J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Dec;22(6):987-992. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.6.987.
Interferon-Stimulated Genes Response in Endothelial Cells Following Hantaan Virus Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Applied Microbiology, College of Natural Resources, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea. hspark@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1785758
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.6.987
Abstract
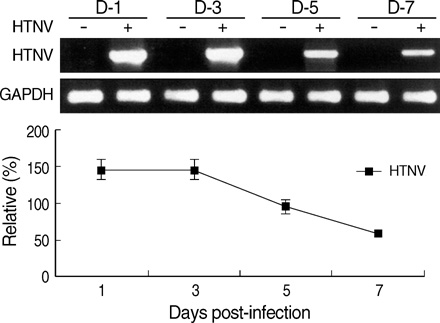
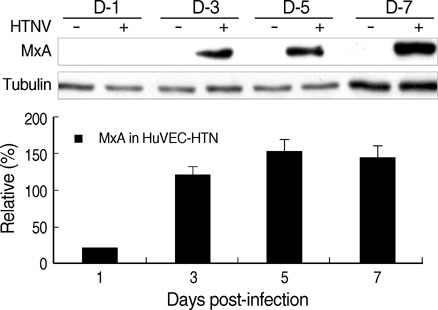
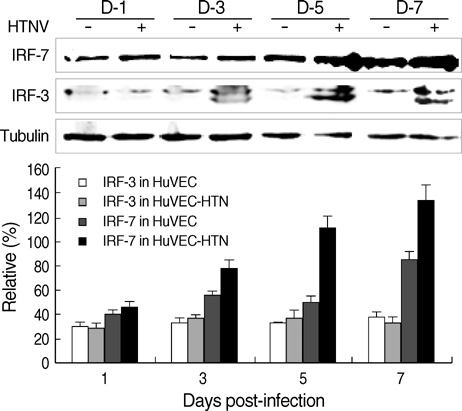
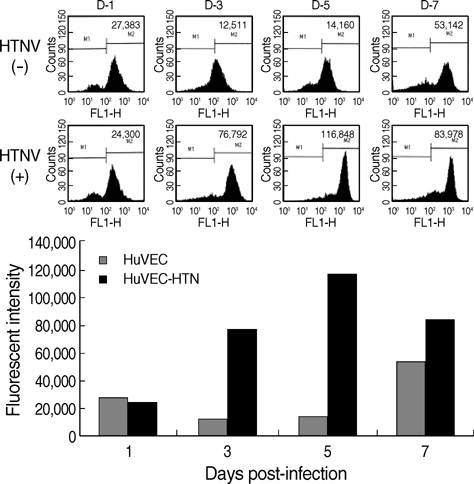
- The regulation mechanism of interferon (IFN) and IFN-stimulated genes is a very complex procedure and is dependent on cell types and virus species. We observed molecular changes related to anti-viral responses in endothelial cells during Hantaan virus (HTNV) infection. We found that there are two patterns of gene expression, the first pattern of gene expression being characterized by early induction and short action, as in that of type I IFNs,' and the other being characterized by delayed induction and long duration, as those of IRF-7, MxA, and TAP-1/2. Even though there are significant differences in their induction folds, we found that all of IFN-alpha/beta , IRF- 3/7, MxA, and TAP-1/2 mRNA expressions reached the peak when the viral replication was most active, which took place 3 days of post infection (d.p.i.). In addition, an interesting phenomenon was observed; only one gene was highly expressed in paired genes such as IFN-alpha/beta??(3/277-folds), IRF-3/7 (2.2/29.4-folds), and TAP- 1/2 (26.2/6.1-folds). Therefore, IFN-beta, IRF-7, and TAP-1 seem to be more important for the anti-viral response in HTNV infection. MxA was increased to 296-folds at 3 d.p.i. and kept continuing 207-folds until 7 d.p.i.. The above results indicate that IFN-beta works for an early anti-viral response, while IRF7, MxA, and TAP-1 work for prolonged anti-viral response in HTNV infection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters/*genetics
Blotting, Western
Cells, Cultured
Endothelial Cells/metabolism/*virology
GTP-Binding Proteins/*genetics
*Gene Expression Regulation
Hantaan virus/*immunology
Histocompatibility Antigens Class I/analysis
Humans
Interferon Regulatory Factor-3/genetics
Interferon Regulatory Factor-7/*genetics
Interferons/*genetics
RNA, Messenger/analysis
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sen GC. Viruses and interferons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001. 55:255–281.
Article2. Sato M, Suemori H, Hata N, Asagiri M, Ogasawara K, Nakao K, Nakaya T, Katsuki M, Noguchi S, Tanaka N, Taniguchi T. Distinct and essential roles of transcription factors IRF-3 and IRF-7 in response to viruses for IFN-α/β gene induction. Immunity. 2000. 13:539–548.
Article3. Marie I, Durbin JE, Levy DE. Differential viral induction of distinct Interferon-α gene by positive feedback through Interferon Regulatory Factor-7. EMBO J. 1998. 17:6660–6669.4. Izaguirre A, Barnes BJ, Amrute S, Yeow WS, Megjugorac N, Dai J, Feng D, Chung E, Pitha PM, Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P. Comparative analysis of IRF and IFN-alpha expression in human plasmacytoid and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2003. 74:1125–1138.
Article5. Prakash A, Levy DE. Regulation of IRF7 through cell type-specific protein stability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. 342:50–56.
Article6. Honda K, Yanai H, Negishi H, Asagiri M, Sato M, Mizutani T, Shimada N, Ohba Y, Takaoka A, Yoshida N, Taniguchi T. IRF-7 is the master regulator of type-I interferon-dependent immune responses. Nature. 2005. 434:772–777.
Article7. Prakash A, Smith E, Lee CK, Levy DE. Tissue-specific positive feedback requirements for production of type I interferon following virus infection. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280:18651–18657.
Article8. Schmaljohn CS, Hasty SE, Harrison SA, Dalrymple JM. Characterization of Hantaan virus, the prototype virus of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1983. 148:1005–1012.9. Linderholm M, Elgh F. Clinical characteristics of hantavirus infections on the Eurasian continent. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001. 256:135–151.
Article10. Nichol ST, Spiropoulou CF, Morzunov S, Rollin PE, Ksiazek TG, Feldmann H, Sanchez A, Childs J, Zaki S, Peters CJ. Genetic identification of a hantavirus associated with an outbreak of acute respiratory illness. Science. 1993. 262:914–917.
Article11. Kanerva M, Melen K, Vaheri A, Julkunen I. Inhibition of Puumala and Tula hantaviruses in Vero cells by MxA protein. Virology. 1996. 224:55–62.
Article12. Alff PJ, Gavrilovskaya IN, Gorbunova E, Endriss K, Chong Y, Geimonen E, Sen N, Reich NC, Mackow ER. The pathogenic NY-1 hantavirus G1 cytoplasmic tail inhibits RIG-I- and TBK-1-directed interferon responses. J Virol. 2006. 80:9676–9686.
Article13. Haller O, Frese M, Kochs G. Mx proteins: mediators of innate resistance to RNA viruses. Rev Sci Tech. 1998. 17:220–230.
Article14. Staeheli P, Pitossi F, Pavlovic J. Mx proteins: GTPases with antiviral activity. Trends Cell Biol. 1993. 3:268–272.
Article15. Makela S, Mustonen J, Ala-Houhala I, Hurme M, Partanen J, Vapalahti O, Vaheri A, Pasternack A. Human leukocyte antigen-B8-DR3 is a more important risk factor for severe Puumala hantavirus infection than the tumor necrosis factor-alpha(-308) G/A polymorphism. J Infect Dis. 2002. 186:843–846.16. Mustonen J, Partanen J, Kanerva M, Pietila K, Vapalahti O, Pasternack A, Vaheri A. Genetic susceptibility to severe course of nephropathia epidemica caused by Puumala hantavirus. Kidney Int. 1996. 49:217–221.
Article17. Lankat-Buttgereit B, Tampe R. The transporter associated with antigen processing: function and implications in human diseases. Physiol Rev. 2002. 82:187–204.
Article18. Raftery MJ, Kraus AA, Ulrich R, Kruger DH, Schonrich G. Hantavirus infection of Dendritic cells. J Virol. 2002. 76:10724–10733.
Article19. Yoneyama M, Suhara W, Fukuhara Y, Fukuda M, Nishida E, Fujita T. Direct triggering of the type I interferon system by virus infection: activationof a transcription factor complex containing IRF-3 and CBP/p300. EMBO J. 1998. 17:1087–1095.20. Frese M, Kochs G, Feldmann H, Hertkorn C, Haller O. Inhibition of bunyaviruses, phleboviruses, and hantaviruses by human MxA protein. J Virol. 1996. 70:915–923.
Article21. Haller O, Kochs G. Interferon-induced Mx proteins: dynamin-like GTPases with antiviral activity. Traffic. 2002. 3:710–717.
Article22. Lin R, Heylbroeck C, Pitha PM, Hiscott J. Virus-dependent phosphorylation of the IRF-3 transactivation potential, and proteasome-mediated degradation. Mol Cell biol. 1998. 18:2986–2996.23. Momburg F, Mullbacher A, Lobigs M. Modulation of transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP)-mediated peptide import into the endoplasmic reticulum by flavivirus infection. J Virol. 2001. 75:5663–5671.
Article24. Cecil AA, Klemsz MJ. p38 activation through Toll-like receptors modulates IFN-gamma-induced expression of the Tap-1 gene only in macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 2004. 75:560–568.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Infected by Hantaan Virus
- Procoagulant activity observed in human umbilical vein endothelial cell line cells infected with Hantaan virus
- Effects of Hantaan Virus and IFN-gammaon Induction of Surface ICAM-1 in Primary Cultured Buman Nasal Epithelial Cells and Human Lung Fibroblasts
- IFN-γ: A Crucial Player in the Fight Against HBV Infection?
- Expression of ICAM-1 on the Hantaan virus-infected human umbilical vein endothelial cells