Improvement of osteogenic potential of biphasic calcium phosphate bone substitute coated with two concentrations of expressed recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Cowell R&D Institute, Cowell Medi, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Dental Biomaterials and Bioengineering, Research Institute of Dental Biomaterials and Bioengineering, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Dental Biomaterials, Institute of Biomaterials-Implant, Wonkwang University School of Dentistry, Iksan, Korea.
- 5Department of Periodontology, Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. kst72@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1783647
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.4.119
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to determine whether biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) bone substitute with two different concentrations of Escherichia coli-expressed recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 (ErhBMP-2) enhances new bone formation in a standardized rabbit sinus model and to evaluate the concentration-dependent effect of ErhBMP-2.
METHODS
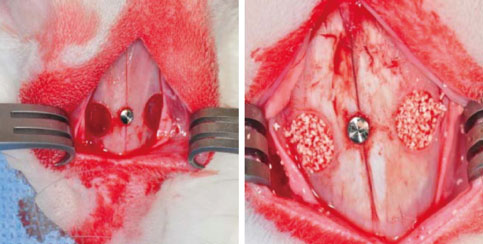
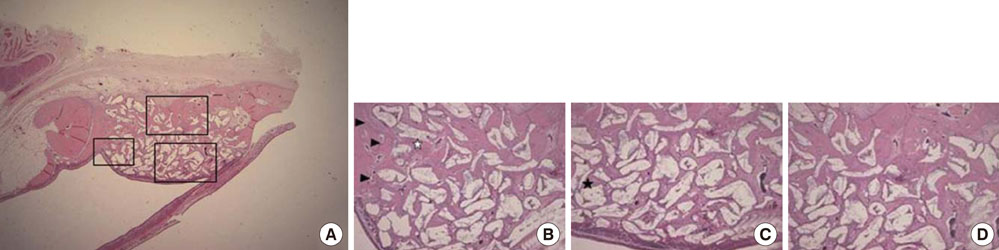
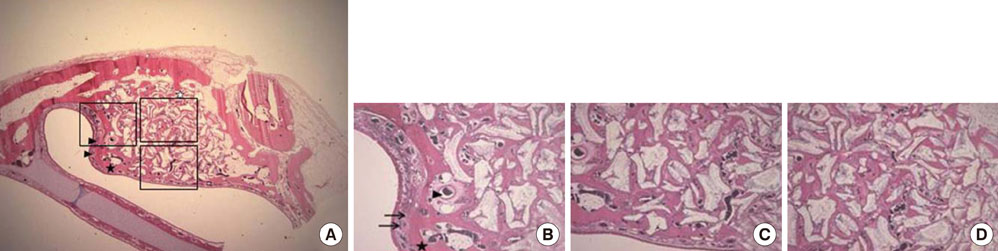
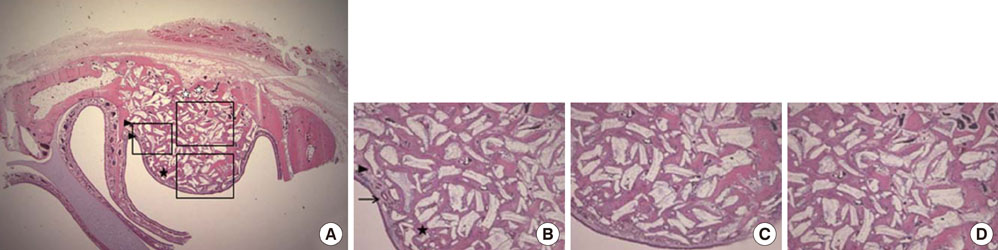
Standardized, 6-mm diameter defects were made bilaterally on the maxillary sinus of 20 male New Zealand white rabbits. Following removal of the circular bony windows and reflection of the sinus membrane, BCP bone substitute without coating (control group) was applied into one defect and BCP bone substitute coated with ErhBMP-2 (experimental group) was applied into the other defect for each rabbit. The experimental group was divided into 2 subgroups according to the concentration of ErhBMP-2 (0.05 and 0.5 mg/mL). The animals were allowed to heal for either 4 or 8 weeks and sections of the augmented sinus and surrounding bone were analyzed by microcomputed tomography and histologically.
RESULTS
Histologic analysis revealed signs of new bone formation in both the control and experimental groups with a statistically significant increase in bone formation in experimental group 1 (0.05 mg/mL ErhBMP-2 coating) after a 4-week healing period. However, no statistically significant difference was found between experimental group 1 and experimental group 2 (0.5 mg/mL ErhBMP-2 coating) in osteoinductive potential (P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
ErhBMP-2 administered using a BCP matrix significantly enhanced osteoinductive potential in a standardized rabbit sinus model. A concentration-dependent response was not found in the present study.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins
Bone Regeneration
Bone Substitutes
Calcium
Durapatite
Escherichia coli
Humans
Hydroxyapatites
Male
Maxillary Sinus
Membranes
Osteogenesis
Rabbits
X-Ray Microtomography
Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins
Bone Substitutes
Calcium
Durapatite
Hydroxyapatites
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Four-week histologic evaluation of grafted calvarial defects with adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen therapy in rats
Hyeyoon Chang, Seo-Eun Oh, Seunghan Oh, Kyung-Seok Hu, Sungtae Kim
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016;46(4):244-253. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2016.46.4.244.Improvement of the osteogenic potential of ErhBMP-2-/EGCG-coated biphasic calcium phosphate bone substitute: in vitro and in vivo activity
Jae-ho Hwang, Seunghan Oh, Sungtae Kim
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2019;49(2):114-126. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2019.49.2.114.Eight-week healing of grafted calvarial bone defects with hyperbaric oxygen therapy in rats
Seo-Eun Oh, Kyung-Seok Hu, Sungtae Kim
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2019;49(4):228-236. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2019.49.4.228.Adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen therapy for irradiated rat calvarial defects
Heesuk An, Jung-Tae Lee, Seo-Eun Oh, Kyeong-mee Park, Kyung-Seok Hu, Sungtae Kim, Moon-Kyu Chung
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2019;49(1):2-13. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2019.49.1.2.Biodegradable Screws Containing Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 in an Osteoporotic Rat Model
Eun-Sun Jin, Ji Yeon Kim, Bora Lee, JoongKee Min, Sang Ryong Jeon, Kyoung Hyo Choi, Je Hoon Jeong
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2018;61(5):559-567. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2017.0297.
Reference
-
1. Bessho K, Konishi Y, Kaihara S, Fujimura K, Okubo Y, Iizuka T. Bone induction by Escherichia coli-derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 compared with Chinese hamster ovary cell-derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000. 38:645–649.
Article2. Lee JH, Kim CS, Choi KH, Jung UW, Yun JH, Choi SH, et al. The induction of bone formation in rat calvarial defects and subcutaneous tissues by recombinant human BMP-2, produced in Escherichia coli. Biomaterials. 2010. 31:3512–3519.
Article3. Long S, Truong L, Bennett K, Phillips A, Wong-Staal F, Ma H. Expression, purification, and renaturation of bone morphogenetic protein-2 from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 2006. 46:374–378.
Article4. Vallejo LF, Brokelmann M, Marten S, Trappe S, Cabrera-Crespo J, Hoffmann A, et al. Renaturation and purification of bone morphogenetic protein-2 produced as inclusion bodies in high-cell-density cultures of recombinant Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol. 2002. 94:185–194.
Article5. Choi KH, Moon K, Kim SH, Yun JH, Jang KL, Cho KS. Purification and biological activity of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 produced by E. coli expression system. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 2008. 38:41–50.
Article6. Walker DH, Wright NM. Bone morphogenetic proteins and spinal fusion. Neurosurg Focus. 2002. 13:e3.
Article7. Wong DA, Kumar A, Jatana S, Ghiselli G, Wong K. Neurologic impairment from ectopic bone in the lumbar canal: a potential complication of off-label PLIF/TLIF use of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2). Spine J. 2008. 8:1011–1018.
Article8. Kaneko H, Arakawa T, Mano H, Kaneda T, Ogasawara A, Nakagawa M, et al. Direct stimulation of osteoclastic bone resorption by bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 and expression of BMP receptors in mature osteoclasts. Bone. 2000. 27:479–486.
Article9. Smucker JD, Rhee JM, Singh K, Yoon ST, Heller JG. Increased swelling complications associated with off-label usage of rhBMP-2 in the anterior cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006. 31:2813–2819.
Article10. Bae JH, Kim YK, Kim SG, Yun PY, Kim JS. Sinus bone graft using new alloplastic bone graft material (Osteon)-II: clinical evaluation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010. 109:e14–e20.
Article11. Kim S, Jung UW, Lee YK, Choi SH. Effects of biphasic calcium phosphate bone substitute on circumferential bone defects around dental implants in dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011. 26:265–273.12. Zhu X, Fan H, Li D, Xiao Y, Zhang X. Protein adsorption and zeta potentials of a biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic under various conditions. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2007. 82:65–73.
Article13. Truumees E, Herkowitz HN. Alternatives to autologous bone harvest in spine surgery. The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal. 1999. 12:77–88.14. Le Nihouannen D, Guehennec LL, Rouillon T, Pilet P, Bilban M, Layrolle P, et al. Micro-architecture of calcium phosphate granules and fibrin glue composites for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006. 27:2716–2722.
Article15. Le Nihouannen D, Saffarzadeh A, Gauthier O, Moreau F, Pilet P, Spaethe R, et al. Bone tissue formation in sheep muscles induced by a biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic and fibrin glue composite. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008. 19:667–675.
Article16. Choi Y, Yun JH, Kim CS, Choi SH, Chai JK, Jung UW. Sinus augmentation using absorbable collagen sponge loaded with Escherichia coli-expressed recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 in a standardized rabbit sinus model: a radiographic and histologic analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012. 23:682–689.
Article17. Jung JH, Yun JH, Um YJ, Jung UW, Kim CS, Choi SH, et al. Bone formation of Escherichia coli expressed rhBMP-2 on absorbable collagen block in rat calvarial defects. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011. 111:298–305.
Article18. Kim JW, Choi KH, Yun JH, Jung UW, Kim CS, Choi SH, et al. Bone formation of block and particulated biphasic calcium phosphate lyophilized with Escherichia coli-derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 in rat calvarial defects. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011. 112:298–306.
Article19. Park JC, So SS, Jung IH, Yun JH, Choi SH, Cho KS, et al. Induction of bone formation by Escherichia coli-expressed recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 using block-type macroporous biphasic calcium phosphate in orthotopic and ectopic rat models. J Periodontal Res. 2011. 46:682–690.
Article20. Asai S, Shimizu Y, Ooya K. Maxillary sinus augmentation model in rabbits: effect of occluded nasal ostium on new bone formation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002. 13:405–409.
Article21. Ijiri S, Yamamuro T, Nakamura T, Kotani S, Notoya K. Effect of sterilization on bone morphogenetic protein. J Orthop Res. 1994. 12:628–636.
Article22. Bravetti P, Membre H, Marchal L, Jankowski R. Histologic changes in the sinus membrane after maxillary sinus augmentation in goats. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998. 56:1170–1176.
Article23. Scala A, Botticelli D, Rangel IG Jr, de Oliveira JA, Okamoto R, Lang NP. Early healing after elevation of the maxillary sinus floor applying a lateral access: a histological study in monkeys. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010. 21:1320–1326.
Article24. Wang X, Mabrey JD, Agrawal CM. An interspecies comparison of bone fracture properties. Biomed Mater Eng. 1998. 8:1–9.25. De Souza Nunes LS, De Oliveira RV, Holgado LA, Nary Filho H, Ribeiro DA, Matsumoto MA. Immunoexpression of Cbfa-1/Runx2 and VEGF in sinus lift procedures using bone substitutes in rabbits. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010. 21:584–590.
Article26. Roberts EG, Breznak N. Mish CE, editor. Bone Physiology and Metabolism. Contemporary implant dentistry. 1994. Orlando: Mosby Year Book;557–598.27. Frenken JW, Bouwman WF, Bravenboer N, Zijderveld SA, Schulten EA, ten Bruggenkate CM. The use of straumann bone ceramic in a maxillary sinus floor elevation procedure: a clinical, radiological, histological and histomorphometric evaluation with a 6-month healing period. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010. 21:201–208.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Improvement of the osteogenic potential of ErhBMP-2-/EGCG-coated biphasic calcium phosphate bone substitute: in vitro and in vivo activity
- The Effect of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2/Macroporous Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Block system on Bone Formation in Rat Calvarial Defects
- Improvement of osteogenic potential of biphasic calcium phosphate bone substitute coated with synthetic cell binding peptide sequences
- Comparison of the Bone Union Rates Using a Local Autobone and Bone Graft Substitute Mixed Graft in Lumbar Posterolateral Fusion
- Bone Healing in Ovariectomized-rabbit Calvarial Defect with Tricalcium Phosphate Coated with Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Genetically Engineered in Escherichia coli