J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Dec;28(12):1835-1838. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.12.1835.
A Case of Liver Fibrosis with Splenomegaly after Oxaliplatin-Based Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Colon Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. mhs1357@cnuh.co.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 1779429
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.12.1835
Abstract
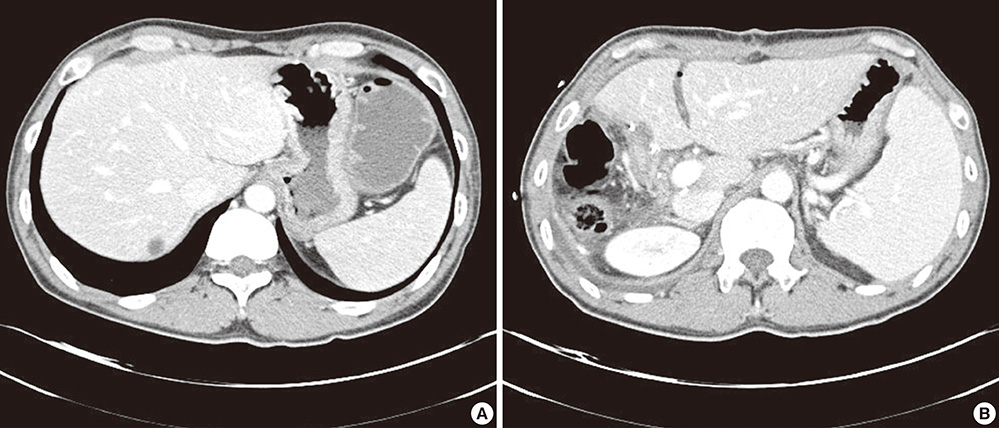
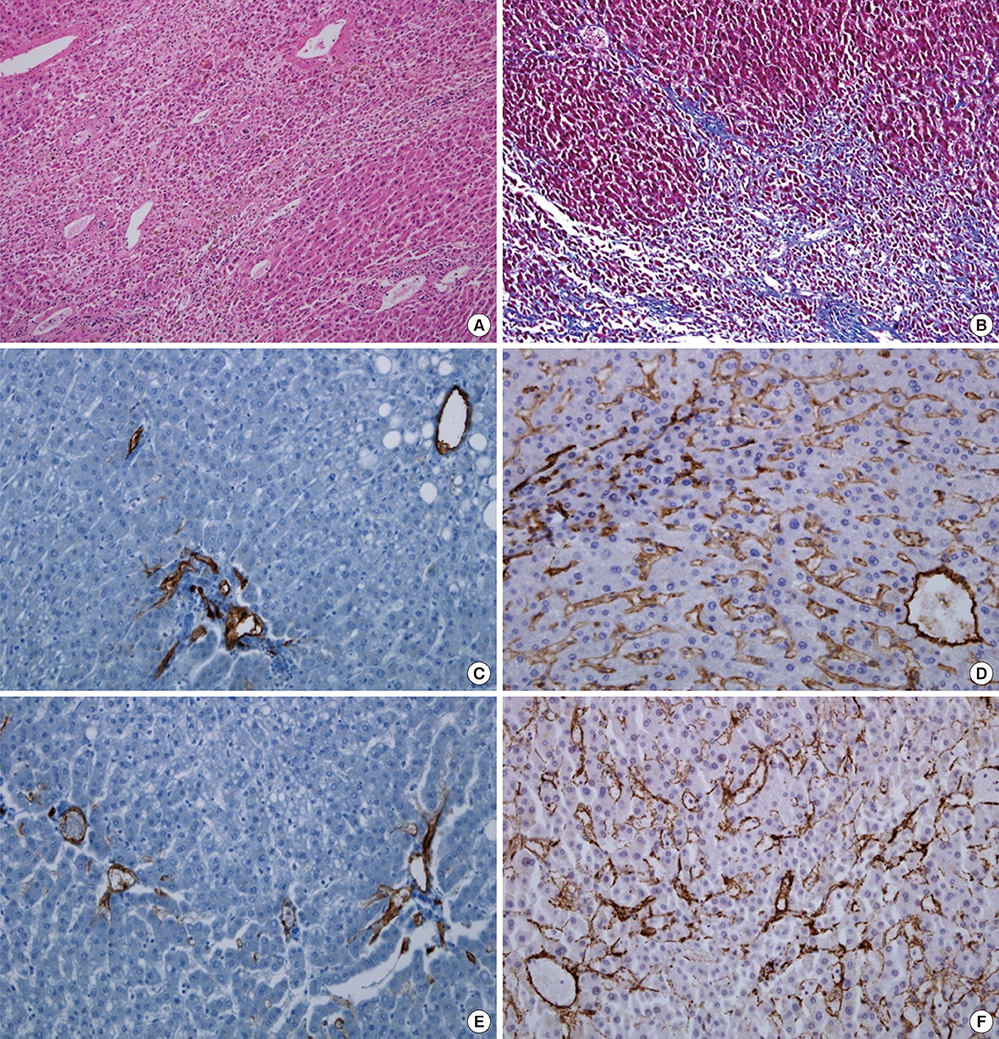
- Previous studies reported that oxaliplatin is associated with sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. However few reports on oxaliplatin induced liver fibrosis are found in the literature. Furthermore pathogenesis of liver fibrosis is not well known. We report a case of 45-yr-old Korean man in whom liver fibrosis with splenomegaly developed after 12 cycles of oxaliplatin based adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer (T4N2M0). Thorough history taking and serological examination revealed no evidence of chronic liver disease. Restaging CT scans demonstrated a good response to chemotherapy. Five month after chemotherapy, he underwent right hepatectomy due to isolated metastatic lesion. The liver parenchyma showed diffuse sinusoidal dilatation and centrilobular vein fibrosis with necrosis without steatosis. We could conclude that splenomegaly was due to perisinusoidal liver fibrosis and liver cell necrosis induced portal hypertension by oxaliplatin. In addition, to investigate the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis, immunohistochemical stains such as CD31 and alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) were conducted with control group. The immunohistochemical stains for CD31 and alpha-SMA were positive along the sinusoidal space in the patient, while negative in the control group. Chemotherapy with oxaliplatin induces liver fibrosis which should be kept in mind as a serious complication.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Actins/metabolism
Antigens, CD31/metabolism
Antineoplastic Combined Chemotherapy Protocols/*therapeutic use
Camptothecin/*analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Chemotherapy, Adjuvant
Colonic Neoplasms/*drug therapy
Fluorouracil/therapeutic use
Humans
Hypertension, Portal/etiology
Immunohistochemistry
Leucovorin/therapeutic use
Liver Cirrhosis/*diagnosis/etiology/pathology
Liver Neoplasms/secondary/surgery
Male
Middle Aged
Organoplatinum Compounds/*administration & dosage/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Splenomegaly/*diagnosis/etiology
Thrombocytopenia/etiology
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Actins
Antigens, CD31
Camptothecin
Fluorouracil
Leucovorin
Organoplatinum Compounds
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kandutsch S, Klinger M, Hacker S, Wrba F, Gruenberger B, Gruenberger T. Patterns of hepatotoxicity after chemotherapy for colorectal cancer liver metastases. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008; 34:1231–1236.2. Khan AZ, Morris-Stiff G, Makuuchi M. Patterns of chemotherapy-induced hepatic injury and their implications for patients undergoing liver resection for colorectal liver metastases. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2009; 16:137–144.3. Rubbia-Brandt L, Audard V, Sartoretti P, Roth AD, Brezault C, Le Charpentier M, Dousset B, Morel P, Soubrane O, Chaussade S, et al. Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004; 15:460–466.4. Kneuertz PJ, Maithel SK, Staley CA, Kooby DA. Chemotherapy-associated liver injury: impact on surgical management of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:181–190.5. Kooby DA, Fong Y, Suriawinata A, Gonen M, Allen PJ, Klimstra DS, DeMatteo RP, D'Angelica M, Blumgart LH, Jarnagin WR. Impact of steatosis on perioperative outcome following hepatic resection. J Gastrointest Surg. 2003; 7:1034–1044.6. Vauthey JN, Pawlik TM, Ribero D, Wu TT, Zorzi D, Hoff PM, Xiong HQ, Eng C, Lauwers GY, Mino-Kenudson M, et al. Chemotherapy regimen predicts steatohepatitis and an increase in 90-day mortality after surgery for hepatic colorectal metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2065–2072.7. Rubbia-Brandt L, Mentha G, Terris B. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome is a major feature of hepatic lesions associated with oxaliplatin neoadjuvant chemotherapy for liver colorectal metastases. J Am Coll Surg. 2006; 202:199–200.8. Mehta NN, Ravikumar R, Coldham CA, Buckels JA, Hubscher SG, Bramhall SR, Wigmore SJ, Mayer AD, Mirza DF. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on liver resection for colorectal liver metastases. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008; 34:782–786.9. Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Prunotto M, Desmoulière A, Varga J, De Wever O, Mareel M, Gabbiani G. Recent developments in myofibroblast biology: paradigms for connective tissue remodeling. Am J Pathol. 2012; 180:1340–1355.10. Terayama N, Terada T, Nakanuma Y. An immunohistochemical study of tumour vessels in metastatic liver cancers and the surrounding liver tissue. Histopathology. 1996; 29:37–43.11. Nakano H, Oussoultzoglou E, Rosso E, Casnedi S, Chenard-Neu MP, Dufour P, Bachellier P, Jaeck D. Sinusoidal injury increases morbidity after major hepatectomy in patients with colorectal liver metastases receiving preoperative chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 2008; 247:118–124.12. Slade JH, Alattar ML, Fogelman DR, Overman MJ, Agarwal A, Maru DM, Coulson RL, Charnsangavej C, Vauthey JN, Wolff RA, et al. Portal hypertension associated with oxaliplatin administration: clinical manifestations of hepatic sinusoidal injury. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2009; 8:225–230.13. White RR, Schwartz LH, Munoz JA, Raggio G, Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, D'Angelica MI, Kemeny NE. Assessing the optimal duration of chemotherapy in patients with colorectal liver metastases. J Surg Oncol. 2008; 97:601–604.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Portal Hypertension after the Treatment of Oxaliplatin Based Adjuvant-Chemotherapy for Rectal Cancer
- Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Colon Cancer
- Adjuvant oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy effect after treatment of colorectal hepatic metastasis
- Chemotherapy for Colorecal Cancer
- ERCC1 and the Prognosis for Patients With Colon Cancer Receiving Oxaliplatin-Based Adjuvant Chemotherapy