J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Sep;22(Suppl):S52-S60. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.S.S52.
Combinational Treatment with Retinoic Acid Derivatives in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma In Vitro
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Brain Korea 21 Program for Biomedical Sciences, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yhk0215@korea.ac.kr
- 2Genomic Research Center for Lung and Breast/Ovarian Cancers, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Milton Academy, Milton, Massachusetts, U.S.A.
- KMID: 1785789
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.S.S52
Abstract
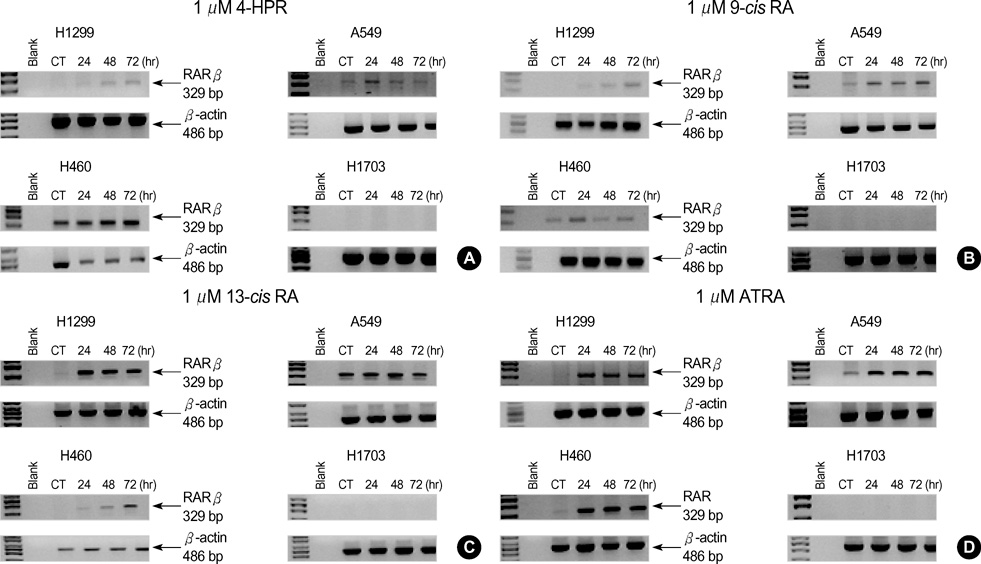
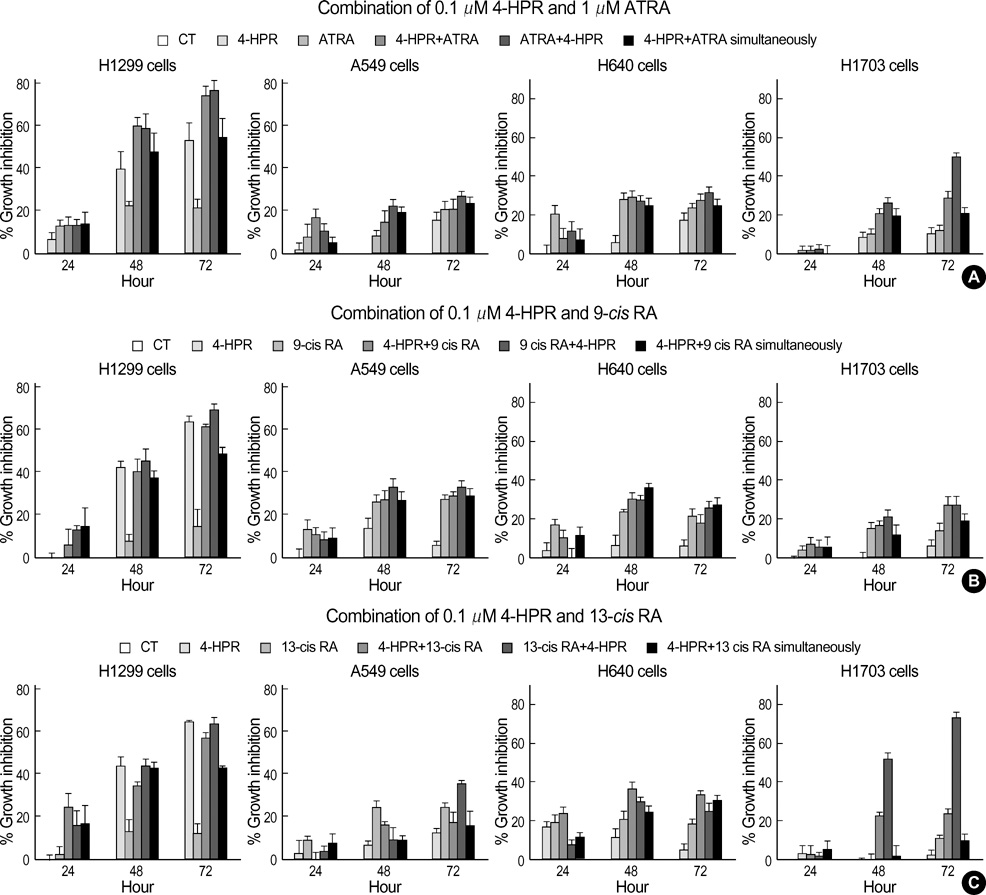
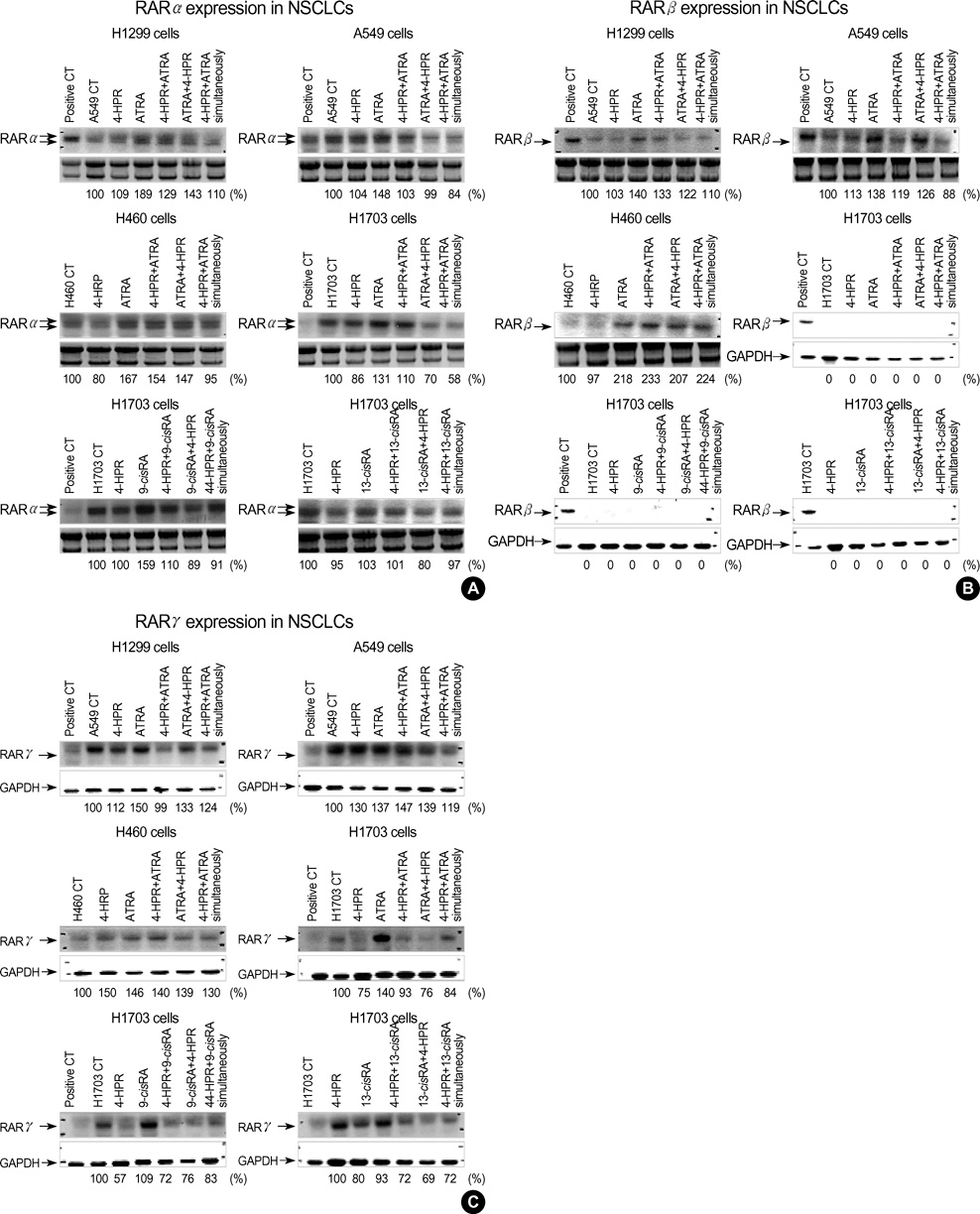
- The growth inhibitory effects of four retinoic acid (RA) derivatives, 9-cis RA, 13-cis RA, N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide (4-HPR), and all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) were compared. In addition, the effects of various combinations of these four agents were examined on non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) cell-lines, and on the expressions of retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and retinoid X receptors (RXRs) on these cells. At the clinically achievable concentration of 1 micrometer, only 4-HPR inhibited the growths of H1299 and H460 cells-lines. However, retinoic acid receptor beta(RAR beta) expression was up-regulated on H460 and H1299 cells treated with 1 micrometer of ATRA, 13-cis RA, or 9-cis RA. All NSCLC cell lines showed growth inhibition when exposed sequentially to 1 micrometer ATRA and 0.1 micrometer 4-HPR. In particular, sequential treatment with 1 micrometer ATRA or 13-cis RA and 4-HPR markedly inhibited H1703 cell growth; these cells exhibited no basal RAR beta expression and were refractory to 4-HPR. However, in NSCLC cell lines that expressed RAR beta, the expressional levels of RAR beta were up-regulated by ATRA alone and by sequential treatment with ATRA and 4-HPR. 4-HPR was found to be the most active of the four agents in terms of NSCLC growth-inhibition. Moreover, sequential treatments with ATRA or 13-cis RA followed by 4-HPR were found to have synergistic growth-inhibitory effects and to regulate RAR expression.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Base Sequence
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung/*drug therapy/genetics/metabolism
Cell Line, Tumor
DNA Primers/genetics
Drug Therapy, Combination
Fenretinide/administration & dosage
Gene Expression/drug effects
Humans
Isotretinoin/administration & dosage
Lung Neoplasms/*drug therapy/genetics/metabolism
Receptors, Retinoic Acid/genetics
Retinoid X Receptors/genetics
Tretinoin/administration & dosage/*analogs & derivatives
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lotan R. Retinoids as modulators of tumor cells invasion and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 1991. 2:197–208.2. Hofmann SL. Retinoids--"differentiation agents" for cancer treatment and prevention. Am J Med Sci. 1992. 304:202–213.
Article3. McBurney MW, Costa S, Pratt MA. Retinoids and cancer: a basis for differentiation therapy. Cancer Invest. 1993. 11:590–598.
Article4. Fanjul AN, Delia D, Pierotti MA, Rideout D, Yu JQ, Pfahl M. 4-Hydroxyphenyl retinamide is a highly selective activator of retinoid receptors. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:22441–22446.
Article5. Lokshin A, Zhang H, Mayotte J, Lokshin M, Levitt ML. Early effects of retinoic acid on proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 1999. 19:5251–5254.6. Treat J, Friedland D, Luginbuhl W, Meehan L, Gorman G, Miller W Jr, Bavaria J, Kaiser L. Phase II trial of all-trans retinoic acid in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Invest. 1996. 14:415–420.
Article7. Lippman SM, Hong WK. 13-cis-retinoic acid and cancer chemoprevention. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1992. 111–115.8. Lippman SM, Lee JJ, Karp DD, Vokes EE, Benner SE, Goodman GE, Khuri FR, Marks R, Winn RJ, Fry W, Graziano SL, Gandara DR, Okawara G, Woodhouse CL, Williams B, Perez C, Kim HW, Lotan R, Roth JA, Hong WK. Randomized phase III intergroup trial of isotretinoin to prevent second primary tumors in stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001. 93:605–618.
Article9. Heyman RA, Mangelsdorf DJ, Dyck JA, Stein RB, Eichele G, Evans RM, Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992. 68:397–406.
Article10. Mernitz H, Smith DE, Zhu AX, Wang XD. 9-cis-Retinoic acid inhibition of lung carcinogenesis in the A/J mouse model is accompanied by increased expression of RAR-beta but no change in cyclooxygenase-2. Cancer Lett. 2006. 244:101–108.11. Kurie JM, Lotan R, Lee JJ, Lee JS, Morice RC, Liu DD, Xu XC, Khuri FR, Ro JY, Hittelman WN, Walsh GL, Roth JA, Minna JD, Hong WK. Treatment of former smokers with 9-cis-retinoic acid reverses loss of retinoic acid receptor-beta expression in the bronchial epithelium: results from a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003. 95:206–214.12. Ohlmann CH, Jung C, Jaques G. Is growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in lung cancer cell lines by fenretinide [N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide] sufficient for cancer therapy? Int J Cancer. 2002. 100:520–526.
Article13. Sabichi AL, Xu H, Fischer S, Zou C, Yang X, Steele VE, Kelloff GJ, Lotan R, Clifford JL. Retinoid receptor-dependent and independent biological activities of novel fenretinide analogues and metabolites. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. 9:4606–4613.14. Um SJ, Lee SY, Kim EJ, Han HS, Koh YM, Hong KJ, Sin HS, Park JS. Antiproliferative mechanism of retinoid derivatives in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2001. 174:127–134.
Article15. Supino R, Crosti M, Clerici M, Warlters A, Cleris L, Zunino F, Formelli F. Induction of apoptosis by fenretinide (4HPR) in human ovarian carcinoma cells and its association with retinoic acid receptor expression. Int J Cancer. 1996. 65:491–497.
Article16. Kim HJ, Chakravarti N, Oridate N, Choe C, Claret FX, Lotan R. N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced apoptosis triggered by reactive oxygen species is mediated by activation of MAPKs in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2006. 25:2785–2794.
Article17. Sun SY, Li W, Yue P, Lippman SM, Hong WK, Lotan R. Mediation of N-(4-hydoxyphenyl)retinamide-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells by different mechanisms. Cancer Res. 1999. 59:2493–2498.18. Zou CP, Kurie JM, Lotan D, Zou CC, Hong WK, Lotan R. Higher potency of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide than all-trans-retinoic acid in induction of apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 1998. 4:1345–1355.19. Garaventa A, Luksch R, Lo Piccolo MS, Cavadini E, Montaldo PG, Pizzitola MR, Boni L, Ponzoni M, Decensi A, De Bernardi B, Bellani FF, Formelli F. Phase I trial and pharmacokinetics of fenretinide in children with neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. 9:2032–2039.20. Budman DR, Calabro A. Studies of synergistic and antagonistic combinations of conventional cytotoxic agents with the multiple eicosanoid pathway modulator LY 293111. Anticancer Drugs. 2004. 15:877–881.
Article21. De Luca LM. Retinoids and their receptors in differentiation, embryogenesis, and neoplasia. FASEB J. 1991. 5:2924–2933.
Article22. Khuri FR, Cohen V. Molecularly targeted approaches to the chemoprevention of lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:4249s–4253s.
Article23. Hong WK, Lippman SM, Itri LM, Karp DD, Lee JS, Byers RM, Schantz SP, Kramer AM, Lotan R, Peters LJ, Dimerg IW, Brown BW, Goepfert H. Prevention of second primary tumors with isotretinoin in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 1990. 323:795–801.
Article24. Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995. 83:841–850.
Article25. Delia D, Aiello A, Formelli F, Fontanella E, Costa A, Miyashita T, Reed JC, Pierotti MA. Regulation of apoptosis induced by the retinoid N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide and effect of deregulated bcl-2. Blood. 1995. 85:359–367.
Article26. Pellegrini R, Mariotti A, Tagliabue E, Bressan R, Bunone G, Coradini D, Della Valle G, Formelli F, Cleris L, Radice P, Pierotti MA, Colnaghi MI, Ménard S. Modulation of markers associated with tumor aggressiveness in human breast cancer cell lines by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide. Cell Growth Differ. 1995. 6:863–869.27. Kurie JM, Lee JS, Khuri FR, Mao L, Morice RC, Lee JJ, Walsh GL, Broxson A, Lippman SM, Ro JY, Kemp BL, Liu D, Fritsche HA, Xu X, Lotan R, Hong WK. N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide in the chemoprevention of squamous metaplasia and dysplasia of the bronchial epithelium. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. 6:2973–2979.28. Sun SY, Yue P, Lotan R. Induction of apoptosis by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide and its association with reactive oxygen species, nuclear retinoic acid receptors, and apoptosis-related genes in human prostate carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1999. 55:403–410.29. Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ. Cellular response to oxidative stress: signaling for suicide and survival. J Cell Physiol. 2002. 192:1–15.
Article30. Holven KB, Natarajan V, Gundersen TE, Moskaug JO, Norum KR, Blomhoff R. Secretion of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide-retinolbinding protein from liver parenchymal cells: evidence for reduced affinity of the complex for transthyretin. Int J Cancer. 1997. 71:654–659.
Article31. Lim SJ, Gutierrez-Puente Y, Tari AM. N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-retinamide selectively increases All-TRANS retinoic acid inhibitory effects in HER2/NEU-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2002. 23:279–286.32. Formelli F, Cleris L. Therapeutic effects of the combination of fenretinide and all-trans-retinoic acid and of the two retinoids with cisplatin in a human ovarian carcinoma xenograft and in a cisplatinresistant sub-line. Eur J Cancer. 2000. 36:2411–2419.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple primary lung cancer: Synchronous small cell lung carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
- Effect of Retinoic Acid on Proliferation and Invasiveness of PC-3 and DU-145,Hormone Resistant Prostatic Cancer Cell Lines
- CT findings of mediastinal lymph node metastasis in bronchogenic carcinoma of the lung: A comparative study of small cell carcinoma vs non-small cell carcinoma
- The Effect of Retinoids in Medulloblastoma Cell Culture
- Druggable Targets of Squamous Cell Lung Cancer