Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Jan;77(1):4-11. 10.4166/kjg.2020.167.
Current Status of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation for Alcoholic Liver Disease in Korea in MELD Era
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2510770
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.167
Abstract
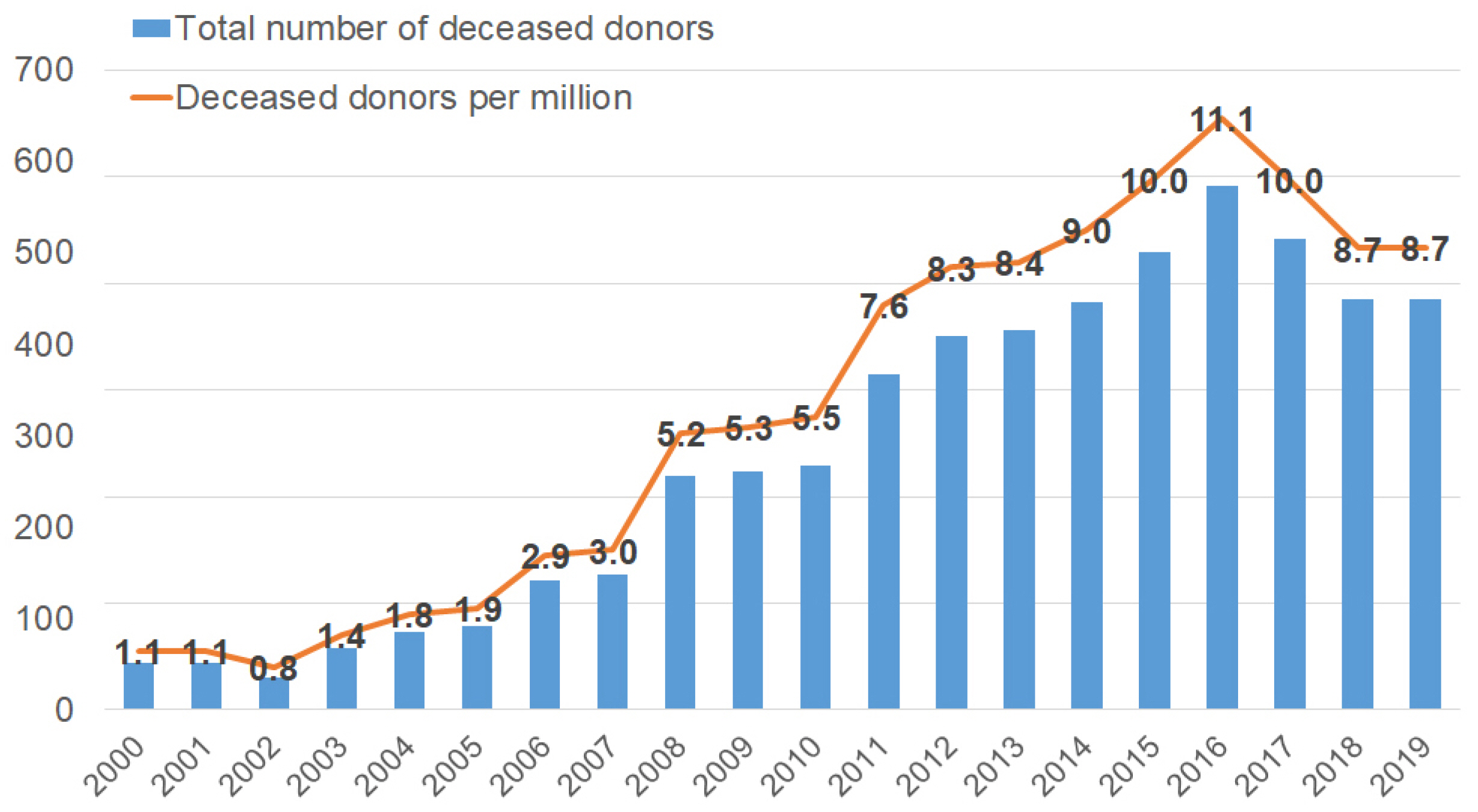
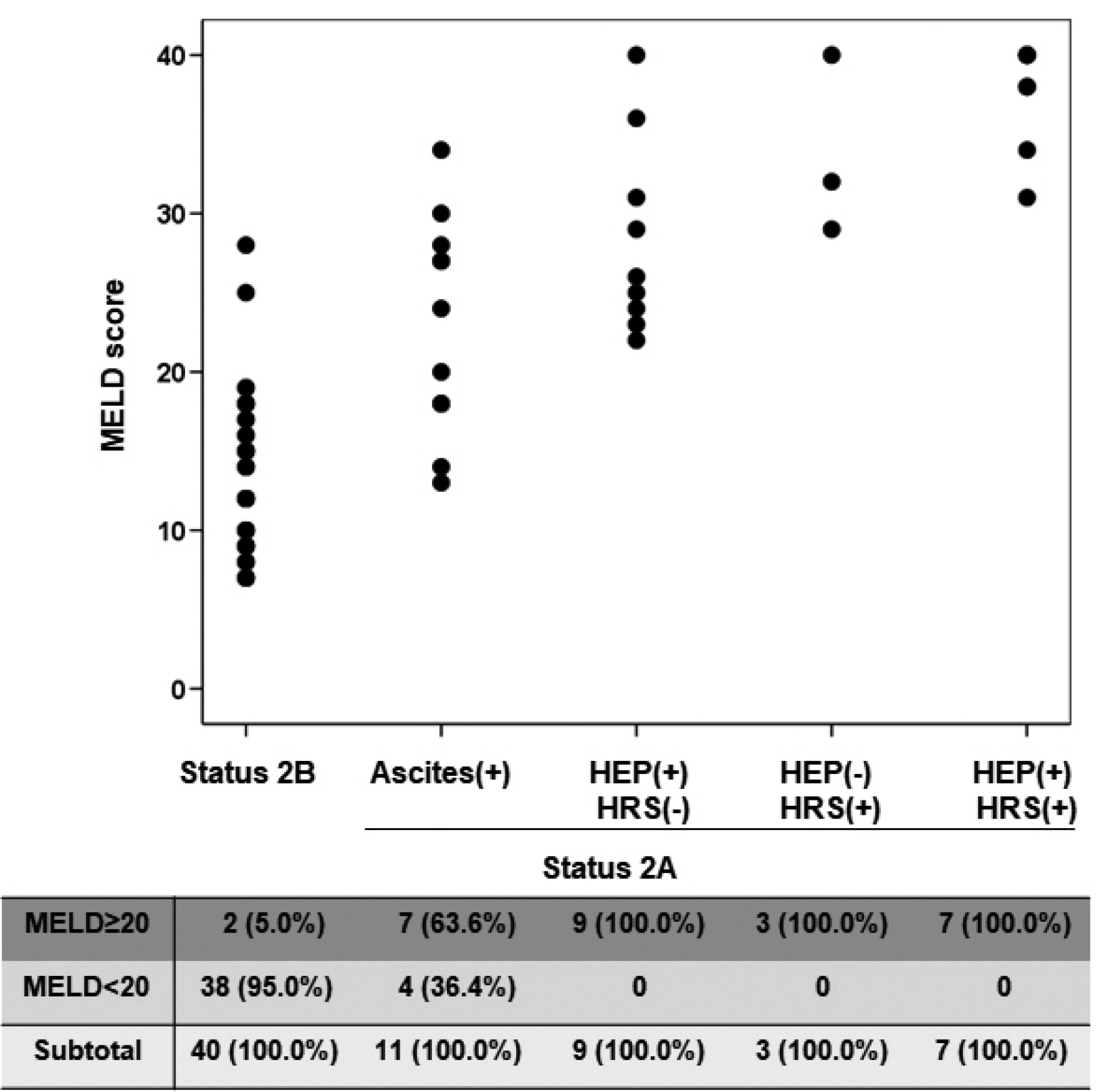
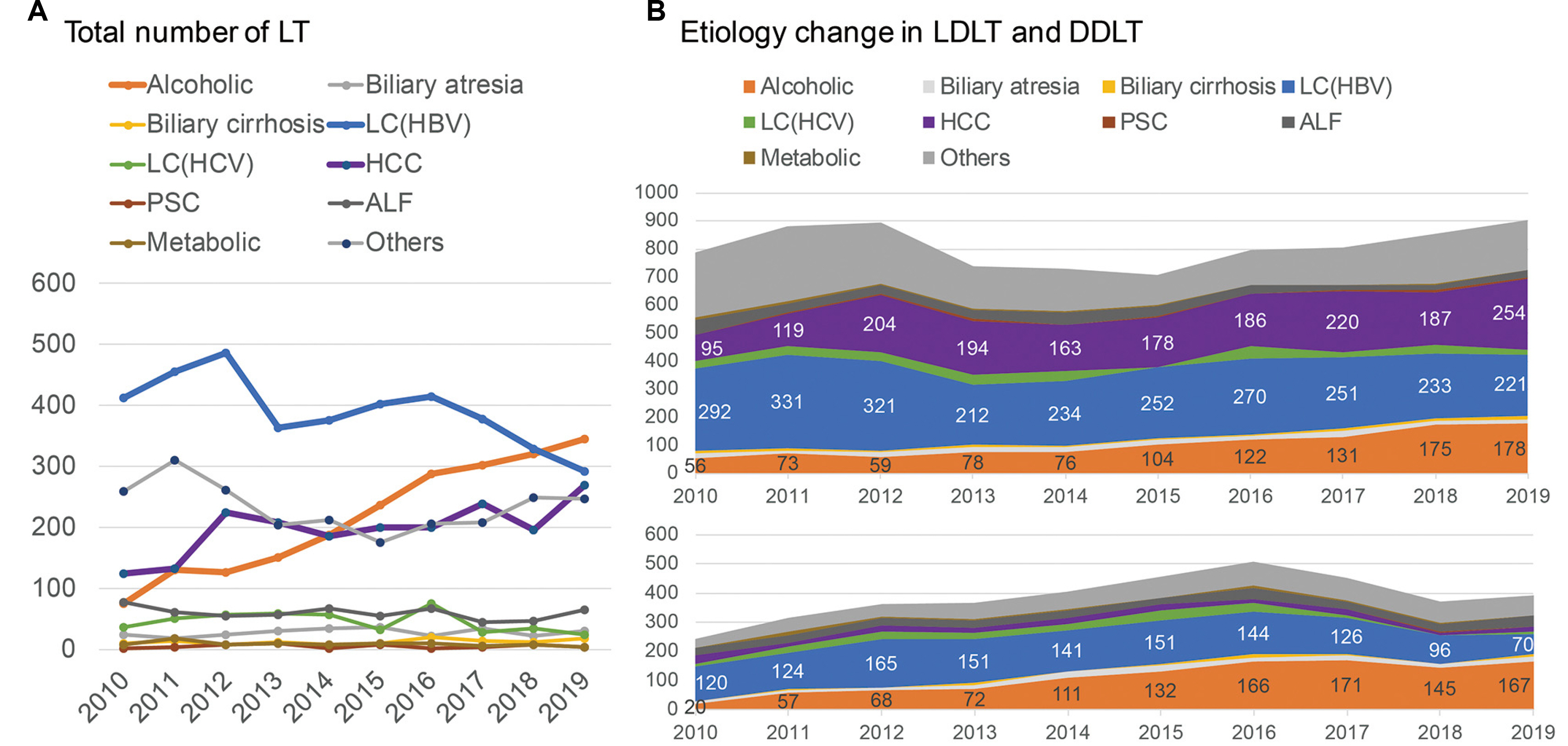
- The organ allocation system should be fair and efficient to predict the prognosis of patients with end-stage organ failure. The liver allocation system in Korea was changed to the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score system from Child-Turcotte-Pugh score-based status system in 2016. Since then, there have been some changes in matching liver graft to recipients in deceased liver transplantation. The severity of sickness of the end-stage liver failure patients has been increased in the MELD era than before. Since 2013, liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease has been gradually increasing in Korea. We should take proper evaluation into consideration when we decide early liver transplantation particularly for patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis, who have a high MELD score. Above all, overcoming organ shortage, it is necessary for us to try to increase the number of deceased donors to meet the need for liver transplantation for end-stage liver disease patients.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Acute Liver Failure: Current Updates and Management
Jin Dong Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2023;81(1):17-28. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2022.148.
Reference
-
1. Wiesner RH, McDiarmid SV, Kamath PS, et al. 2001; MELD and PELD: application of survival models to liver allocation. Liver Transpl. 7:567–580. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2001.25879. PMID: 11460223.
Article2. Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC. 2000; A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology. 31:864–871. DOI: 10.1053/he.2000.5852. PMID: 10733541.
Article3. Trapani S, Morabito V, Oliveti A, et al. 2016; Liver allocation in urgent MELD score ≥30: the italian experience. Transplant Proc. 48:299–303. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.12.047. PMID: 27109940.4. Ruf AE, Kremers WK, Chavez LL, Descalzi VI, Podesta LG, Villamil FG. 2005; Addition of serum sodium into the MELD score predicts waiting list mortality better than MELD alone. Liver Transpl. 11:336–343. DOI: 10.1002/lt.20329. PMID: 15719386.
Article5. Huo TI, Huang YH, Lin HC, et al. 2006; Proposal of a modified Cancer of the Liver Italian Program staging system based on the model for end-stage liver disease for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing loco-regional therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 101:975–982. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00462.x. PMID: 16573785.
Article6. Sharma P, Harper AM, Hernandez JL, et al. 2006; Reduced priority MELD score for hepatocellular carcinoma does not adversely impact candidate survival awaiting liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 6:1957–1962. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2006.01411.x. PMID: 16771808.
Article7. Lee JA, Choi GS, Kim JM, Kwon CHD, Joh JW. 2018; Comparison study of outcomes of deceased donor liver transplantation before and after Korean model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) system: single center experience. J Korean Soc Transplant. 32:7–11. DOI: 10.4285/jkstn.2018.32.1.7.
Article8. 2020. 2019 Annual report of organ and tissue donation and transplantation. [Internet]. KONOS;Seoul (KR): Available from: https://www.konos.go.kr/konosis/common/. cited 2020 Dec 1.9. 2020. Data extracted from OPTN. [Internet]. OPTN;Available from: https://srtr.transplant.hrsa.gov/annual_reports/2018/Liver.aspx#LI_55_tx_counts_race_1_b64. cited 2020 Dec 1.10. Martin AP, Bartels M, Hauss J, Fangmann J. 2007; Overview of the MELD score and the UNOS adult liver allocation system. Transplant Proc. 39:3169–3174. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2007.04.025. PMID: 18089345.
Article11. Freeman RB, Wiesner R. 2012; Should we change the priority for liver allocation for patients with the highest MELD score? Hepatology. 55:14–15. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24775. PMID: 22095707.
Article12. Teixeira AC, Souza FF, Mota Gde A, Martinelli Ade L, Sankarankutty AK, Silva Ode C. 2006; Liver transplantation: expectation with MELD score for liver allocation in Brazil. Acta Cir Bras. 21(Suppl 1):12–14. DOI: 10.1590/S0102-86502006000700003. PMID: 17013505.
Article13. Llado L, Figueras J, Memba R, et al. 2002; Is MELD really the definitive score for liver allocation? Liver Transpl. 8:795–798. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2002.34637. PMID: 12200780.14. Biggins SW, Kim WR, Terrault NA, et al. 2006; Evidence-based incorporation of serum sodium concentration into MELD. Gastro- enterology. 130:1652–1660. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.02.010. PMID: 16697729.
Article15. Hong G, Lee KW, Suh S, et al. 2013; The model for end-stage liver disease score-based system predicts short term mortality better than the current Child-Turcotte-Pugh score-based allocation system during waiting for deceased liver transplantation. J Korean Med Sci. 28:1207–1212. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1207. PMID: 23960449. PMCID: PMC3744710.
Article16. Joo DJ, Kim MS, Kim SI, et al. 2012; Severity of End-stage liver disease in liver transplant candidate; comparison of KONOS status with MELD score. J Korean Soc Transplant. 26:112–119. DOI: 10.4285/jkstn.2012.26.2.112.
Article17. Kim MS. 2016; Modification of emergency status in deceased donor liver allocation: evidence for Korean model of end-stage liver disease (MELD) system. J Korean Soc Transplant. 30:51–58. DOI: 10.4285/jkstn.2016.30.2.51.
Article18. 2020. Transplant waiting list. [Internet]. KONOS;Seoul (KR): Available from https://www.konos.go.kr/konosis/sub4/sub04_05_01_pop.jsp. cited 2020 Dec 1.19. 2020. Rate of deceased organ donors in selected countries in 2019. [Internet]. Statista;Hamburg (Germany): Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/406893/rate-of-organ-donation-by-deceased-donors-in-select-countries /#:~:text=In%202019%2C%20Spain%20had%20the,failure%20and%20late%2Dstage%20disease2019. cited 2020 Dec 1.20. Lee BP, Mehta N, Platt L, et al. 2018; Outcomes of early liver transplantation for patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 155:422–430. e1. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.04.009. PMID: 29655837. PMCID: PMC6460480.
Article21. Varma V, Webb K, Mirza DF. 2010; Liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 16:4377–4393. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i35.4377. PMID: 20845504. PMCID: PMC2941060.
Article22. 2006. Aug. Surveillance report #75: liver cirrhosis mortality in the United States, 1970-2003. [Internet]. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism;Bethesda (MD): Available from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Young_Yoon13/publication/318982538_SURVEILLANCE_REPORT_75_LIVER_CIRRHOSIS_MORTALITY_IN_THE_UNITED_STATES_1970-2003/links/59893f1045851560584f99b6/SURVEILLANCE-REPORT-75-LIVER-CIRRHOSIS-MORTALITY-IN-THE-UNITED-STATES-1970-2003.pdf. cited 2020 Dec 1.23. Lucey MR, Brown KA, Everson GT, et al. 1998; Minimal criteria for placement of adults on the liver transplant waiting list: a report of a national conference organized by the American Society of Transplant Physicians and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Transplantation. 66:956–962. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-199810150-00034. PMID: 9798717.
Article24. Chandok N, Aljawad M, White A, Hernandez-Alejandro R, Marotta P, Yoshida EM. 2013; Liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease among Canadian transplant centres: a national study. Can J Gastroenterol. 27:643–646. DOI: 10.1155/2013/897467. PMID: 24040631. PMCID: PMC3816946.
Article25. Beresford TP, Everson GT. 2000; Liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease: bias, beliefs, 6-month rule, and relapse--but where are the data? Liver Transpl. 6:777–778. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2000.19027. PMID: 11084067.
Article26. Weinrieb RM, Van Horn DH, McLellan AT, Lucey MR. 2000; Interpreting the significance of drinking by alcohol-dependent liver transplant patients: fostering candor is the key to recovery. Liver Transpl. 6:769–776. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2000.18497. PMID: 11084066.
Article27. Pereira SP, Howard LM, Muiesan P, Rela M, Heaton N, Williams R. 2000; Quality of life after liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. Liver Transpl. 6:762–768. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2000.19030. PMID: 11084065.
Article28. Dew MA, DiMartini AF, Steel J, et al. 2008; Meta-analysis of risk for relapse to substance use after transplantation of the liver or other solid organs. Liver Transpl. 14:159–172. DOI: 10.1002/lt.21278. PMID: 18236389. PMCID: PMC2883859.
Article29. Marroni CA. 2015; Management of alcohol recurrence before and after liver transplantation. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 39(Suppl 1):S109–S114. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.06.005. PMID: 26193869.
Article30. Testino G, Leone S, Ansaldi F, Borro P. 2016; Alcohol and liver transplantation: the 6-month abstinence rule is not a dogma. Transpl Int. 29:953–954. DOI: 10.1111/tri.12790. PMID: 27160851.
Article31. Lucey MR, Mathurin P, Morgan TR. 2009; Alcoholic hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 360:2758–2769. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra0805786. PMID: 19553649.
Article32. Singal AK. 2010; Comment on ACG guidelines--management of alcoholic liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 105:1449–1450. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2010.144. PMID: 20523323.
Article33. Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). 2013; KASL clinical practice guidelines: management of alcoholic liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 19:216–254. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2013.19.3.216. PMID: 24133661. PMCID: PMC3796673.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A study on differences in deceased donor liver transplantation before and after the introduction of the model for end-stage liver disease system: three low volume centers, multi-center trial
- Impact of MELD allocation system on the outcomes of deceased donor liver transplantation: a single-center experience
- Impact of the introduction of the model for end-stage liver disease system on the low volume liver transplant centers: a multicenter study
- Impact of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease allocation system on outcomes of deceased donor liver transplantation: A single-center experience
- Outcome of patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis after Model for End-Stage Liver Disease-based allocation system implementation in Korea