Yonsei Med J.
2014 Jan;55(1):107-112. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.107.
Clinical Characteristics of Primary Epstein Barr Virus Hepatitis with Elevation of Alkaline Phosphatase and gamma-Glutamyltransferase in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. pedkim@cnuh.co.kr
- KMID: 1779893
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.107
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the clinical characteristics of the primary Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) hepatitis with elevation of both serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and gamma-glutamyltransferase (gamma-GT) levels in children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
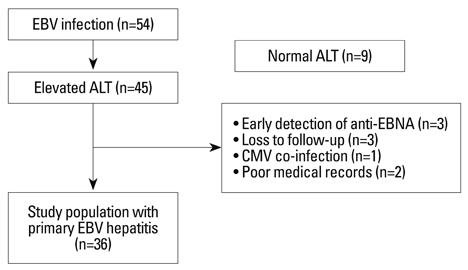
A retrospective study was performed by reviewing of the medical records of 36 patients who were diagnosed with primary EBV hepatitis. The patients were divided into 2 groups: patients with elevated serum ALP and gamma-GT levels (group 1) and patients without (group 2).
RESULTS
The classic features of infectious mononucleosis (fever, pharyngitis and/or tonsillitis, and cervical lymphadenitis) were seen in 20 (57.1%) of group 1 patients and 18 (50.0%) of group 2 patients. Hepatitis with elevated serum ALP and gamma-GT levels were present in 14 (38.9%) of the all patients. Of these patients, Jaundice occurred in only 2 (5.6%). The mean levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) as well as the number of patients with ALT greater than 400 IU/L were significantly different between the groups (177 IU/L vs. 94 IU/L, 418 IU/L vs. 115 IU/L, and 50.0% vs. 13.6%; p=0.001, p=0.001, p=0.026, respectively). The mean duration of elevated serum ALT levels was 17.5 days in group 1 and 9.0 days in group 2 (p=0.013). All patients recovered fully without any chronic or serious complications.
CONCLUSION
Primary EBV hepatitis with predominant biochemical abnormalities of the elevation of ALP and gamma-GT is frequent and mostly anicteric. This may represent a benign disease, but a delay in recovery of liver function as well.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sumaya CV, Ench Y. Epstein-Barr virus infectious mononucleosis in children. I. Clinical and general laboratory findings. Pediatrics. 1985; 75:1003–1010.2. Luzuriaga K, Sullivan JL. Infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:1993–2000.3. Straus SE, Cohen JI, Tosato G, Meier J. NIH conference. Epstein-Barr virus infections: biology, pathogenesis, and management. Ann Intern Med. 1993; 118:45–58.
Article4. Crum NF. Epstein Barr virus hepatitis: case series and review. South Med J. 2006; 99:544–547.
Article5. Shaw NJ, Evans JH. Liver failure and Epstein-Barr virus infection. Arch Dis Child. 1988; 63:432–433.
Article6. Feranchak AP, Tyson RW, Narkewicz MR, Karrer FM, Sokol RJ. Fulminant Epstein-Barr viral hepatitis: orthotopic liver transplantation and review of the literature. Liver Transpl Surg. 1998; 4:469–476.
Article7. Kofteridis DP, Koulentaki M, Valachis A, Christofaki M, Mazokopakis E, Papazoglou G, et al. Epstein Barr virus hepatitis. Eur J Intern Med. 2011; 22:73–76.
Article8. Vine LJ, Shepherd K, Hunter JG, Madden R, Thornton C, Ellis V, et al. Characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus hepatitis among patients with jaundice or acute hepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 36:16–21.
Article9. Finkel M, Parker GW, Fanselau HA. The Hepatitis of infectious mononucluosis: experience with 235 cases. Mil Med. 1964; 129:533–538.10. Horwitz CA, Burke MD, Grimes P, Tombers J. Hepatic function in mononucleosis induced by Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus. Clin Chem. 1980; 26:243–246.
Article11. Méndez-Sánchez N, Aguilar-Domínguez C, Chávez-Tapia NC, Uribe M. Hepatic manifestations of Epstein-Barr viral infection. Ann Hepatol. 2005; 4:205–209.
Article12. Hara S, Hoshino Y, Naitou T, Nagano K, Iwai M, Suzuki K, et al. Association of virus infected-T cell in severe hepatitis caused by primary Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Clin Virol. 2006; 35:250–256.
Article13. Hinedi TB, Koff RS. Cholestatic hepatitis induced by Epstein-Barr virus infection in an adult. Dig Dis Sci. 2003; 48:539–541.14. Chang JJ, Lewin SR. Immunopathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. Immunol Cell Biol. 2007; 85:16–23.
Article15. Rosen HR. Hepatitis C pathogenesis: mechanisms of viral clearance and liver injury. Liver Transpl. 2003; 9:S35–S43.
Article16. Kimura H, Nagasaka T, Hoshino Y, Hayashi N, Tanaka N, Xu JL, et al. Severe hepatitis caused by Epstein-Barr virus without infection of hepatocytes. Hum Pathol. 2001; 32:757–762.
Article17. Küsters S, Gantner F, Künstle G, Tiegs G. Interferon gamma plays a critical role in T cell-dependent liver injury in mice initiated by concanavalin A. Gastroenterology. 1996; 111:462–471.
Article18. Bradham CA, Plümpe J, Manns MP, Brenner DA, Trautwein C. Mechanisms of hepatic toxicity. I. TNF-induced liver injury. Am J Physiol. 1998; 275(3 Pt 1):G387–G392.19. Kondo T, Suda T, Fukuyama H, Adachi M, Nagata S. Essential roles of the Fas ligand in the development of hepatitis. Nat Med. 1997; 3:409–413.
Article20. Son KH, Shin MY. Clinical features of Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis in hospitalized Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2011; 54:409–413.
Article21. Yamada K, Yamada H. Gallbladder wall thickening in mononucleosis syndromes. J Clin Ultrasound. 2001; 29:322–325.
Article22. Lagona E, Sharifi F, Voutsioti A, Mavri A, Markouri M, Attilakos A. Epstein-Barr virus infectious mononucleosis associated with acute acalculous cholecystitis. Infection. 2007; 35:118–119.
Article23. Iaria C, Arena L, Di Maio G, Fracassi MG, Leonardi MS, Famulari C, et al. Acute acalculous cholecystitis during the course of primary Epstein-Barr virus infection: a new case and a review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis. 2008; 12:391–395.
Article24. Patriquin HB, DiPietro M, Barber FE, Teele RL. Sonography of thickened gallbladder wall: causes in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983; 141:57–60.
Article25. White NJ, Juel-Jensen BE. Infectious mononucleosis hepatitis. Semin Liver Dis. 1984; 4:301–306.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Autoimmune Cholangiopathy
- Several Cases of Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Hepatitis
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome with Ascites
- Epstein-Barr Virus Infection with Acute Pancreatitis Associated with Cholestatic Hepatitis
- A case of primary biliary cirrhosis associated with autoimmune primary hypothyroidism