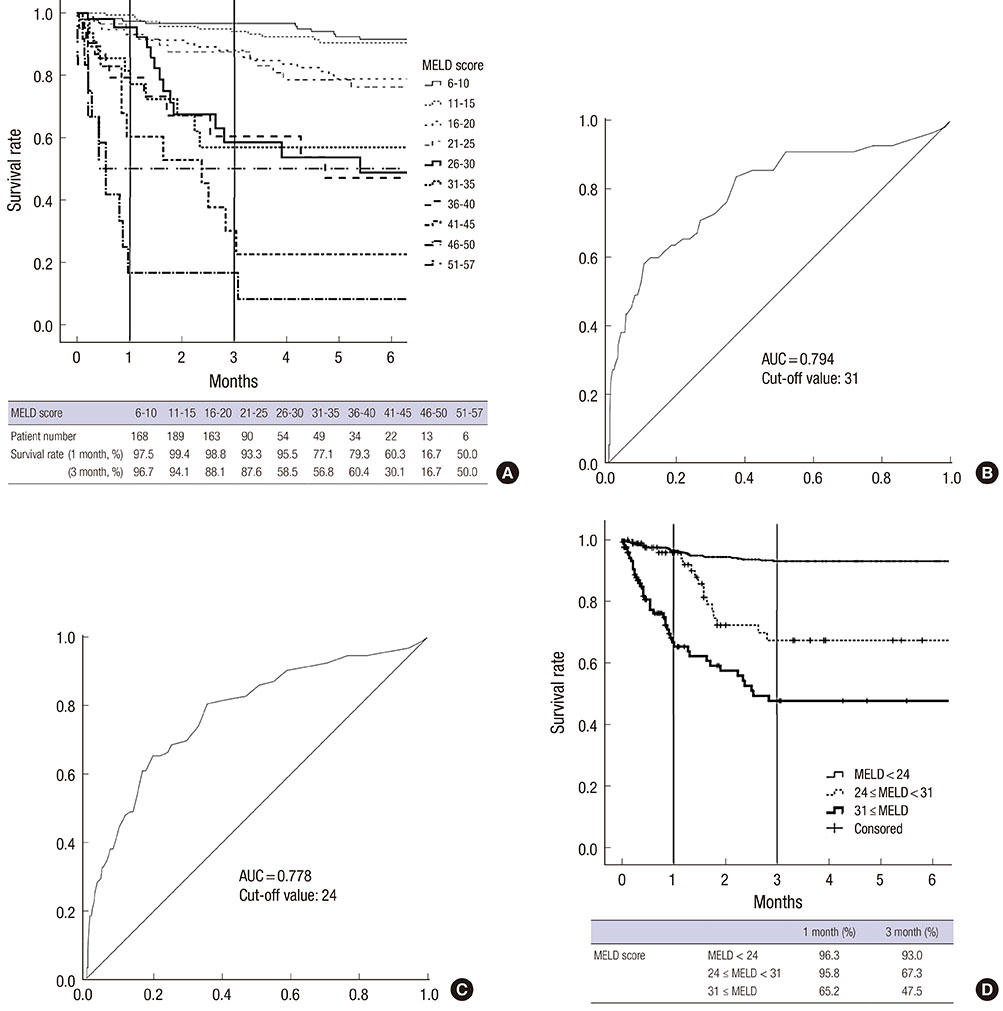
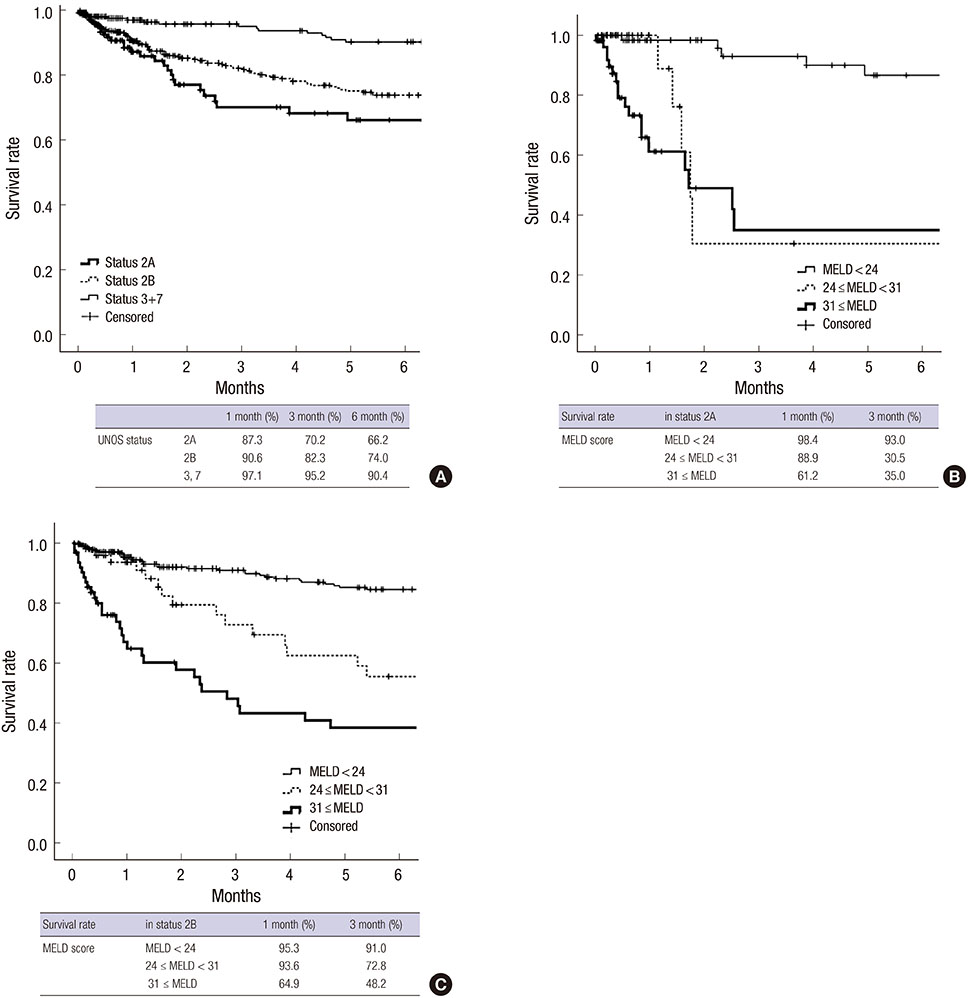
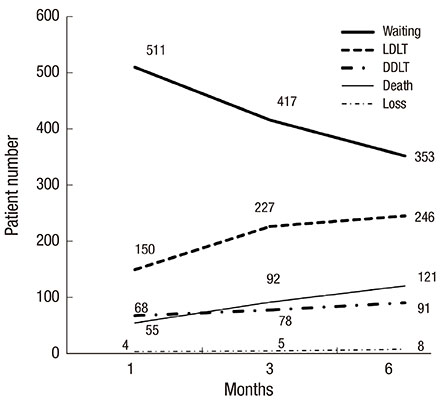
- To adopt the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score-based system in Korea, the feasibility should be evaluated by analysis of Korean database. The aim of this study was to investigate the feasibility of the MELD score-based system compared with the current Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) based-system and to suggest adequate cut-off to stratify waiting list mortality among Korean population. We included 788 adult patients listed in waiting list in Seoul National University Hospital from January 2008 to May 2011. The short-term survival until 6 months after registration was evaluated. Two hundred forty six (31.2%) patients underwent live donor liver transplantation and 353 (44.8%) patients were still waiting and 121 (15.4%) patients were dropped out due to death. Significant difference was observed when MELD score 24 and 31 were used as cut-off. Three-months survival of Status 2A was 70.2%. However, in Status 2A patients whose MELD score less than 24 (n=82), 86.6% of patients survived until 6 month. Furthermore, patients with high MELD score (> or =31) among Status 2B group showed poorer survival rate (45.8%, 3-month) than Status 2A group. In conclusion, MELD score-based system can predict short term mortality better and select more number of high risk patients in Korean population.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Current Status of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation for Alcoholic Liver Disease in Korea in MELD Era
Dong Jin Joo
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2021;77(1):4-11. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.167.Research for Modification of Emergency Status in Deceased Donor Liver Allocation – Survival Analysis of Waiting Patients for Liver Transplantation
Myoung Soo Kim, Kwang Woong Lee, Shin Hwang, Choon Hyuck David Kwon, Young Kyoung You, Yang Won Nah, Hee Chul Yu, Dong Sik Kim, Hee Jung Wang, Dong Lak Choi, In Seok Choi, Soon Il Kim
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2014;28(2):59-68. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2014.28.2.59.The impact of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score on deceased donor liver transplant outcomes in low volume liver transplantation center: a retrospective and single-center study
Doo-Ho Lee, Yeon Ho Park, Seok Won Choi, Kug Hyun Nam, Sang Tae Choi, Doojin Kim
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2021;101(6):360-367. doi: 10.4174/astr.2021.101.6.360.Comparison Study of Outcomes of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation before and after Korean Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) System: Single Center Experience
Ji A Lee, Gyu-seong Choi, Jong Man Kim, Chun Hyuck David Kwon, Jae-Won Joh
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2018;32(1):7-11. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2018.30.1.07.Modification of Emergency Status in Deceased Donor Liver Allocation: Evidence for Korean Model of End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) System
Myoung Soo Kim
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2016;30(2):51-58. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2016.30.2.51.
Reference
-
1. Wiesner RH, McDiarmid SV, Kamath PS, Edwards EB, Malinchoc M, Kremers WK, Krom RA, Kim WR. MELD and PELD: application of survival models to liver allocation. Liver Transpl. 2001; 7:567–580.2. Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology. 2000; 31:864–871.3. Wiesner RH. Evidence-based evolution of the MELD/PELD liver allocation policy. Liver Transpl. 2005; 11:261–263.4. Biselli M, Gitto S, Gramenzi A, Di Donato R, Brodosi L, Ravaioli M, Grazi GL, Pinna AD, Andreone P, Bernardi M. Six score systems to evaluate candidates with advanced cirrhosis for orthotopic liver transplant: which is the winner? Liver Transpl. 2010; 16:964–973.5. Kim WR, Biggins SW, Kremers WK, Wiesner RH, Kamath PS, Benson JT, Edwards E, Therneau TM. Hyponatremia and mortality among patients on the liver-transplant waiting list. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1018–1026.6. Leise MD, Kim WR, Kremers WK, Larson JJ, Benson JT, Therneau TM. A revised model for end-stage liver disease optimizes prediction of mortality among patients awaiting liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:1952–1960.7. Lim YS, Larson TS, Benson JT, Kamath PS, Kremers WK, Therneau TM, Kim WR. Serum sodium, renal function, and survival of patients with end-stage liver disease. J Hepatol. 2010; 52:523–528.8. Hwang S, Lee SG, Jung DH, Kim KH, Ha TY, Song GW. Simulation of deceased-donor liver graft allocation as UNOS status I or IIa on the current Korean setting for patients with hepatitis B virus-induced fulminant hepatic failure. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2009; 13:31–36.9. Lee JS. Changes of MELD: can exceed Child-Pugh's authority? Korean J Hepatol. 2006; 12:475–478.10. Lim YS. Prediction of post-operative mortality in patients with cirrhosis: growth of child to MELD. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011; 57:333–334.11. Song CS, Yoon MY, Kim HJ, Park JH, Park DI, Cho YK, Sohn CI, Jeon WK, Kim BI. Usefulness of model for end-stage liver disease score for predicting mortality after intra-abdominal surgery in patients with liver cirrhosis in a single hospital. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011; 57:340–345.12. Kim SY, Yim HJ, Lee J, Lee BJ, Kim DI, Jung SW, Han WS, Lee JS, Koo JS, Seo YS, et al. Comparison of CTP, MELD, and MELD-Na scores for predicting short term mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2007; 50:92–100.13. OPTN: Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network. accessed on January 2013. Available at http://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/organDatasource/OrganSpecificPolicies.asp?display=Liver.14. Wiesner R, Edwards E, Freeman R, Harper A, Kim R, Kamath P, Kremers W, Lake J, Howard T, Merion RM, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and allocation of donor livers. Gastroenterology. 2003; 124:91–96.15. Kamath PS, Kim WR. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group. The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology. 2007; 45:797–805.16. Freeman RB Jr. Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) for liver allocation: a 5-year score card. Hepatology. 2008; 47:1052–1057.17. Stewart CA, Malinchoc M, Kim WR, Kamath PS. Hepatic encephalopathy as a predictor of survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2007; 13:1366–1371.18. Pomfret EA, Washburn K, Wald C, Nalesnik MA, Douglas D, Russo M, Roberts J, Reich DJ, Schwartz ME, Mieles L, et al. Report of a national conference on liver allocation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Liver Transpl. 2010; 16:262–278.19. Washburn K, Edwards E, Harper A, Freeman R. Hepatocellular carcinoma patients are advantaged in the current liver transplant allocation system. Am J Transplant. 2010; 10:1643–1648.20. Yao FY, Bass NM, Ascher NL, Roberts JP. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: lessons from the first year under the Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) organ allocation policy. Liver Transpl. 2004; 10:621–630.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation for Alcoholic Liver Disease in Korea in MELD Era
- Comparison Study of Outcomes of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation before and after Korean Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) System: Single Center Experience
- New Scoring Systems for Severity Outcome of Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Issues Concerning The Child-Turcotte-Pugh Score and The Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score
- Modification of Emergency Status in Deceased Donor Liver Allocation: Evidence for Korean Model of End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) System
- Research for Modification of Emergency Status in Deceased Donor Liver Allocation: Survival Analysis of Waiting Patients for Liver Transplantation