Evaluation of the correlation between insertion torque and primary stability of dental implants using a block bone test
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. periokoo@snu.ac.kr
- 2Implant R&D Center, Osstem Implant Co., Busan, Korea.
- 3Dental Clinic, Healthcare System Gangnam Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1783675
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.1.30
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Implant stability at the time of surgery is crucial for the long-term success of dental implants. Primary stability is considered of paramount importance to achieve osseointegration. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the correlation between the insertion torque and primary stability of dental implants using artificial bone blocks with different bone densities and compositions to mimic different circumstances that are encountered in routine daily clinical settings.
METHODS
In order to validate the objectives, various sized holes were made in bone blocks with different bone densities (#10, #20, #30, #40, and #50) using a surgical drill and insertion torque together with implant stability quotient (ISQ) values that were measured using the Osstell Mentor. The experimental groups under evaluation were subdivided into 5 subgroups according to the circumstances.
RESULTS
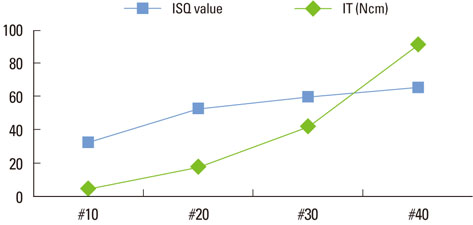
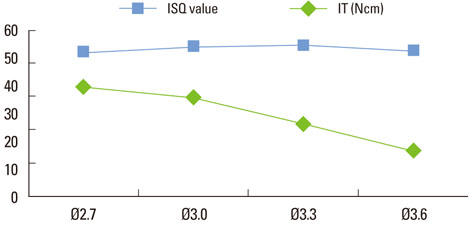
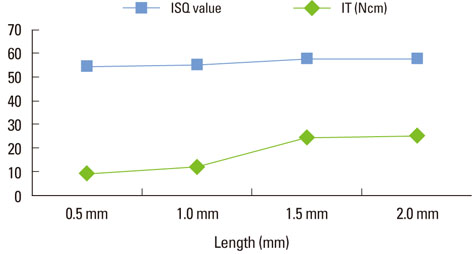
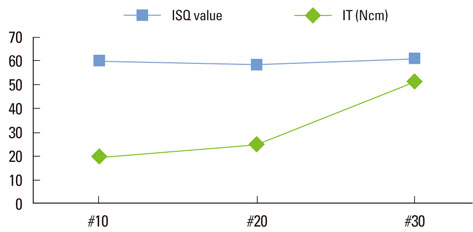
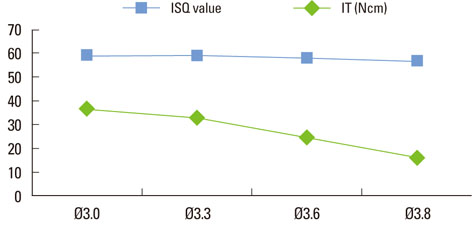
In group 1, the mean insertion torque and ISQ values increased as the density of the bone blocks increased. For group 2, the mean insertion torque values decreased as the final drill size expanded, but this was not the case for the ISQ values. The mean insertion torque values in group 3 increased with the thickness of the cortical bone, and the same was true for the ISQ values. For group 4, the mean insertion torque values increased as the cancellous bone density increased, but the correlation with the ISQ values was weak. Finally, in group 5, the mean insertion torque decreased as the final drill size increased, but the correlation with the ISQ value was weak.
CONCLUSIONS
Within the limitations of the study, it was concluded that primary stability does not simply depend on the insertion torque, but also on the bone quality.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Bone cement grafting increases implant primary stability in circumferential cortical bone defects
Seung-Yun Shin, Seung-Il Shin, Seung-Beom Kye, Seok-Woo Chang, Jongrak Hong, Jun-Young Paeng, Seung-Min Yang
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2015;45(1):30-35. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2015.45.1.30.The effects of bone density and crestal cortical bone thickness on micromotion and peri-implant bone strain distribution in an immediately loaded implant: a nonlinear finite element analysis
Tsutomu Sugiura, Kazuhiko Yamamoto, Satoshi Horita, Kazuhiro Murakami, Sadami Tsutsumi, Tadaaki Kirita
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016;46(3):152-165. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2016.46.3.152.Effects of implant tilting and the loading direction on the displacement and micromotion of immediately loaded implants: an in vitro experiment and finite element analysis
Tsutomu Sugiura, Kazuhiko Yamamoto, Satoshi Horita, Kazuhiro Murakami, Sadami Tsutsumi, Tadaaki Kirita
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2017;47(4):251-262. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2017.47.4.251.
Reference
-
1. Degidi M, Daprile G, Piattelli A, Iezzi G. Development of a new implant primary stability parameter: insertion torque revisited. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2011; 10. 18. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2011.00392.x.
Article2. Dilek O, Tezulas E, Dincel M. Required minimum primary stability and torque values for immediate loading of mini dental implants: an experimental study in nonviable bovine femoral bone. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008; 105:e20–e27.
Article3. Stacchi C, Vercellotti T, Torelli L, Furlan F, Di Lenarda R. Changes in implant stability using different site preparation techniques: twist drills versus piezosurgery: a single-blinded, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2011; 04. 19. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2011.00341.x.
Article4. Nedir R, Bischof M, Szmukler-Moncler S, Bernard JP, Samson J. Predicting osseointegration by means of implant primary stability. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004; 15:520–528.
Article5. Isoda K, Ayukawa Y, Tsukiyama Y, Sogo M, Matsushita Y, Koyano K. Relationship between the bone density estimated by cone-beam computed tomography and the primary stability of dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23:832–836.
Article6. Bilhan H, Geckili O, Mumcu E, Bozdag E, Sunbuloglu E, Kutay O. Influence of surgical technique, implant shape and diameter on the primary stability in cancellous bone. J Oral Rehabil. 2010; 37:900–907.
Article7. Esposito M, Hirsch JM, Lekholm U, Thomsen P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (II). Etiopathogenesis. Eur J Oral Sci. 1998; 106:721–764.
Article8. Degidi M, Daprile G, Piattelli A. Primary stability determination by means of insertion torque and RFA in a sample of 4,135 implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2010; 09. 17. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2010.00302.x.
Article9. Degidi M, Perrotti V, Strocchi R, Piattelli A, Iezzi G. Is insertion torque correlated to bone-implant contact percentage in the early healing period? A histological and histomorphometrical evaluation of 17 human-retrieved dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:778–781.
Article10. Tabassum A, Meijer GJ, Wolke JG, Jansen JA. Influence of surgical technique and surface roughness on the primary stability of an implant in artificial bone with different cortical thickness: a laboratory study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010; 21:213–220.
Article11. Turkyilmaz I. A comparison between insertion torque and resonance frequency in the assessment of torque capacity and primary stability of Brånemark system implants. J Oral Rehabil. 2006; 33:754–759.
Article12. Kahraman S, Bal BT, Asar NV, Turkyilmaz I, Tozum TF. Clinical study on the insertion torque and wireless resonance frequency analysis in the assessment of torque capacity and stability of self-tapping dental implants. J Oral Rehabil. 2009; 36:755–761.
Article13. Roze J, Babu S, Saffarzadeh A, Gayet-Delacroix M, Hoornaert A, Layrolle P. Correlating implant stability to bone structure. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:1140–1145.
Article14. Huang HM, Lee SY, Yeh CY, Lin CT. Resonance frequency assessment of dental implant stability with various bone qualities: a numerical approach. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002; 13:65–74.
Article15. Hong J, Lim YJ, Park SO. Quantitative biomechanical analysis of the influence of the cortical bone and implant length on primary stability. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23:1193–1197.
Article16. Dos Santos MV, Elias CN, Cavalcanti Lima JH. The effects of superficial roughness and design on the primary stability of dental implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2011; 13:215–223.
Article17. Bischof M, Nedir R, Szmukler-Moncler S, Bernard JP, Samson J. Implant stability measurement of delayed and immediately loaded implants during healing. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004; 15:529–539.
Article18. Trisi P, De Benedittis S, Perfetti G, Berardi D. Primary stability, insertion torque and bone density of cylindric implant ad modum Branemark: is there a relationship? An in vitro study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011; 22:567–570.
Article19. Moon SH, Um HS, Lee JK, Chang BS, Lee MK. The effect of implant shape and bone preparation on primary stability. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2010; 40:239–243.
Article20. Hsu JT, Fuh LJ, Tu MG, Li YF, Chen KT, Huang HL. The effects of cortical bone thickness and trabecular bone strength on noninvasive measures of the implant primary stability using synthetic bone models. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2011; 05. 20. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2011.00349.x.
Article21. Merheb J, Van Assche N, Coucke W, Jacobs R, Naert I, Quirynen M. Relationship between cortical bone thickness or computerized tomography-derived bone density values and implant stability. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010; 21:612–617.
Article22. Khayat PG, Arnal HM, Tourbah BI, Sennerby L. Clinical outcome of dental implants placed with high insertion torques (up to 176 Ncm). Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2011; 05. 20. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2011.00351.x.23. Molly L. Bone density and primary stability in implant therapy. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006; 17:Suppl 2. 124–135.
Article24. Sim CP, Lang NP. Factors influencing resonance frequency analysis assessed by Osstell mentor during implant tissue integration: I. Instrument positioning, bone structure, implant length. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010; 21:598–604.
Article25. Martinez H, Davarpanah M, Missika P, Celletti R, Lazzara R. Optimal implant stabilization in low density bone. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001; 12:423–432.
Article26. Katsoulis J, Avrampou M, Spycher C, Stipic M, Enkling N, Mericske-Stern R. Comparison of implant stability by means of resonance frequency analysis for flapless and conventionally inserted implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012; 14:915–923.
Article27. Ostman PO, Hellman M, Sennerby L. Direct implant loading in the edentulous maxilla using a bone density-adapted surgical protocol and primary implant stability criteria for inclusion. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2005; 7:Suppl 1. S60–S69.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of predictable stability test for assessment of optimum loading time in dental implant
- The effect of the thread depth on the mechanical properties of the dental implant
- A study on the correlation between implant stability values and initial insertion torque
- Differences in percussion-type measurements of implant stability according to height of healing abutments and measurement angle
- Effect of implant designs on insertion torque and implant stability quotient (ISQ) value