J Korean Soc Transplant.
2014 Jun;28(2):59-68. 10.4285/jkstn.2014.28.2.59.
Research for Modification of Emergency Status in Deceased Donor Liver Allocation: Survival Analysis of Waiting Patients for Liver Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Committee of Liver Disease Severity for Liver Transplantation, The Korean Society for Transplantation, Korea. ysms91@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2202532
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2014.28.2.59
Abstract
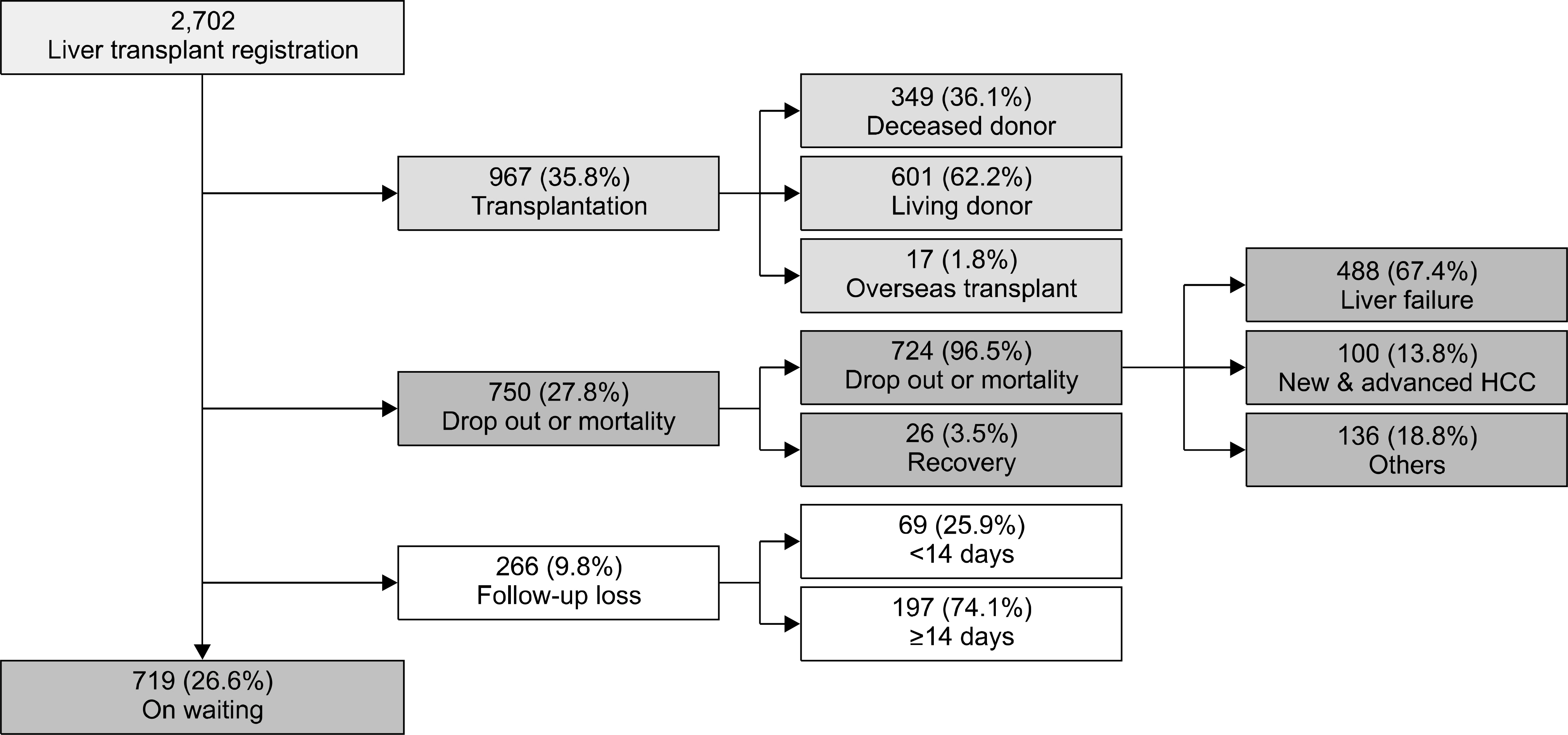
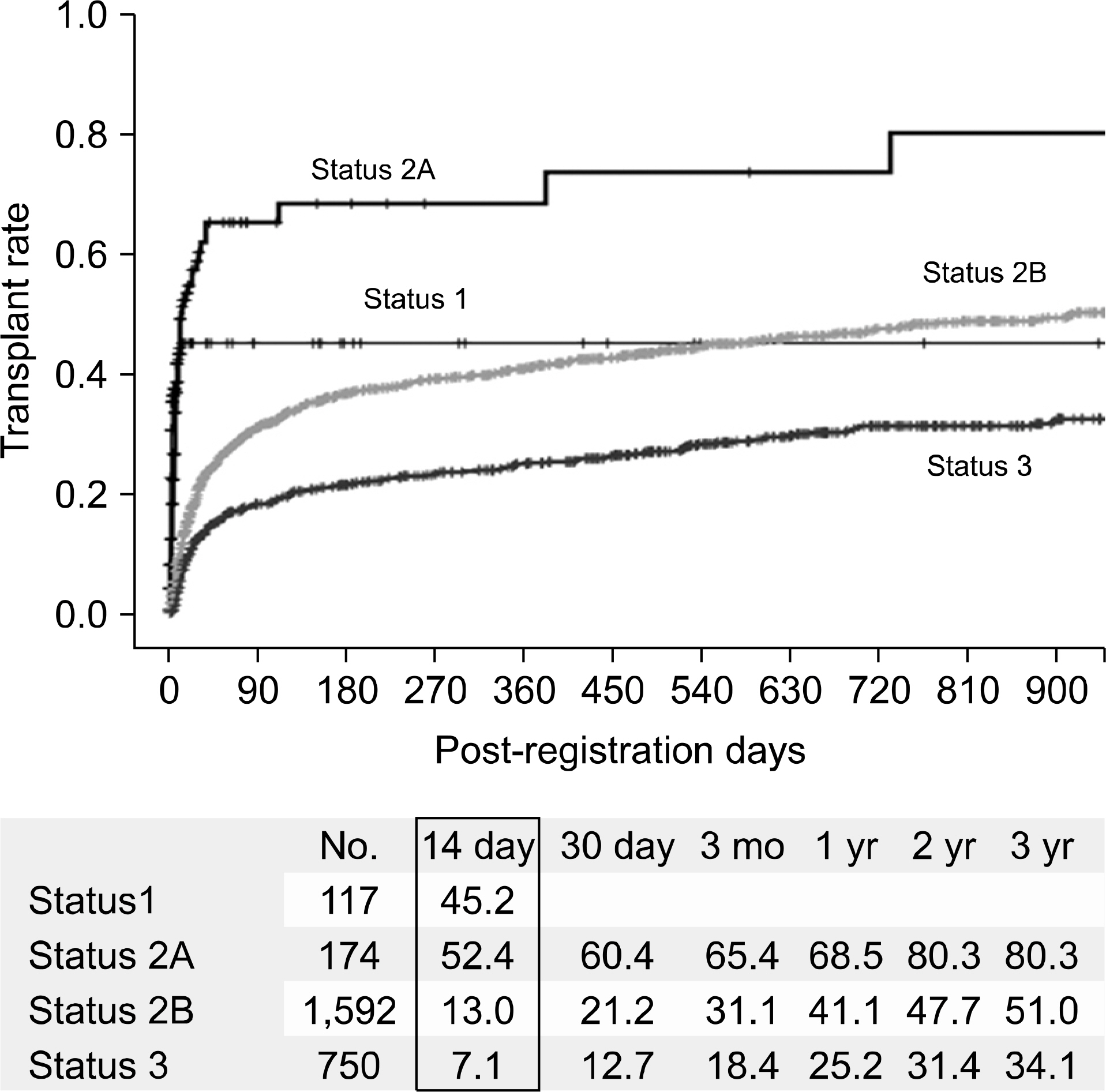
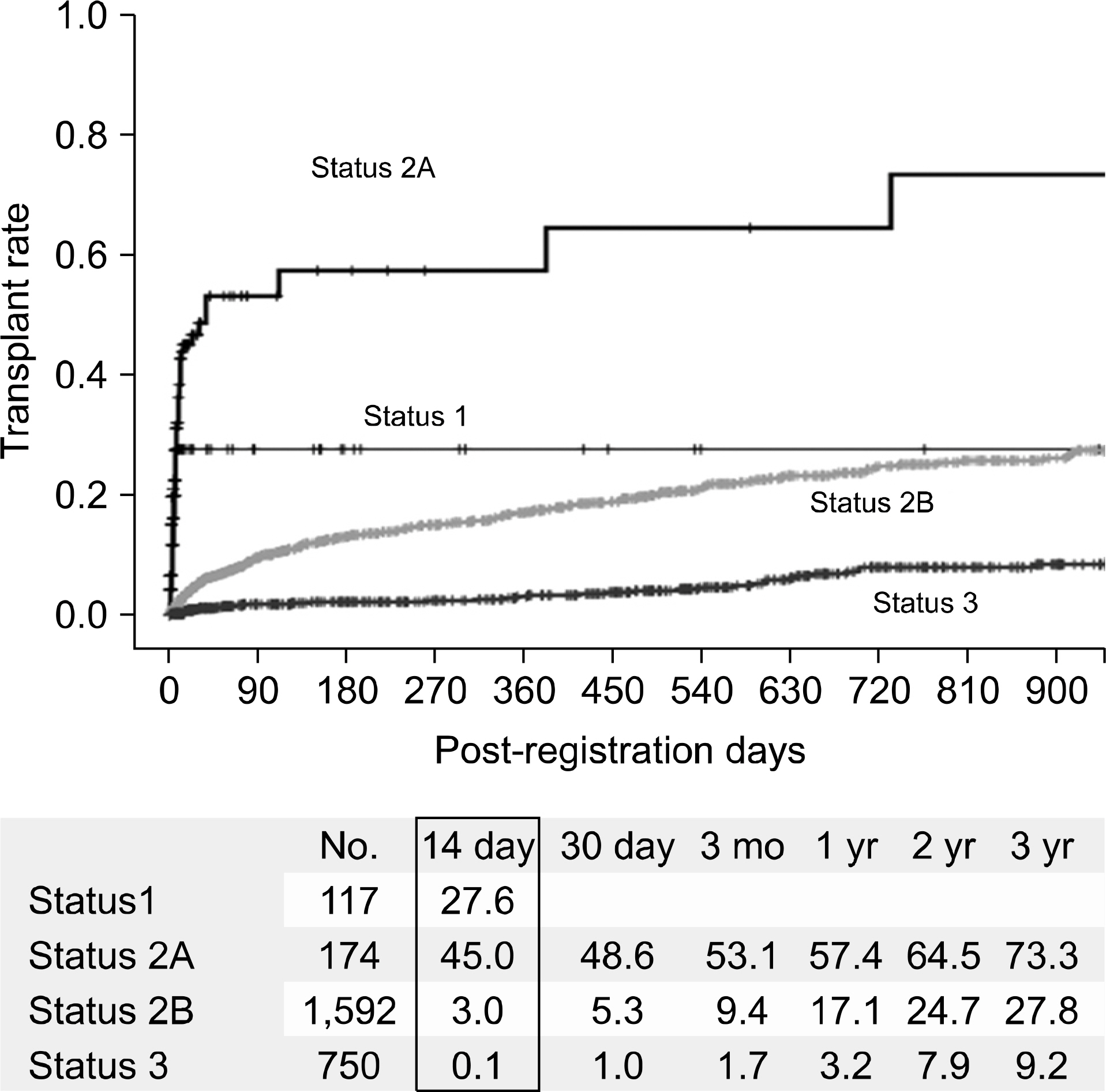
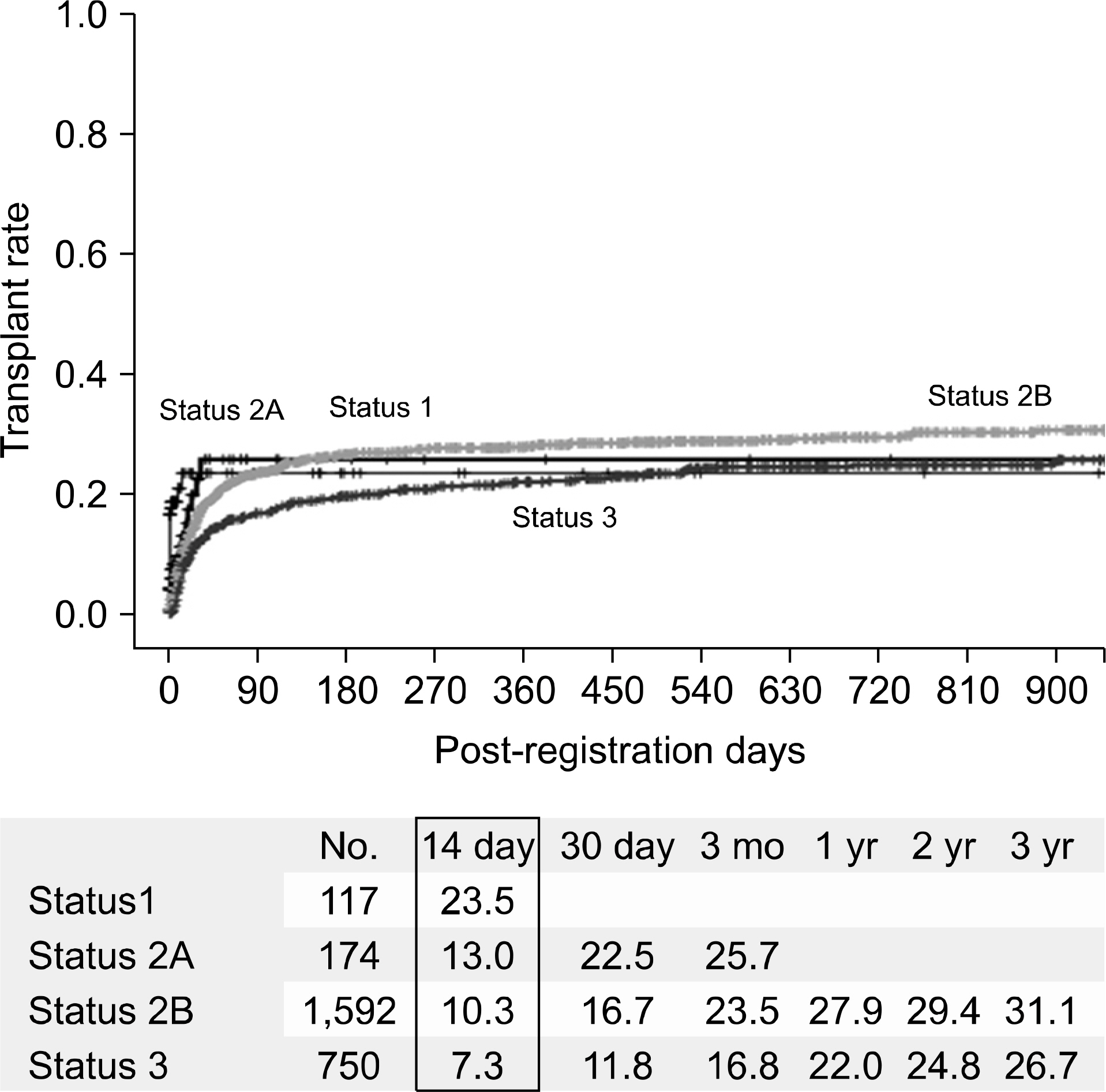
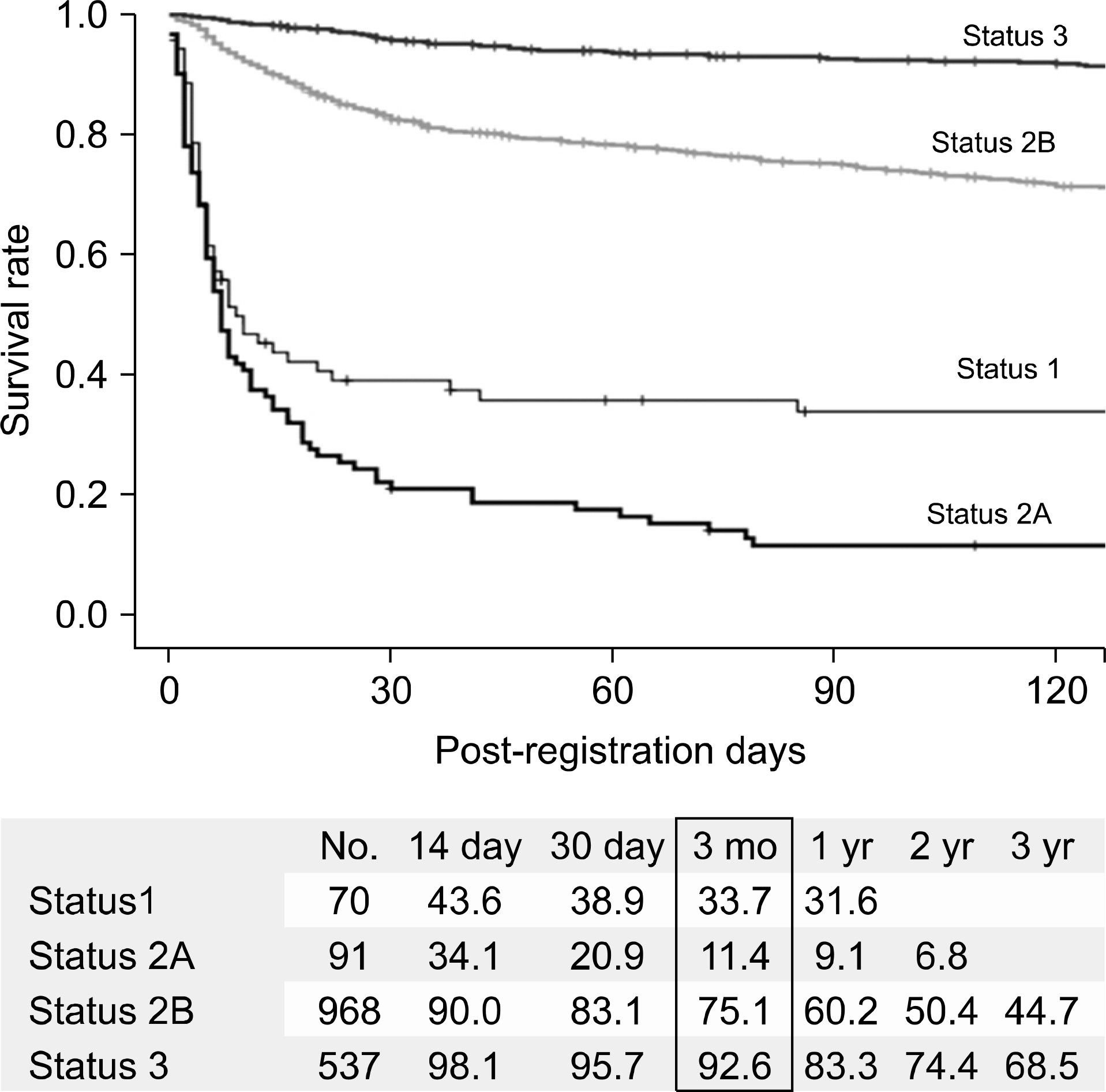
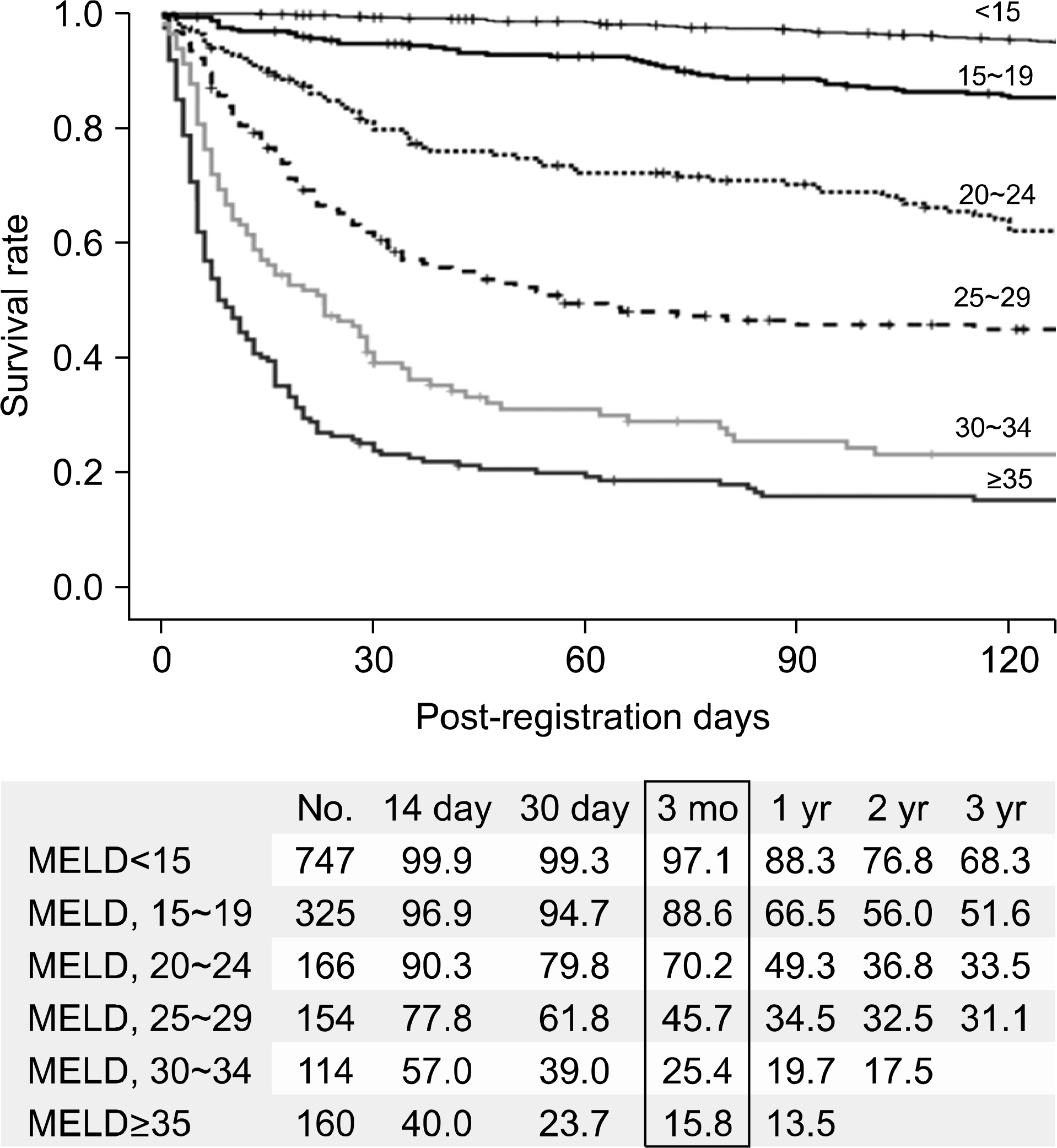
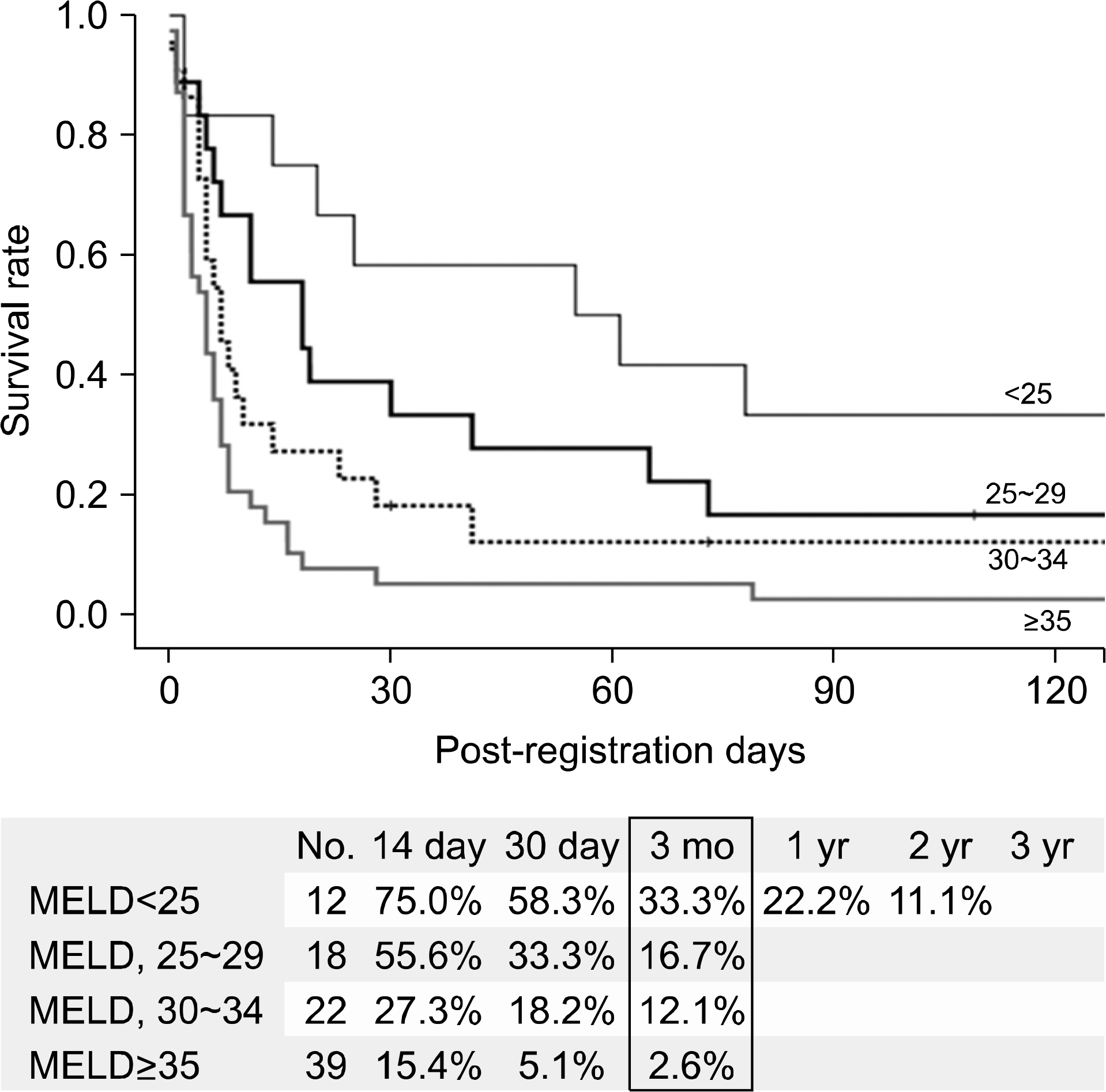
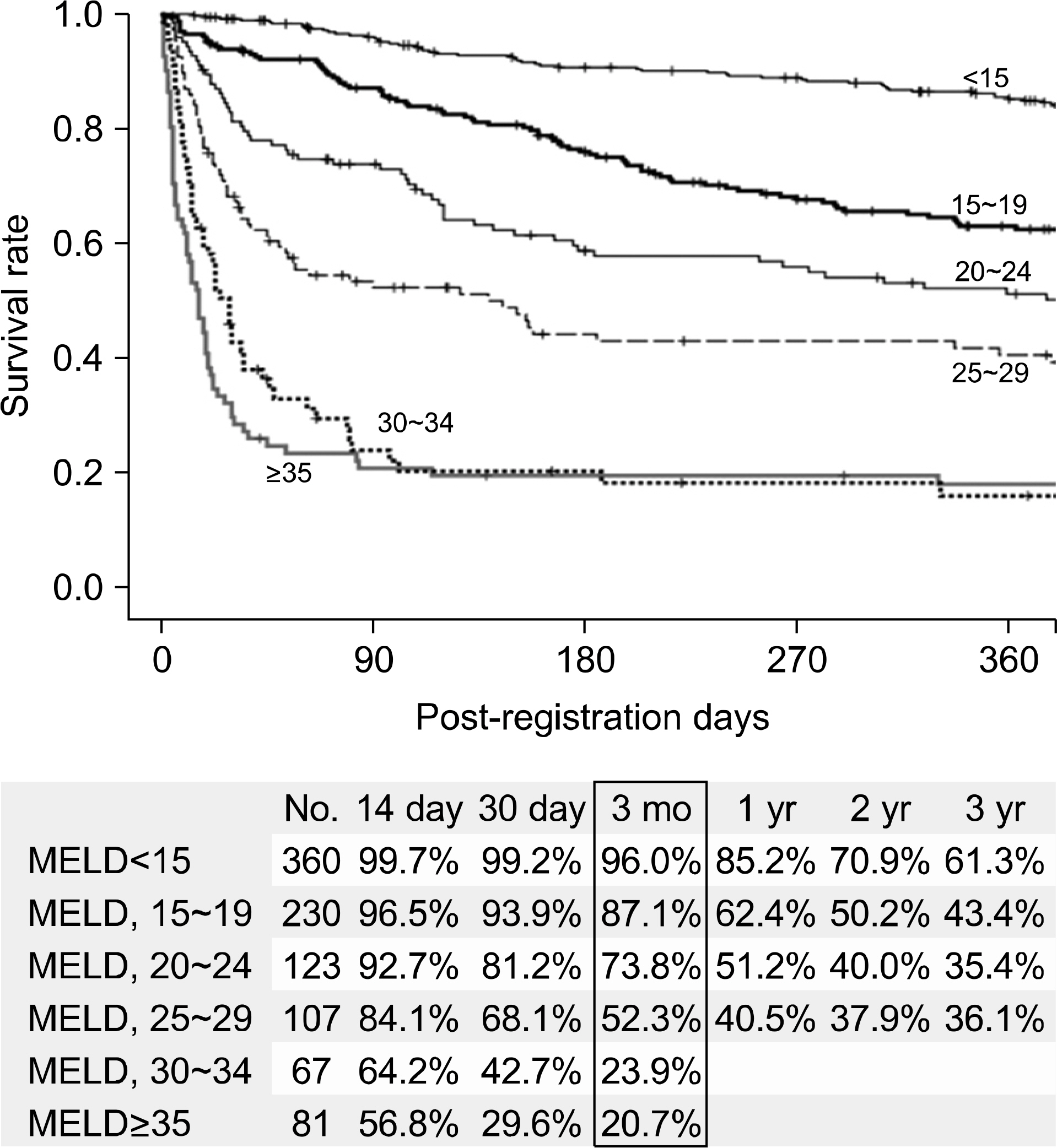
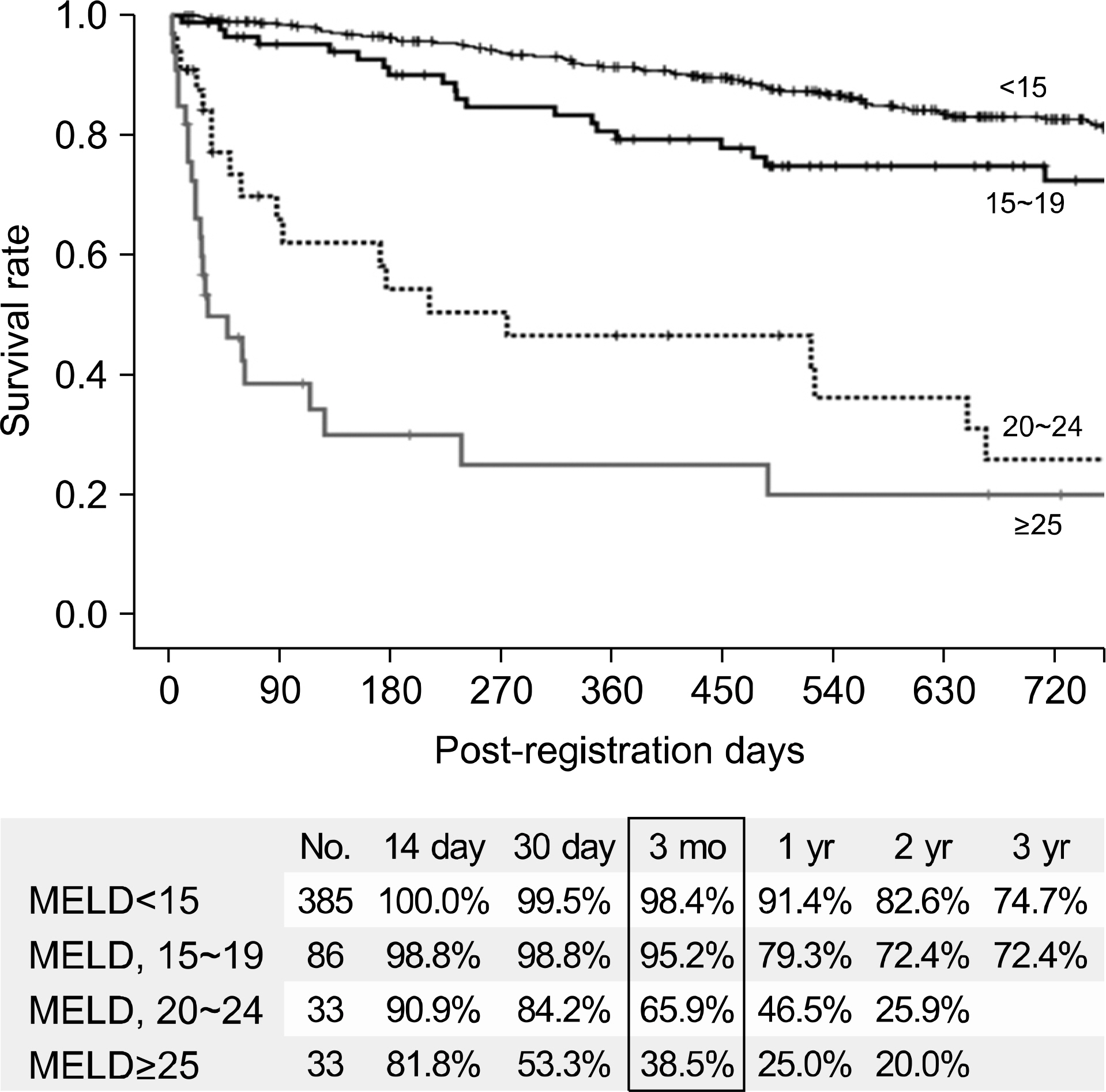
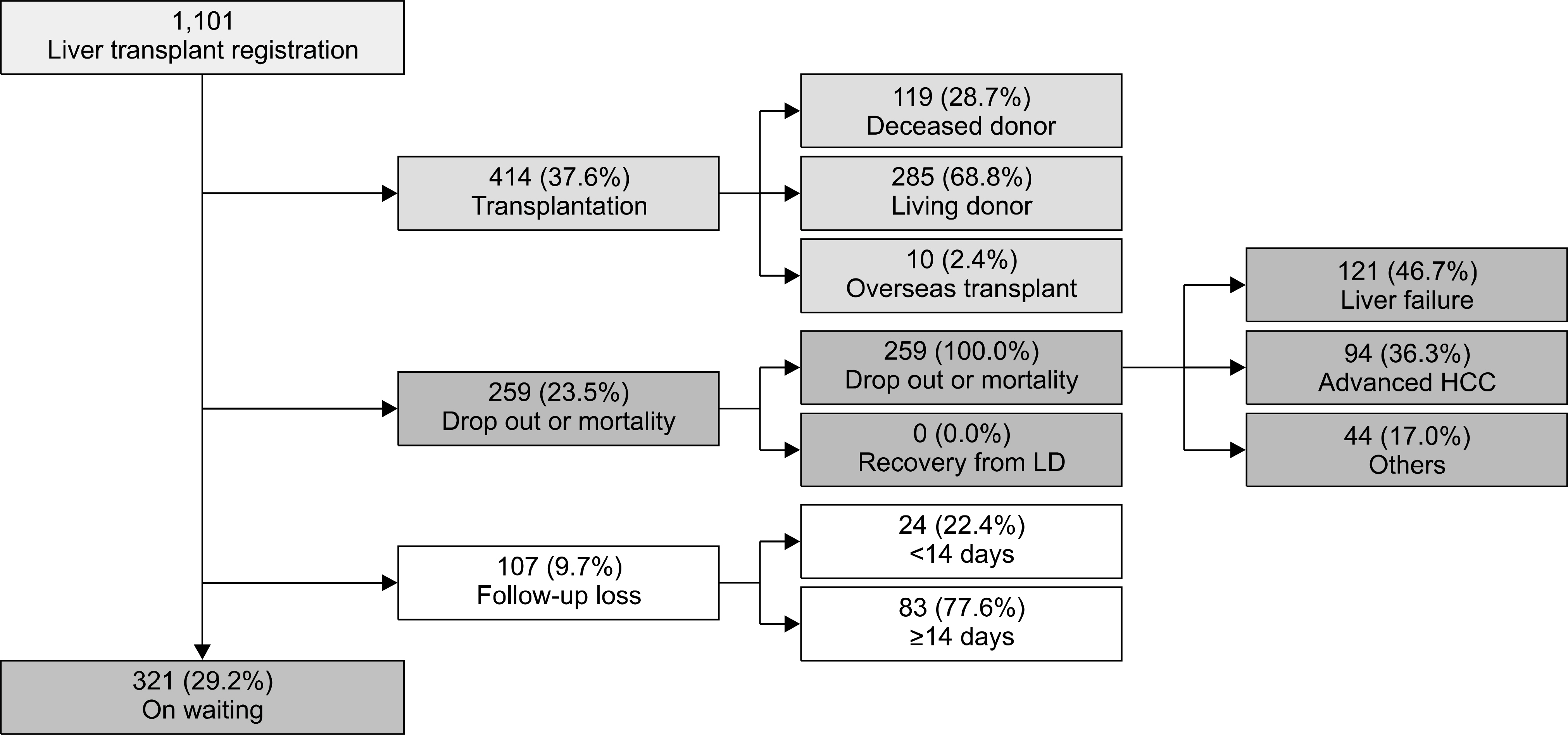
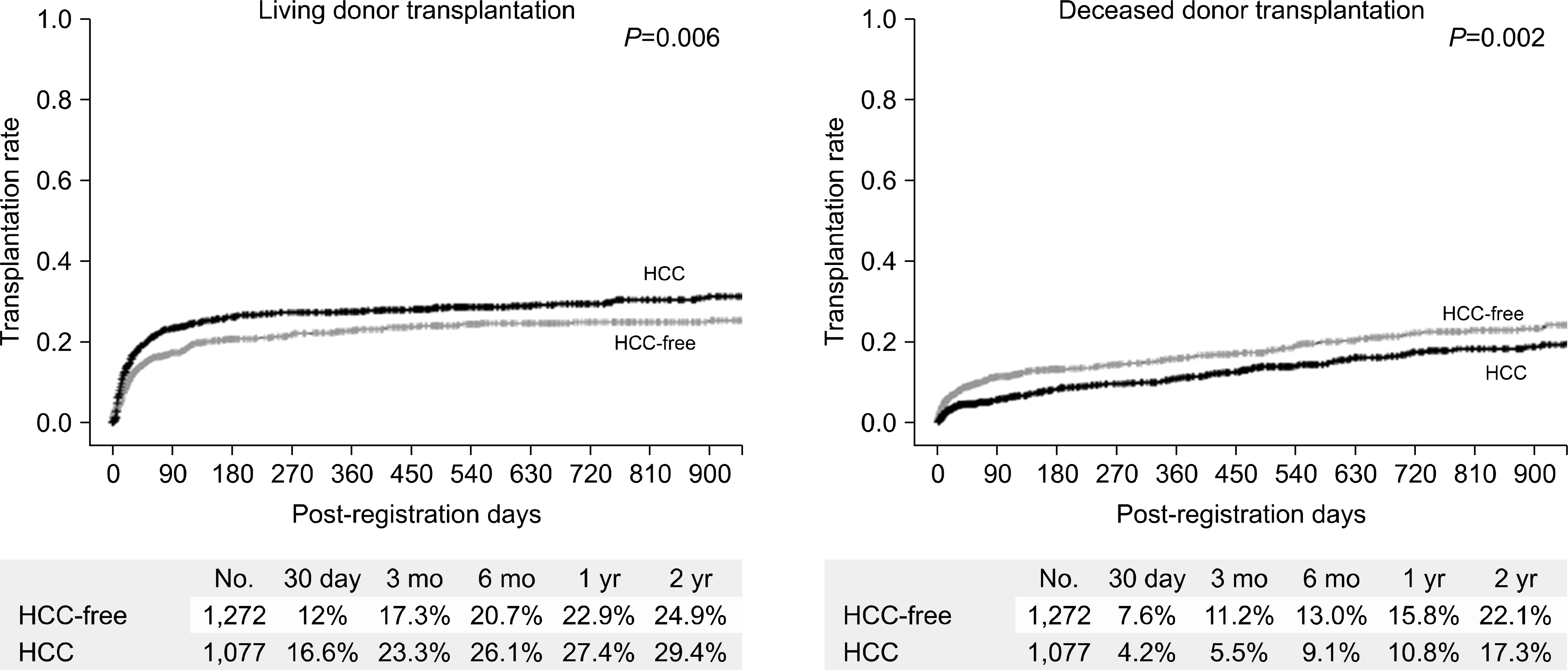
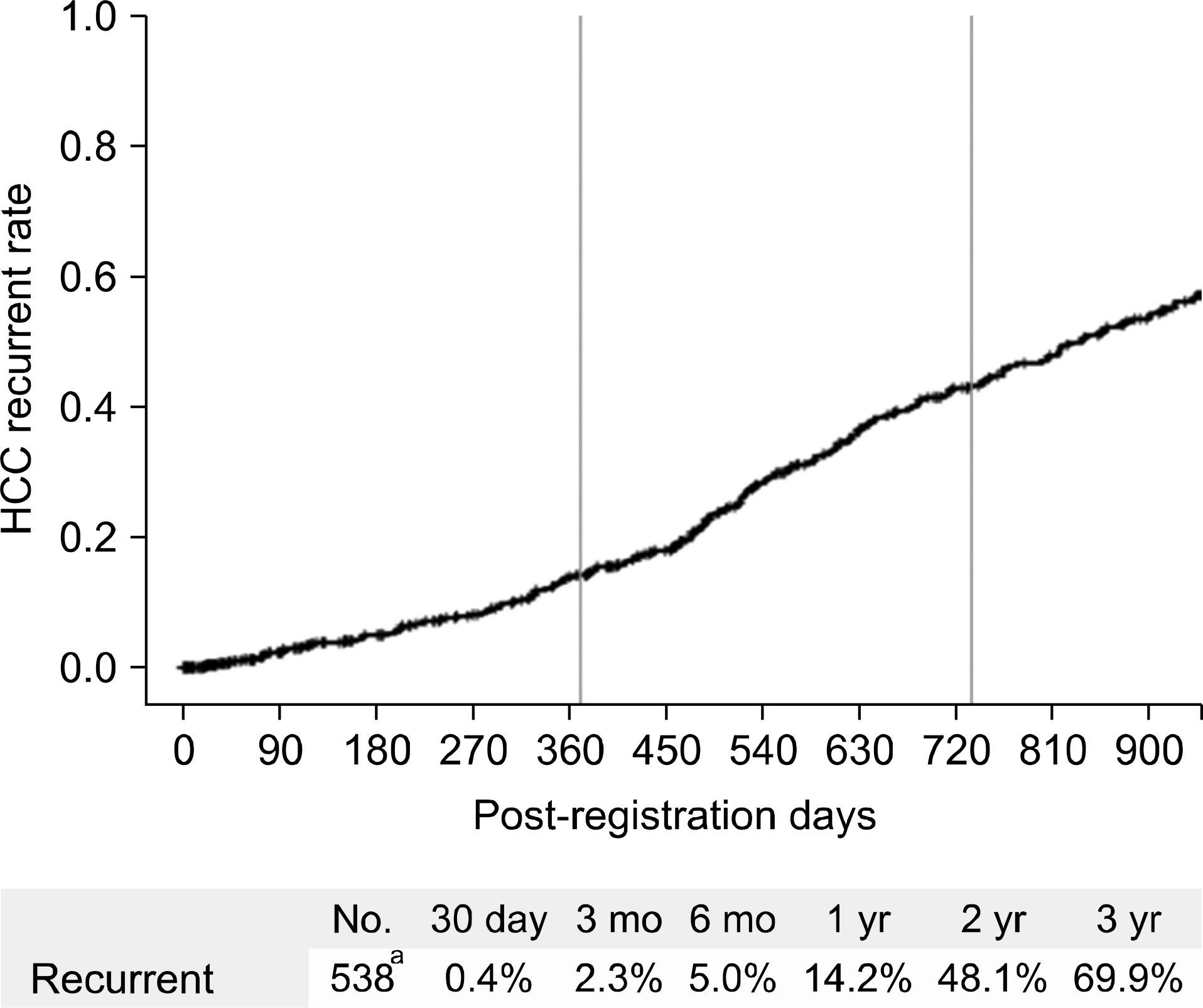
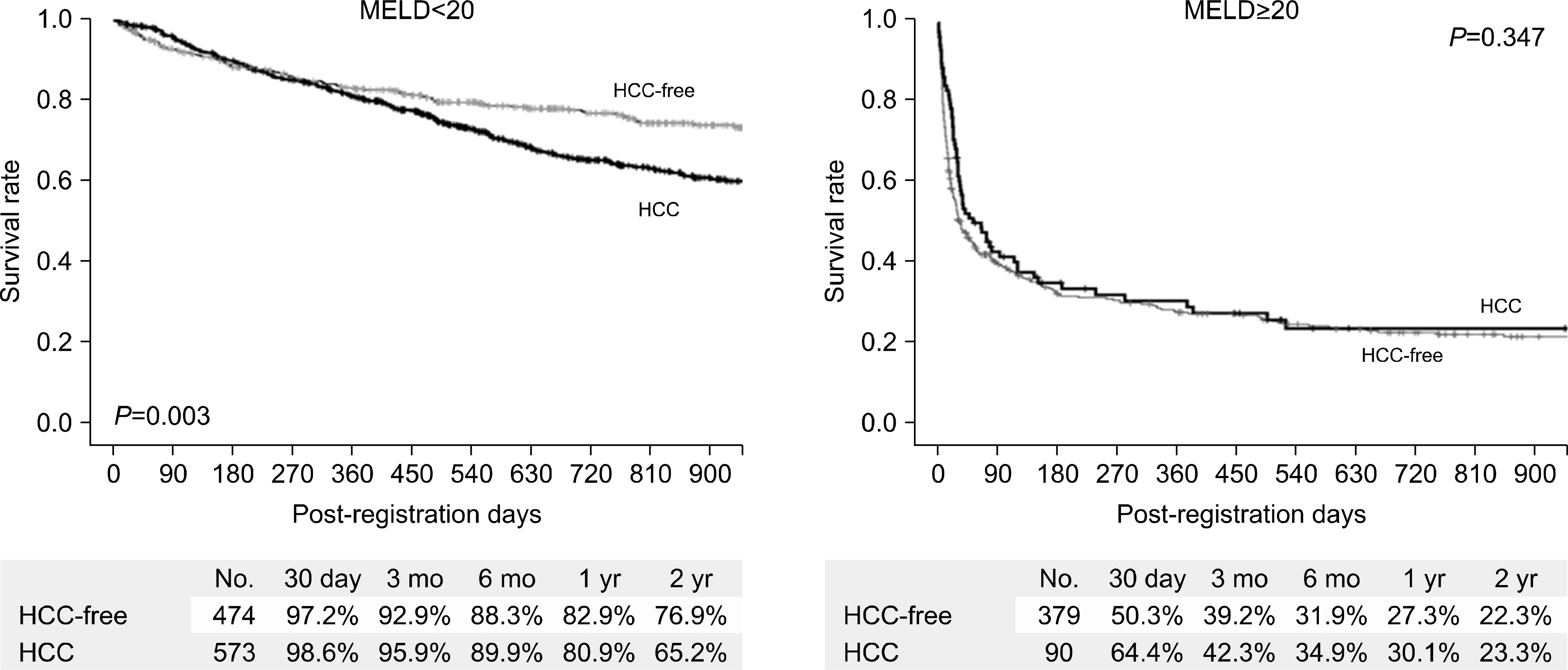
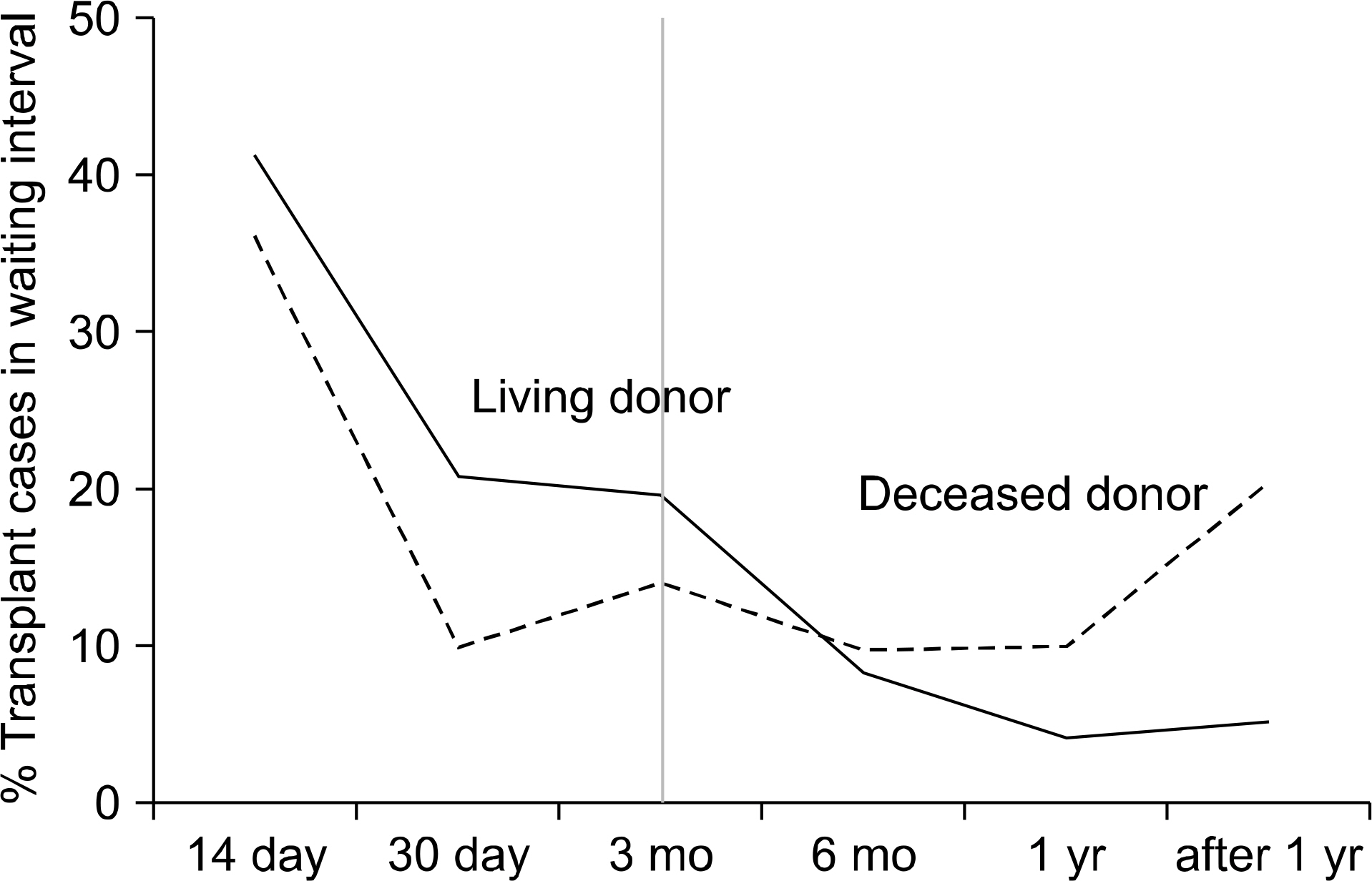
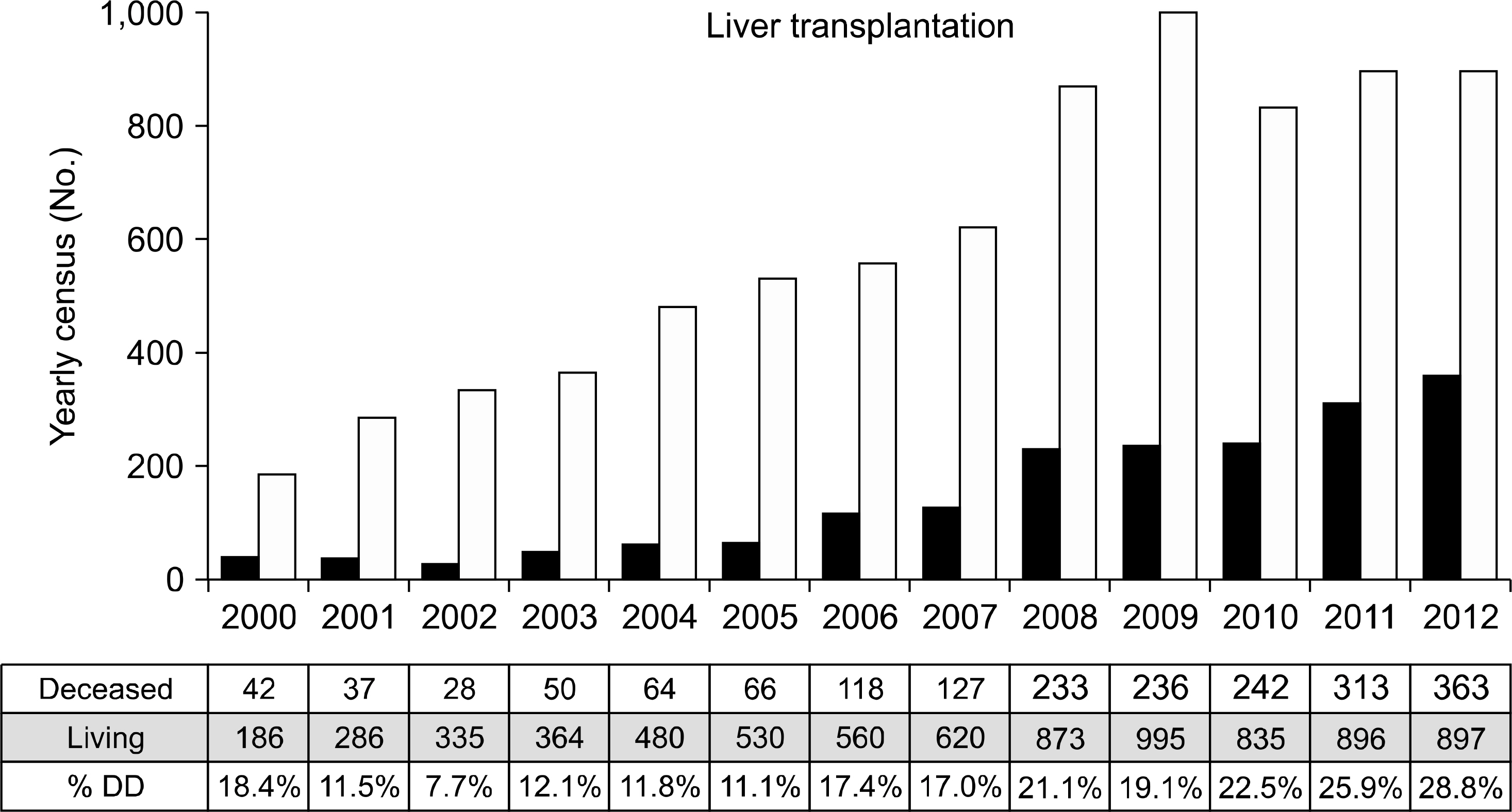
- Despite a remarkable increase of deceased donors, organ shortage is the main hurdle of organ transplantation in Korea. Therefore, liver transplantation priority is a major issue of liver allocation. We confront a situation that needs to change in order to achieve more adequate and objective allocation of the system. We considered the MELD system as an alternative to the CTP score and Status system. For application of the MELD system, comparison between two systems is required; and a national-based retrospective review of liver transplantation candidates (waiting list) was conducted as a multi-center collaborative study. Eleven transplant centers participated in this national study. From 2009 to 2012, 2,702 waiting lists were enrolled. After mean 349+/-412 days follow-up, 967 patients (35.8%) of liver transplantation, 750 patients (27.8%) of drop-out/mortality, and 719 patients (26.6%) on waiting were identified. In analysis of patient mortality during waiting time, status system showed significant difference of waiting mortality by status at registration. However, differences of waiting mortality by MELD system were more prominent and discriminate. In comparisons by MELD score in exclusive Status 2A waiting patients, there was a significant difference of waiting mortality by MELD score. This means that the MELD system is a good predictor of short-term survival after listing compared with status system with CTP score. Korean national-based retrospective study showed the superiority of the MELD system in prediction of short-term mortality and usefulness as a determinant for allocation priority.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison Study of Outcomes of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation before and after Korean Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) System: Single Center Experience
Ji A Lee, Gyu-seong Choi, Jong Man Kim, Chun Hyuck David Kwon, Jae-Won Joh
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2018;32(1):7-11. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2018.30.1.07.
Reference
-
References
1). Kim MS, Kim SI, Kim YS. Current status of deceased donor organ recovery and sharing in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008; 51:685–91.
Article2). Wiesner RH, McDiarmid SV, Kamath PS, Edwards EB, Malinchoc M, Kremers WK, et al. MELD and PELD: application of survival models to liver allocation. Liver Transpl. 2001; 7:567–80.
Article3). Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology. 2000; 31:864–71.
Article4). Santori G, Andorno E, Morelli N, Antonucci A, Bottino G, Mondello R, et al. MELD score versus conventional UNOS status in predicting short-term mortality after liver transplantation. Transpl Int. 2005; 18:65–72.
Article5). Dutkowski P, Oberkofler CE, Béchir M, Müllhaupt B, Geier A, Raptis DA, et al. The model for end-stage liver disease allocation system for liver transplantation saves lives, but increases morbidity and cost: a prospective outcome analysis. Liver Transpl. 2011; 17:674–84.
Article6). Cywinski JB, Mascha EJ, You J, Sessler DI, Kapural L, Argalious M, et al. Pre-transplant MELD and sodium MELD score are poor predictors of graft failure and mortality after liver transplantation. Hepatol Int. 2011; 5:841–9.7). Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS). 2010 Annual Data Report [Internet]. Seoul: KONOS;2011. [cited 2012 May 5]. Available from:. http://www.konos.go.kr.8). Kim MS, Kim SI, Kim YS. Current status of deceased donor organ recovery and sharing in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008; 51:685–91.
Article9). Joo DJ, Kim MS, Kim SI, Jeon KO, Huh KH, Choi GH, et al. Severity of end-stage liver disease in liver transplant candidate; comparison of KONOS status with MELD score. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2012; 26:112–9.
Article10). Hong G, Lee KW, Suh SW, Yoo T, Kim H, Park MS, et al. The model for end-stage liver disease score-based system predicts short term mortality better than the current Child-Turcotte-Pugh score-based allocation system during waiting for deceased liver transplantation. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:1207–12.
Article11). Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS). 2012 Annual Data Report [Internet]. Seoul: KONOS;2012. [cited 2013 Nov 5]. Available from:. http://www.konos.go.kr.12). Institute of Medicine (U.S.). Analysis of waiting times. Committee on Organ Procurement and Transplantation Policy, Institute of Medicine (U.S.). Organ procurement and transplantation: assessing current policies and the potential impact of the DHHS final rule. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press;1999. p. 57–9.13). Said A, Williams J, Holden J, Remington P, Gangnon R, Musat A, et al. Model for end stage liver disease score predicts mortality across a broad spectrum of liver disease. J Hepatol. 2004; 40:897–903.
Article14). Freeman RB Jr, Wiesner RH, Harper A, McDiarmid SV, Lake J, Edwards E, et al. The new liver allocation system: moving toward evidence-based transplantation policy. Liver Transpl. 2002; 8:851–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Modification of Emergency Status in Deceased Donor Liver Allocation: Evidence for Korean Model of End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) System
- Current Status of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation for Alcoholic Liver Disease in Korea in MELD Era
- Deceased donor liver transplantation under Korean MELD score-based liver allocation system at a high-volume transplantation center
- Experience of split liver transplantation from deceased marginal donor: eight adult recipients from four deceased donors
- Status and Current Problems in the Allocation System for Pediatric Liver Transplantation in Korea