J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Oct;24(5):837-843. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.837.
Regulation of Type IV Collagen alpha Chains of Glomerular Epithelial Cells in Diabetic Conditions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. tsha@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pharmacology, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 1782003
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.837
Abstract
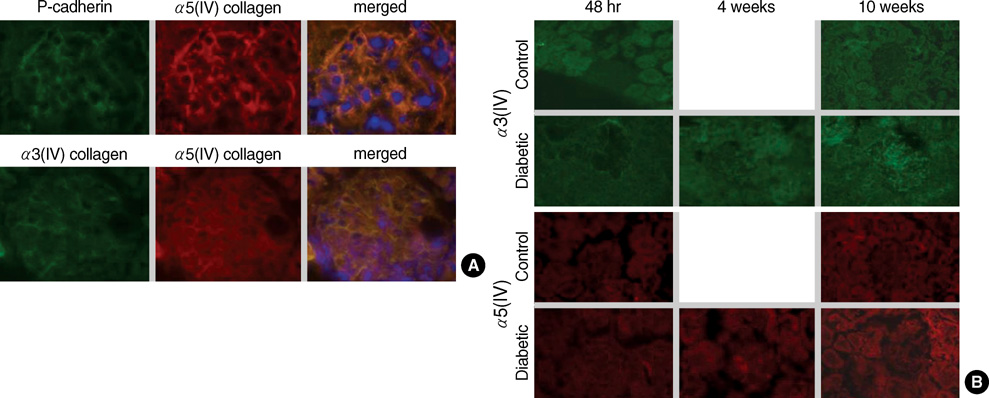
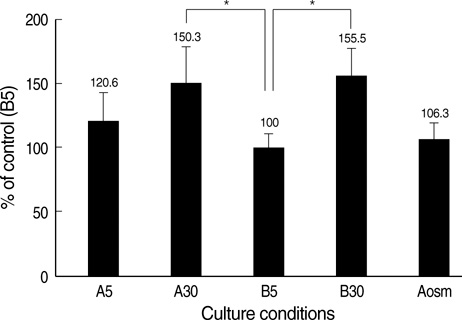
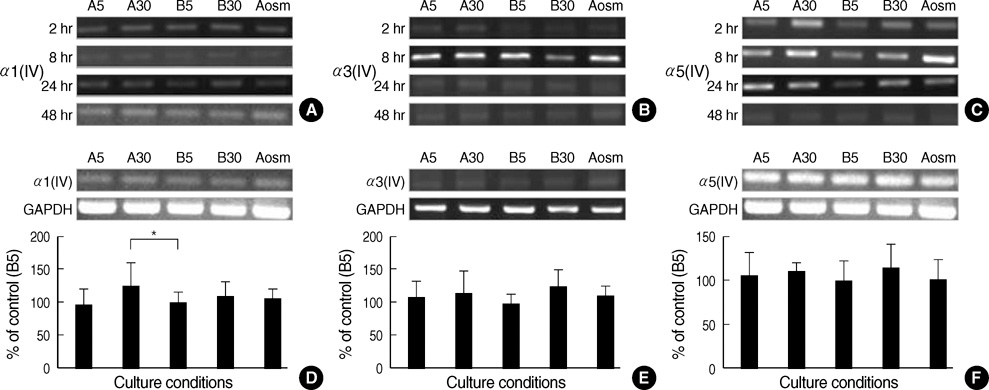
- An early feature of diabetic nephropathy is the alteration of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM), which may result in microalbuminuria, subsequent macroproteinuria, and eventual chronic renal failure. Although type IV collagen is the main component of thickened GBM in diabetic nephropathy, cellular metabolism of each alpha chains of type IV collagen has not been well studied. To investigate the regulation of alpha(IV) chains in diabetic conditions, we examined whether glucose and advanced glycosylation endproduct (AGE) regulate the metabolism of each alpha(IV) chains in the diabetic tissue and glomerular epithelial cells (GEpC). Glomerular collagen alpha3(IV) and alpha5(IV) chains protein were higher and more intense in immunofluorescence staining according to diabetic durations compared to controls. In vitro, mainly high glucose and partly AGE usually increased total collagen protein of GEpC by [3H]-proline incorporation assay and each alpha(IV) chain proteins including alpha1(IV), alpha3(IV), and alpha5(IV) in time-dependent and subchain-specific manners. However, the changes of each alpha(IV) chains mRNA expression was not well correlated to the those of each chain proteins. The present findings suggest that the metabolism of individual alpha(IV) chains of GBM is differentially regulated in diabetic conditions and those changes might be induced not only by transcriptional level but also by post-translational modifications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Cells, Cultured
Collagen Type IV/genetics/*metabolism/physiology
Diabetic Nephropathies/*metabolism
Epithelial Cells/*metabolism
Glomerular Basement Membrane/metabolism
Glucose/metabolism
Glycosylation End Products, Advanced/metabolism
Male
Podocytes/*metabolism
RNA, Messenger/metabolism
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sowers JR, Epstein M, Frohlich ED. Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: an update. Hypertension. 2001. 37:1053–1059.2. Sharma K, Ziyadeh FN. Hyperglycemia and diabetic kidney disease. The case for transforming growth factor-beta as a key mediator. Diabetes. 1995. 44:1139–1146.
Article3. Cooper ME. Pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Lancet. 1998. 352:213–219.
Article4. Ziyadeh FN, Sharma K, Ericksen M, Wolf G. Stimulation of collagen gene expression and protein synthesis in murine mesangial cells by high glucose is mediated by autocrine activation of transforming growth factor-beta. J Clin Invest. 1994. 93:536–542.
Article5. Hoffman B, Sharma K, Zhu Y, Ziyadeh FN. Transcriptional activation of transforming growth factor-beta1 in mesangial cell culture by high glucose concentration. Kidney Int. 1998. 54:1107–1116.6. Ziyadeh FN. The extracellular matrix in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993. 22:736–744.
Article7. Yurchenco PD, Smirnov S, Mathus T. Analysis of basement membrane self-assembly and cellular interactions with native and recombinant glycoproteins. Methods Cell Biol. 2002. 69:111–144.
Article8. Aumailley M, Gayraud B. Structure and biological activity of the extracellular matrix. J Mol Med. 1998. 76:253–265.
Article9. Miner JH. Renal basement membrane components. Kidney Int. 1999. 56:2016–2024.
Article10. Hostikka SL, Eddy RL, Byers MG, Hoyhtya M, Shows TB, Tryggvason K. Identification of a distinct type IV collagen alpha chain with restricted kidney distribution and assignment of its gene to the locus of X chromosome-linked Alport syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990. 87:1606–1610.
Article11. Hudson BG, Tryggvason K, Sundaramoorthy M, Neilson EG. Alport's syndrome, Goodpasture's syndrome, and type IV collagen. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:2543–2556.
Article12. Timpl R, Wiedemann H, van Delden V, Furthmayr H, Kuhn K. A network model for the organization of type IV collagen molecules in basement membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1981. 120:203–211.
Article13. Boutaud A, Borza DB, Bondar O, Gunwar S, Netzer KO, Singh N, Ninomiya Y, Sado Y, Noelken ME, Hudson BG. Type IV collagen of the glomerular basement membrane: evidence that the chain specificity of network assembly is encoded by the noncollagenous NC1 domains. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:30716–30724.14. Kreisberg JI, Hoover RL, Karnovsky MJ. Isolation and characterization of rat glomerular epithelial cells in vitro. Kidney Int. 1978. 14:21–30.
Article15. Ha TS, Song CJ, Lee JH. Effects of advanced glycosylation endproducts on perlecan core protein of glomerular epithelium. Pediatr Nephrol. 2004. 19:1219–1224.
Article16. Zhu D, Kim Y, Steffes MW, Groppoli TJ, Butkowski RJ, Mauer SM. Glomerular distribution of type IV collagen in diabetes by high resolution quantitative immunochemistry. Kidney Int. 1994. 45:425–433.
Article17. Wolf G, Chen S, Ziyadeh FN. From the periphery of the glomerular capillary wall toward the center of disease: podocyte injury comes of age in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2005. 54:1626–1634.
Article18. Isogai S, Mogami K, Shiina N, Yoshino G. Initial ultrastructural changes in pore size and anionic sites of the glomerular basement membrane in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and their prevention by insulin treatment. Nephron. 1999. 83:53–58.
Article19. Sharma K, Ziyadeh FN. Biochemical events and cytokine interactions linking glucose metabolism to the development of diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 1997. 17:80–92.20. White KE, Bilous RW. Diabiopsies Study Group. Structural alterations to the podocyte are related to proteinuria in type 2 diabetic patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004. 19:1437–1440.
Article21. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998. 352:837–853.22. Miner JH, Sanes JR. Collagen IV alpha 3, alpha 4, and alpha 5 chains in rodent basal laminae: sequence, distribution, association with laminins, and developmental switches. J Cell Biol. 1994. 127:879–891.
Article23. Miner JH. Developmental biology of glomerular basement membrane components. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1998. 7:13–19.24. Fukui M, Nakamura T, Ebihara I, Shirato I, Tomino Y, Koide H. ECM gene expression and its modulation by insulin in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1992. 41:1520–1527.
Article25. Kang SW, Natarajan R, Shahed A, Nast CC, LaPage J, Mundel P, Kashtan C, Adler SG. Role of 12-lipoxygenase in the stimulation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and collagen α5(IV) in experimental diabetic nephropathy and in glucose-stimulated podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003. 14:3178–3187.
Article26. Cohen MP, Lautenslager GT, Hud E, Shea E, Wang A, Chen S, Shearman CW. Inhibiting albumin glycation attenuates dysregulation of VEGFR-1 and collagen IV subchain production and the development of renal insufficiency. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007. 292:F789–F795.
Article27. Kim Y, Kleppel MM, Butkowski R, Mauer SM, Wieslander J, Michael AF. Differential expression of basement membrane collagen chains in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Pathol. 1991. 138:413–420.28. Yagame M, Kim Y, Zhu D, Suzuki D, Eguchi K, Nomoto Y, Sakai H, Groppoli T, Steffes MW, Mauer SM. Differential distribution of type IV collagen chains in patients with diabetic nephropathy in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nephron. 1995. 70:42–48.29. Bai Y, Wang L, Li Y, Liu S, Li J, Wang H, Huang H. High ambient glucose levels modulates the production of MMP-9 and α5(IV) collagen by cultured podocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2006. 17:57–68.30. Chen S, Lee JS, Iglesias-de la Cruz MC, Wang A, Izquierdo-Lahuerta A, Gandhi NK, Danesh FR, Wolf G, Ziyadeh FN. Angiotensin II stimulates α3(IV) collagen production in mouse podocytes via TGF-beta and VEGF signalling: implications for diabetic glomerulopathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005. 20:1320–1328.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Type IV Collagen mRNA Expression in Human Membranous Nephropathy
- Mechanism of Glomerular Basement Membrane Thickening in Human Membranous Nephropathy
- Extracellular Matrix of the Cultured Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- High glucose stimulates the expression of erythropoietin in rat glomerular epithelial cells
- Changes of Type IV Collagen and Laminin of Glomeruli in Vacor-induced Diabetic Rat