Korean J Transplant.
2021 Mar;35(1):24-32. 10.4285/kjt.20.0054.
Outcome of patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis after Model for End-Stage Liver Disease-based allocation system implementation in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2514405
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.20.0054
Abstract
- Background
The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)-based allocation system was implemented in Korea in July 2016 without a mandatory abstinence period for liver transplantation (LT) listing. However, the impact of the allocation policy has not been evaluated in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis (AH).
Methods
A total of 81 consecutive patients with severe AH between January 2014 and December 2018 were analyzed. The clinical course of patients before and after the implementation of the MELD-based allocation system was assessed.
Results
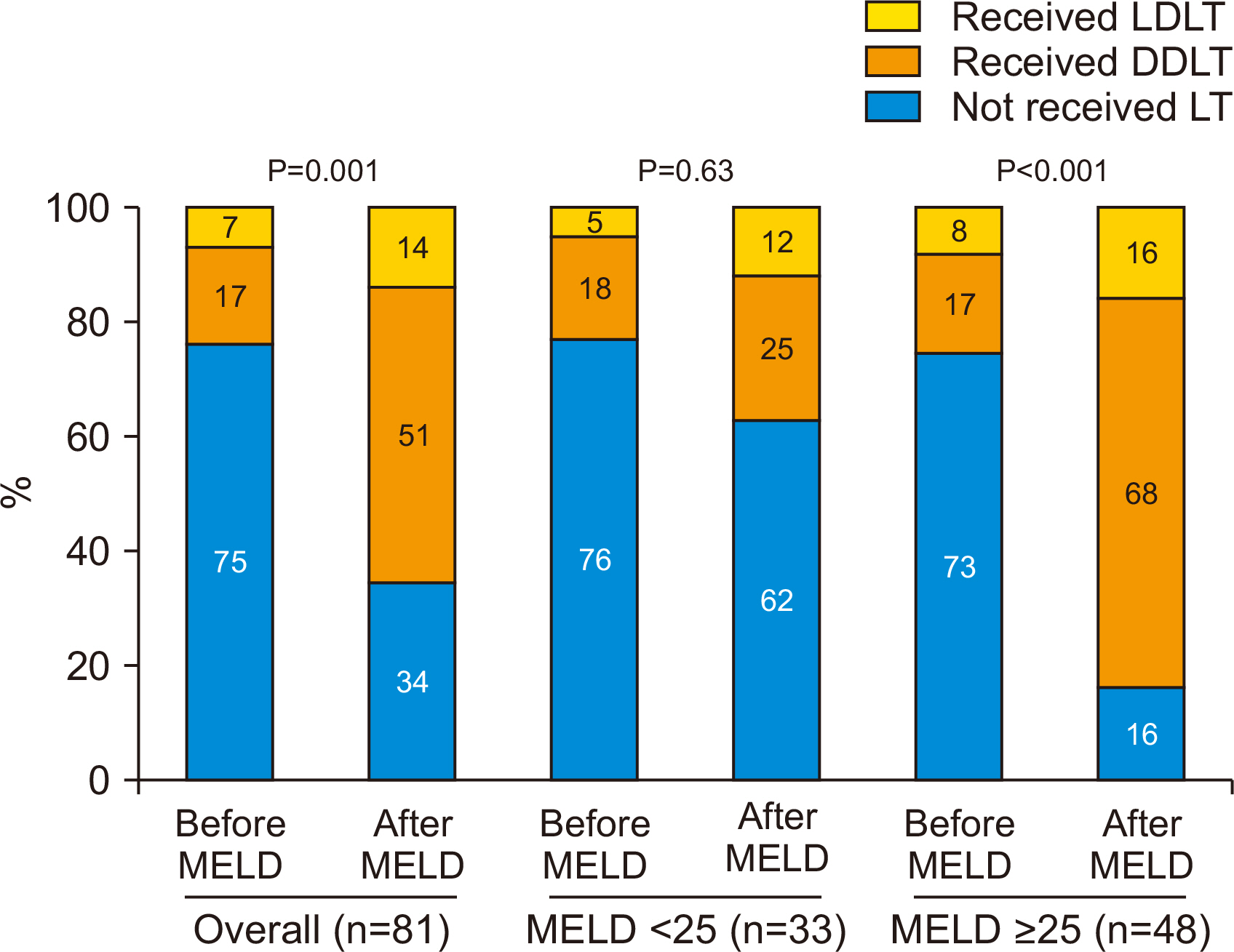
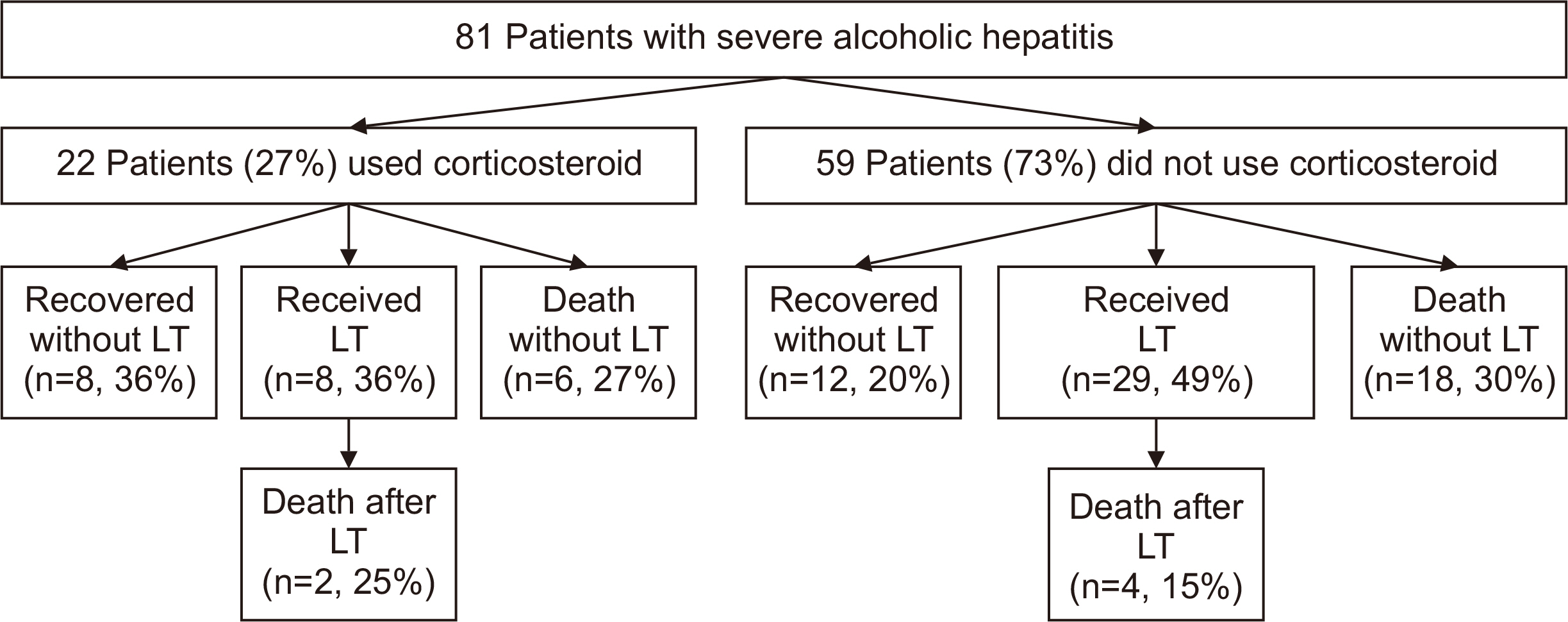
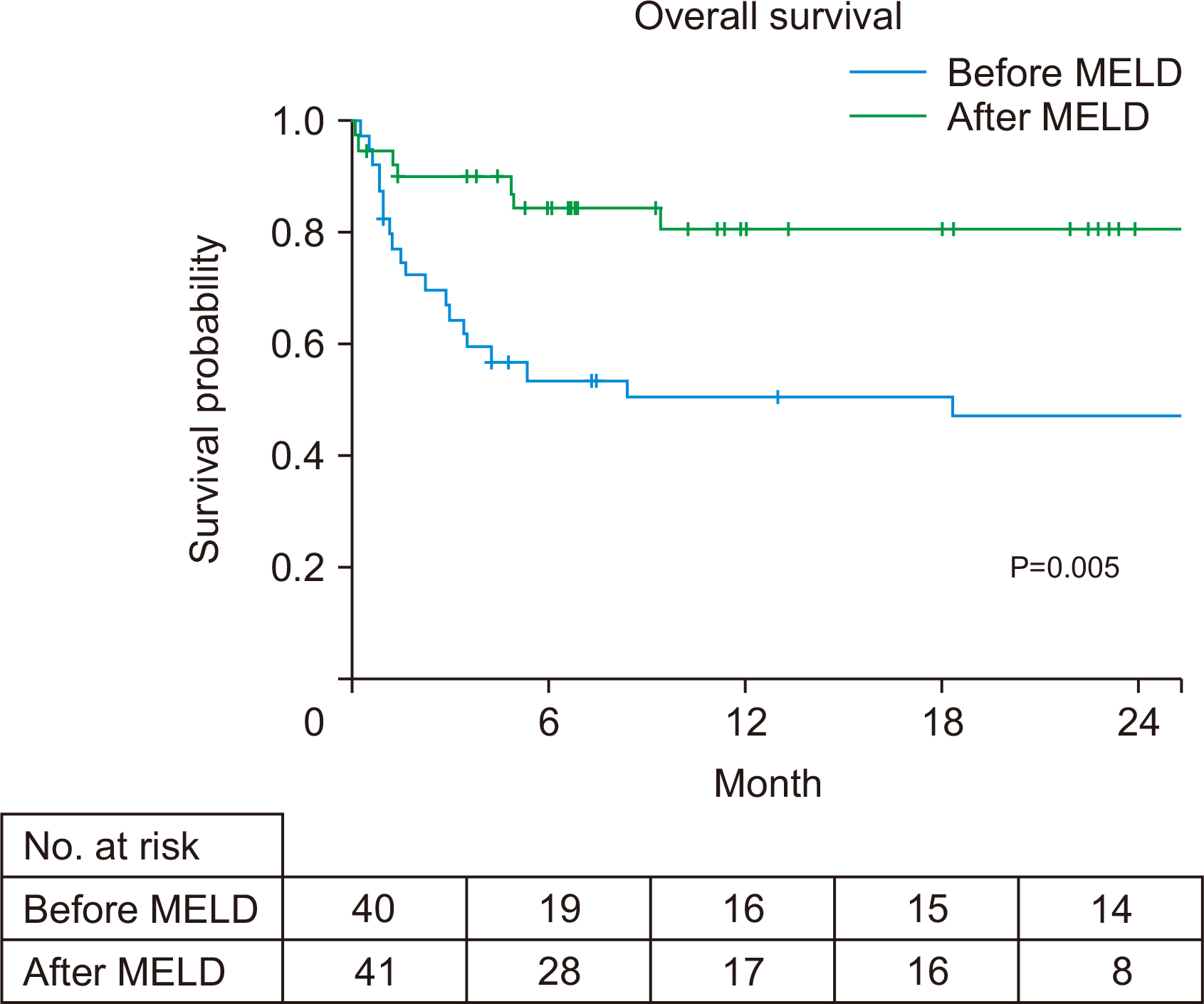
More patients received LT (25%–65%) after the MELD allocation system was implemented. The increase in patients receiving deceased donor LT was dramatic (17%– 51%, P=0.001) compared to patients receiving living donor LT (7%–14%, P=0.30). The overall survival was better for those who received LT (88% vs. 44% at 1 year, P<0.001), and after the MELD era (1-year survival rate: 80% vs. 50%, P=0.005). Post-LT mortality was observed in six patients, with one case of mortality related to recidivism. Baseline MELD and steroid response were factors associated with transplant-free survival.
Conclusions
After implementation of the MELD-based allocation system, deceased donor LT dramatically increased in patients with severe AH. This translated into increased overall survival, but at a cost of mortality due to recidivism. Urgent evaluation is warranted to identify criteria to justify the use of precious liver grafts from deceased donors for severe AH patients in Korea.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The impact of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score on deceased donor liver transplant outcomes in low volume liver transplantation center: a retrospective and single-center study
Doo-Ho Lee, Yeon Ho Park, Seok Won Choi, Kug Hyun Nam, Sang Tae Choi, Doojin Kim
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2021;101(6):360-367. doi: 10.4174/astr.2021.101.6.360.
Reference
-
1. Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). 2013; KASL clinical practice guidelines: management of alcoholic liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 19:216–54. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2013.19.3.216. PMID: 24133661. PMCID: PMC3796673.2. Lucey MR, Mathurin P, Morgan TR. 2009; Alcoholic hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 360:2758–69. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra0805786. PMID: 19553649.
Article3. Shipley LC, Kodali S, Singal AK. 2019; Recent updates on alcoholic hepatitis. Dig Liver Dis. 51:761–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2019.03.023. PMID: 31010745.
Article4. Mathurin P, O'Grady J, Carithers RL, Phillips M, Louvet A, Mendenhall CL, et al. 2011; Corticosteroids improve short-term survival in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis: meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gut. 60:255–60. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2010.224097. PMID: 20940288.
Article5. Liu M, Shah VH. 2019; New prospects for medical management of acute alcoholic hepatitis. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 13:131–5. DOI: 10.1002/cld.792. PMID: 31236260. PMCID: PMC6544414.
Article6. Vergis N, Atkinson SR, Thursz MR. 2019; The future of therapy for alcoholic hepatitis: beyond corticosteroids. J Hepatol. 70:785–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.01.016. PMID: 30791978. PMCID: PMC6420340.7. Pavlov CS, Varganova DL, Casazza G, Tsochatzis E, Nikolova D, Gluud C. 2019; Glucocorticosteroids for people with alcoholic hepatitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 4:CD001511. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001511.pub4. PMID: 30964545. PMCID: PMC6455893.
Article8. Vergis N, Atkinson SR, Knapp S, Maurice J, Allison M, Austin A, et al. 2017; In patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis, prednisolone increases susceptibility to infection and infection-related mortality, and is associated with high circulating levels of bacterial DNA. Gastroenterology. 152:1068–77. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.019. PMID: 28043903. PMCID: PMC6381387.9. Obed A, Bashir A, Stern S, Jarrad A. 2018; Severe acute alcoholic hepatitis and liver transplant: a never-ending mournful story. Clin Mol Hepatol. 24:358–66. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2018.0044. PMID: 30360030. PMCID: PMC6313024.
Article10. Haugen CE, Cameron AM. 2020; Early liver transplantation in acute alcoholic hepatitis. Semin Liver Dis. 40:29–33. DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-3399560. PMID: 31711253.
Article11. Mathurin P, Moreno C, Samuel D, Dumortier J, Salleron J, Durand F, et al. 2011; Early liver transplantation for severe alcoholic hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 365:1790–800. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1105703. PMID: 22070476.
Article12. Lee BP, Mehta N, Platt L, Gurakar A, Rice JP, Lucey MR, et al. 2018; Outcomes of early liver transplantation for patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 155:422–30. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.04.009. PMID: 29655837. PMCID: PMC6460480.
Article13. Alsahhar JS, Mehta A, Lepe R. 2019; Con: liver transplantation should not be performed in patients with acute alcoholic hepatitis. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 13:144–7. DOI: 10.1002/cld.779. PMID: 31236263. PMCID: PMC6544416.
Article14. Kubiliun MJ, Rich NE, Singal A, Mufti AR. 2019; Pro: liver transplantation should be considered in select patients with acute alcoholic hepatitis. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 13:140–3. DOI: 10.1002/cld.780. PMID: 31236262. PMCID: PMC6544410.
Article15. Donckier V, Lucidi V, Gustot T, Moreno C. 2014; Ethical considerations regarding early liver transplantation in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis not responding to medical therapy. J Hepatol. 60:866–71. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.11.015. PMID: 24291238.
Article16. Daswani R, Kumar A, Sharma P, Singla V, Bansal N, Arora A. 2018; Role of liver transplantation in severe alcoholic hepatitis. Clin Mol Hepatol. 24:43–50. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2017.0027. PMID: 29316778. PMCID: PMC5875200.
Article17. Min SI, Ahn C, Han DJ, Kim SI, Chung SY, Lee SK, et al. 2015; To achieve national self-sufficiency: recent progresses in deceased donation in Korea. Transplantation. 99:765–70. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000412. PMID: 25226175.18. Kim MS. 2016; Modification of emergency status in deceased donor liver allocation: evidence for Korean Model of End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) system. J Korean Soc Transplant. 30:51–8. DOI: 10.4285/jkstn.2016.30.2.51.
Article19. Crabb DW, Bataller R, Chalasani NP, Kamath PS, Lucey M, Mathurin P, et al. 2016; Standard definitions and common data elements for clinical trials in patients with alcoholic hepatitis: recommendation from the NIAAA alcoholic hepatitis consortia. Gastroenterology. 150:785–90. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.042. PMID: 26921783. PMCID: PMC5287362.
Article20. Bajaj JS, O'Leary JG, Reddy KR, Wong F, Olson JC, Subramanian RM, et al. 2012; Second infections independently increase mortality in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis: the North American consortium for the study of end-stage liver disease (NACSELD) experience. Hepatology. 56:2328–35. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25947. PMID: 22806618. PMCID: PMC3492528.
Article21. Dunn W, Jamil LH, Brown LS, Wiesner RH, Kim WR, Menon KV, et al. 2005; MELD accurately predicts mortality in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology. 41:353–8. DOI: 10.1002/hep.20503. PMID: 15660383.
Article22. Louvet A, Naveau S, Abdelnour M, Ramond MJ, Diaz E, Fartoux L, et al. 2007; The Lille model: a new tool for therapeutic strategy in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis treated with steroids. Hepatology. 45:1348–54. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21607. PMID: 17518367.
Article23. Shawcross DL, O'Grady JG. 2010; The 6-month abstinence rule in liver transplantation. Lancet. 376:216–7. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60487-4. PMID: 20656110.
Article24. Brown RS Jr. 2011; Transplantation for alcoholic hepatitis: time to rethink the 6-month "rule". N Engl J Med. 365:1836–8. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMe1110864. PMID: 22070481.25. Lee BP, Terrault NA. 2018; Early liver transplantation for severe alcoholic hepatitis: moving from controversy to consensus. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 23:229–36. DOI: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000507. PMID: 29389821. PMCID: PMC6423506.26. Chung HG, Sinn DH, Kang W, Choi GS, Kim JM, Joh JW. 2021; Incidence of and risk factors for alcohol relapse after liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease: comparison between deceased donor and living donor liver transplantation. J Gastrointest Surg. 25:672–80. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-020-04540-7. PMID: 32095927.
Article27. Lee J, Kim DG, Lee JY, Lee JG, Joo DJ, Kim SI, et al. 2019; Impact of model for end-stage liver disease score-based allocation system in Korea: a nationwide study. Transplantation. 103:2515–22. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002755. PMID: 30985735.
Article28. Im GY, Cameron AM, Lucey MR. 2019; Liver transplantation for alcoholic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 70:328–34. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.11.007. PMID: 30658734.
Article29. Lee BP, Samur S, Dalgic OO, Bethea ED, Lucey MR, Weinberg E, et al. 2019; Model to calculate harms and benefits of early vs delayed liver transplantation for patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 157:472–80. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.04.012. PMID: 30998988. PMCID: PMC6650344.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation for Alcoholic Liver Disease in Korea in MELD Era
- Impact of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease allocation system on outcomes of deceased donor liver transplantation: A single-center experience
- Impact of MELD allocation system on the outcomes of deceased donor liver transplantation: a single-center experience
- Comparison Study of Outcomes of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation before and after Korean Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) System: Single Center Experience
- Modification of Emergency Status in Deceased Donor Liver Allocation: Evidence for Korean Model of End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) System