J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Apr;26(4):513-520. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.4.513.
VEGF as a Predictor for Response to Definitive Chemoradiotherapy and COX-2 as a Prognosticator for Survival in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. tknam@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1777881
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.4.513
Abstract
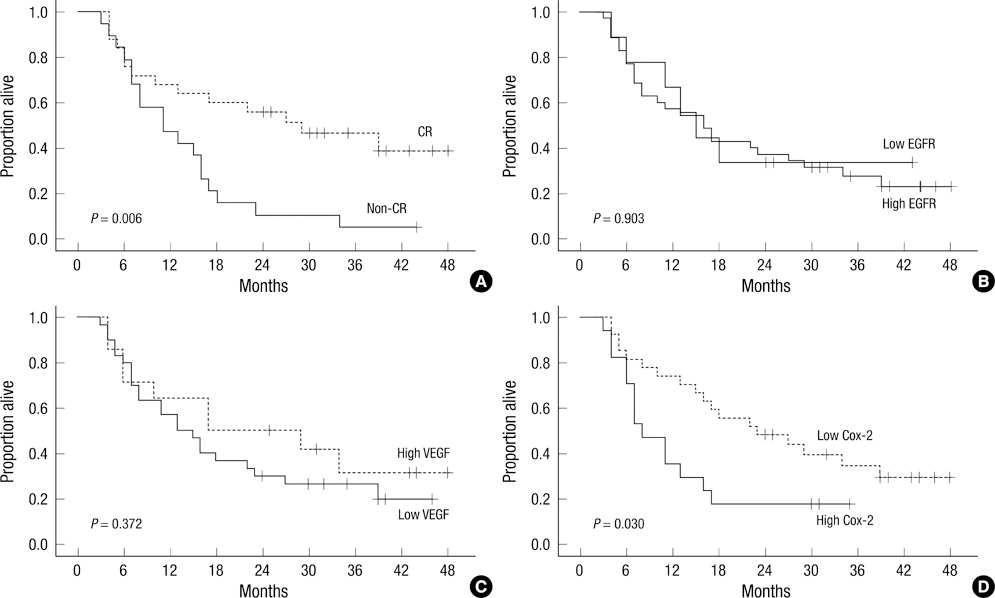
- We investigated the patterns of pretreatment expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) by immunohistochemical staining and determined their correlation with treatment response and survival in 44 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) treated with definitive concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT). The definitive CCRT consisted of a median dose of 54 Gy (range: 40.0-68.4 Gy) and two cycles of concurrent administration of mostly 5-fluorouracil + cisplatinum. High expression of EGFR, VEGF, and COX-2 was found in 79.5%, 31.8%, and 38.6%, respectively. The Cox regression analysis for overall survival (OS) showed that both the treatment response and COX-2 expression were significant. The 3-yr OS rates of patients that achieved a complete response and those that did not were 46.7% and 5.3%, respectively (P = 0.006). The logistic regression analysis for treatment response with various parameters showed that only a high expression of VEGF was significantly associated with a complete response. Unlike other well-known studies, higher expression of VEGF was significantly correlated with a complete response to CCRT in this study. However, higher expression of COX-2 was significantly associated with shorter survival. These results suggest that VEGF might be a predictive factor for treatment response and COX-2 a prognostic factor for OS in patients with ESCC after definitive CCRT.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Antineoplastic Agents/therapeutic use
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell/drug therapy/*mortality/radiotherapy/*therapy
Cisplatin/therapeutic use
Combined Modality Therapy
Cyclooxygenase 2/*metabolism
Drug Therapy, Combination
Esophageal Neoplasms/drug therapy/*mortality/radiotherapy/*therapy
Female
Fluorouracil/therapeutic use
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Male
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Staging
Predictive Value of Tests
Radiation Dosage
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor/metabolism
Regression Analysis
Survival Rate
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A/*metabolism
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008. 58:71–96.2. Araújo CM, Souhami L, Gil RA, Carvalho R, Garcia JA, Froimtchuk MJ, Pinto LH, Canary PC. A randomized trial comparing radiation therapy versus concomitant radiation therapy and chemotherapy in carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. Cancer. 1991. 67:2258–2261.3. al-Sarraf M, Martz K, Herskovic A, Leichman L, Brindle JS, Vaitkevicius VK, Cooper J, Byhardt R, Davis L, Emami B. Progress report of combined chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in patients with esophageal cancer: an intergroup study. J Clin Oncol. 1997. 15:277–284.4. Stahl M, Stuschke M, Lehmann N, Meyer HJ, Walz MK, Seeber S, Klump B, Budach W, Teichmann R, Schmitt M, Schmitt G, Franke C, Wilke H. Chemoradiation with and without surgery in patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:2310–2317.5. Bedenne L, Michel P, Bouché O, Milan C, Mariette C, Conroy T, Pezet D, Roullet B, Seitz JF, Herr JP, Paillot B, Arveux P, Bonnetain F, Binquet C. Chemoradiation followed by surgery compared with chemoradiation alone in squamous cancer of the esophagus: FFCD 9102. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:1160–1168.6. Nam TK, Lee JH, Cho SH, Chung IJ, Ahn SJ, Song JY, Yoon MS, Chung WK, Nah BS. Low hMLH1 expression prior to definitive chemoradiotherapy predicts poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2008. 260:109–117.7. Gotoh M, Takiuchi H, Kawabe S, Ohta S, Kii T, Kuwakado S, Katsu K. Epidermal growth factor receptor is a possible predictor of sensitivity to chemoradiotherapy in the primary lesion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2007. 37:652–657.8. Gibault L, Metges JP, Conan-Charlet V, Lozac'h P, Robaszkiewicz M, Bessaguet C, Lagarde N, Volant A. Diffuse EGFR staining is associated with reduced overall survival in locally advanced oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Br J Cancer. 2005. 93:107–115.9. Uchida S, Shimada Y, Watanabe G, Tanaka H, Shibagaki I, Miyahara T, Ishigami S, Imamura M. In oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with p53 mutation, advanced stage and poor prognosis. Br J Cancer. 1998. 77:1704–1709.10. Ogata Y, Fujita H, Yamana H, Sueyoshi S, Shirouzu K. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor as a prognostic factor in node-positive squamous cell carcinoma in the thoracic esophagus: long-term follow-up study. World J Surg. 2003. 27:584–589.11. Huang WZ, Fu JH, Wang DK, Hu Y, Liu MZ, Yang H, Feng YF, Zheng B, Wang G, Luo KJ, Wen J, Rong TH. Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with chemoradiotherapy resistance and prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. Dis Esophagus. 2008. 21:679–684.12. American Joint Committee on Cancer. Manual for staging of cancer. 2010. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott.13. Ali-Fehmi R, Che M, Khalifeh I, Malone JM, Morris R, Lawrence WD, Munkarah AR. The effect of cyclooxygenase-2 expression on tumor vascularity in advanced stage ovarian serous carcinoma. Cancer. 2003. 98:1423–1429.14. Shimada H, Hoshino T, Okazumi S, Matsubara H, Funami Y, Nabeya Y, Hayashi H, Takeda A, Shiratori T, Uno T, Ito H, Ochiai T. Expression of angiogenic factors predicts response to chemoradiotherapy and prognosis of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2002. 86:552–557.15. Shih CH, Ozawa S, Ando N, Ueda M, Kitajima M. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression predicts outcome and lymph node metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. 6:1161–1168.16. Rosa AR, Schirmer CC, Gurski RR, Meurer L, Edelweiss MI, Kruel CD. Prognostic value of p53 protein expression and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in resected squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Dis Esophagus. 2003. 16:112–118.17. Hironaka S, Hasebe T, Kamijo T, Ohtsu A, Boku N, Yoshida S, Saitoh H, Ochiai A. Biopsy specimen microvessel density is a useful prognostic marker in patients with T(2-4)M(0) esophageal cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. 8:124–130.18. Kii T, Takiuchi H, Kawabe S, Gotoh M, Ohta S, Tanaka T, Kuwakado S, Nishitani H, Katsu K. Evaluation of prognostic factors of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (stage II-III) after concurrent chemoradiotherapy using biopsy specimens. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2007. 37:583–589.19. Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ, Holash J. Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature. 2000. 407:242–248.20. Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:1011–1027.21. Murata R, Nishimura Y, Hiraoka M. An antiangiogenic agent (TNP-470) inhibited reoxygenation during fractionated radiotherapy of murine mammary carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997. 37:1107–1113.22. Ou G, Itasaka S, Zeng L, Shibuya K, Yi J, Harada H, Hiraoka M. Usefulness of HIF-1 imaging for determining optimal timing of combining bevacizumab and radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. 75:463–467.23. Inoue K, Ozeki Y, Suganuma T, Sugiura Y, Tanaka S. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in primary esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Association with angiogenesis and tumor progression. Cancer. 1997. 79:206–213.24. Nico B, Benagiano V, Mangieri D, Maruotti N, Vacca A, Ribatti D. Evaluation of microvascular density in tumors: pro and contra. Histol Histopathol. 2008. 23:601–607.25. Sato F, Shimada Y, Watanabe G, Uchida S, Makino T, Imamura M. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, matrix metalloproteinase-9 and E-cadherin in the process of lymph node metastasis in oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 1999. 80:1366–1372.26. Mukherjee T, Kumar A, Mathur M, Chattopadhyay TK, Ralhan R. Ets-1 and VEGF expression correlates with tumor angiogenesis, lymph node metastasis, and patient survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003. 129:430–436.27. Ahn MJ, Jang SJ, Park YW, Choi JH, Oh HS, Lee CB, Paik HK, Park CK. Clinical prognostic values of vascular endothelial growth factor, microvessel density, and p53 expression in esophageal carcinomas. J Korean Med Sci. 2002. 17:201–207.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pretreatment 18F‑FDG PET/CT‑Derived Parameters in Predicting Clinical Outcomes of Locally Advanced Upper Third Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma After Definitive Chemoradiation Therapy
- Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal Cancer
- Salvage Endoscopic Resection for Residual Lesion after Definitive Chemoradiotherapy in Esophageal Cancer
- Comparison of the Clinical Outcomes of Esophagectomy and Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Cutaneous Metastasis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mimicking Benign Soft Tissue Tumor