J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Dec;26(12):1563-1568. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.12.1563.
Novel EGFR-TK Inhibitor EKB-569 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation by AKT and MAPK Pathways
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Research, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hoylim@skku.edu
- KMID: 1786011
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.12.1563
Abstract
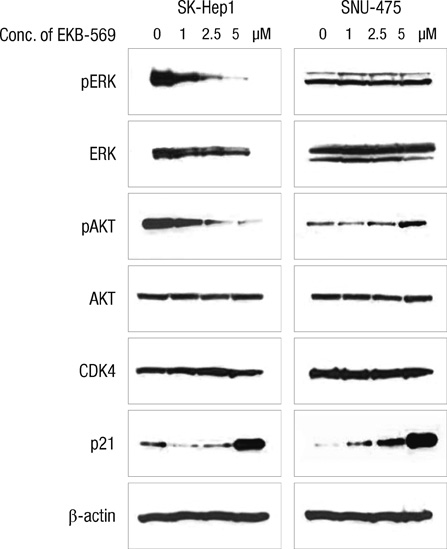
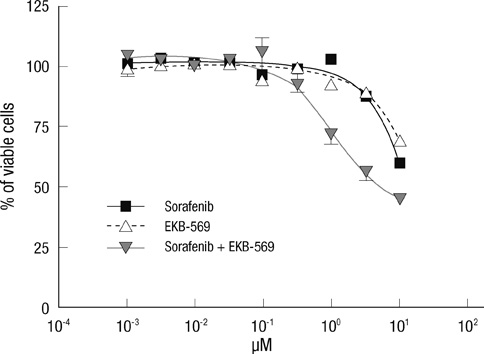
- Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted therapies have been effective in some cancers, but not in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The aim of this study was to investigate the drug potential to overcome multi-drug resistance in HCC cells. Thirteen drug-sensitive HCC cells were assessed using the CCK-8 assay. G0-G1 arrest was measured by FACS. Western blot analysis was used to detect the key enzymes in both the Ras/Raf and PI3K pathways. When establishing the IC50 of HCC to several drugs, including EKB-569, sorafenib, erlotinib, gefitinib, pazopanib, and brivanib, SK-Hep1 cells treated with EKB-569 have shown the highest (72.8%-86.4%) G0-G1 arrest and decreased the phosphorylation of AKT and ERK at the protein level. We found that EKB-569 had higher efficacy in HCC, compared to first generation, reversible EGFR-TK inhibitors. Furthermore, the combination of sorafenib and EKB-569 showed a synergistic effect to inhibit proliferation of SNU-475, previously the most resistant cell to EGFR-TKIs. Therefore, novel EKB-569 in combination with sorafenib may be able to overcome HCC resistance to EGFR-TK inhibitors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aminoquinolines/*pharmacology
Aniline Compounds/*pharmacology
Antineoplastic Agents/*pharmacology
Antineoplastic Combined Chemotherapy Protocols/pharmacology
Benzenesulfonates/pharmacology
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular/*drug therapy/pathology
Cell Cycle Checkpoints/drug effects
Cell Line, Tumor
Cell Proliferation/drug effects
Drug Resistance, Neoplasm
Drug Synergism
Humans
Liver Neoplasms/drug therapy/pathology
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases/*metabolism
Phosphorylation
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-akt/*metabolism
Pyridines/pharmacology
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor/*antagonists & inhibitors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Online analysis. GLOBOCAN 2008. accessed on 26 Oct 2011. Available at http://globocan.iarc.fr/.2. Related statistics. Korean National Cancer Center. accessed on 1 April 2011. Available at http://www.ncc.re.kr.3. Strumberg D. Preclinical and clinical development of the oral multikinase inhibitor sorafenib in cancer treatment. Drugs Today (Barc). 2005. 41:773–784.4. Sze KM, Wong KL, Chu GK, Lee JM, Yau TO, Oi-Lin Ng I. Loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog enhances cell invasion and migration through AKT/Sp-1 transcription factor/matrix metalloproteinase 2 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma and has clinicopathologic significance. Hepatology. 2011. 53:1558–1569.5. Minguez B, Tovar V, Chiang D, Villanueva A, Llovet JM. Pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma and molecular therapies. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009. 25:186–194.6. Chaparro M, González Moreno L, Trapero-Marugán M, Medina J, Moreno-Otero R. Pharmacological therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with sorafenib and other oral agents. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008. 28:1269–1277.7. Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, Liu J, Wang J, Tak WY, Pan H, Burock K, Zou J, Voliotis D, Guan Z. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009. 10:25–34.8. Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S, Amadori D, Santoro A, Figer A, De Greve J, Douillard JY, Lathia C, Schwartz B, Taylor I, Moscovici M, Saltz LB. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:4293–4300.9. Bhide RS, Cai ZW, Zhang YZ, Qian L, Wei D, Barbosa S, Lombardo LJ, Borzilleri RM, Zheng X, Wu LI, Barrish JC, Kim SH, Leavitt K, Mathur A, Leith L, Chao S, Wautlet B, Mortillo S, Jeyaseelan R Sr, Kukral D, Hunt JT, Kamath A, Fura A, Vyas V, Marathe P, D'Arienzo C, Derbin G, Fargnoli J. Discovery and preclinical studies of (R)-1-(4-(4-fluoro-2-methyl-1H-indol-5-yloxy)-5-methylpyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4] triazin-6-yloxy)propan-2-ol(BMS-540215), an in vivo active potent VEGFR-2 inhibitor. J Med Chem. 2006. 49:2143–2146.10. Huynh H, Ngo VC, Fargnoli J, Ayers M, Soo KC, Koong HN, Thng CH, Ong HS, Chung A, Chow P, Pollock P, Byron S, Tran E. Brivanib alaninate, a dual inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, induces growth inhibition in mouse models of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. 14:6146–6153.11. Zhu XD, Zhang JB, Fan PL, Xiong YQ, Zhuang PY, Zhang W, Xu HX, Gao DM, Kong LQ, Wang L, Wu WZ, Tang ZY, Ding H, Sun HC. Antiangiogenic effects of pazopanib in xenograft hepatocellular carcinoma models: evaluation by quantitative contrast enhanced ultrasonography. BMC Cancer. 2011. 11:28.12. Mendelsohn J. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2002. 20:1S–13S.13. Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ Jr, Prager D, Belani CP, Schiller JH, Kelly K, Spiridonidis H, Sandler A, Albain KS, Cella D, Wolf MK, Averbuch SD, Ochs JJ, Kay AC. Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2003. 290:2149–2158.14. Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, Campos D, Maoleekoonpiroj S, Smylie M, Martins R, van Kooten M, Dediu M, Findlay B, Tu D, Johnston D, Bezjak A, Clark G, Santabárbara P, Seymour L. National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:123–132.15. Thomas MB, Chadha R, Glover K, Wang X, Morris J, Brown T, Rashid A, Dancey J, Abbruzzese JL. Phase 2 study of erlotinib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2007. 110:1059–1067.16. Philip PA, Mahoney MR, Allmer C, Thomas J, Pitot HC, Kim G, Donehower RC, Fitch T, Picus J, Erlichman C. Phase II study of Erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with advanced hepatocellular cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:6657–6663.17. Wissner A, Overbeek E, Reich MF, Floyd MB, Johnson BD, Mamuya N, Rosfjord EC, Discafani C, Davis R, Shi X, Rabindran SK, Gruber BC, Ye F, Hallett WA, Nilakantan R, Shen R, Wang YF, Greenberger LM, Tsou HR. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 6,7-disubstituted 4-anilinoquinoline-3-carbonitriles. The design of an orally active, irreversible inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER-2). J Med Chem. 2003. 46:49–63.18. Ganne-Carrié N, Trinchet JC. Systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. 16:275–281.19. Herr I, Schemmer P, Buchler MW. On the TRAIL to therapeutic intervention in liver disease. Hepatology. 2007. 46:266–274.20. Ivanchuk SM, Rutka JT. The cell cycle: accelerators, brakes, and checkpoints. Neurosurgery. 2004. 54:692–699.21. Massagué J. G1 cell cycle control and cancer. Nature. 2004. 432:298–306.22. Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, Lindeman N, Gale CM, Zhao X, Christensen J, Kosaka T, Holmes AJ, Rogers AM, Cappuzzo F, Mok T, Lee C, Johnson BE, Cantley LC, Jänne PA. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007. 316:1039–1043.23. Desbois-Mouthon C, Cacheux W, Blivet-Van Eggelpoël MJ, Barbu V, Fartoux L, Poupon R, Housset C, Rosmorduc O. Impact of IGF-1R/EGFR cross-talks on hepatoma cell sensitivity to gefitinib. Int J Cancer. 2006. 119:2557–2566.24. García JM, Silva J, Peña C, Garcia V, Rodríguez R, Cruz MA, Cantos B, Provencio M, España P, Bonilla F. Promoter methylation of the PTEN gene is a common molecular change in breast cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2004. 41:117–124.25. Wang X, Trotman LC, Koppie T, Alimonti A, Chen Z, Gao Z, Wang J, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Cordon-Cardo C, Pandolfi PP, Jiang X. NEDD4-1 is a proto-oncogenic ubiquitin ligase for PTEN. Cell. 2007. 128:129–139.26. Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Yan H, Gazdar A, Powell SM, Riggins GJ, Willson JK, Markowitz S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science. 2004. 304:554.27. Rouleau E, Spyratos F, Dieumegard B, Guinebretière JM, Lidereau R, Bièche I. KRAS mutation status in colorectal cancer to predict response to EGFR targeted therapies: the need for a more precise definition. Br J Cancer. 2008. 99:2100.28. Su MC, Lien HC, Jeng YM. Absence of epidermal growth factor receptor exon 18-21 mutation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2005. 224:117–121.29. Lee SC, Lim SG, Soo R, Hsieh WS, Guo JY, Putti T, Tao Q, Soong R, Goh BC. Lack of somatic mutations in EGFR tyrosine kinase domain in hepatocellular and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2006. 16:73–74.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anti-proliferative Effect of 15,16-Dihydrotanshinone I Through Cell Cycle Arrest and the Regulation of AMP-activated Protein Kinase/Akt/mTOR and Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
- Could HBx Protein Expression Affect Signal Pathway Inhibition by Gefitinib or Selumetinib, a MEK Inhibitor, in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines?
- Combination Therapy of the Active KRAS-Targeting Antibody inRas37 and a PI3K Inhibitor in Pancreatic Cancer
- Growth inhibition in head and neck cancer cell lines by gefitinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- IQGAP1 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation by Akt activation