Yonsei Med J.
2009 Dec;50(6):818-824. 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.6.818.
Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression Is Related to the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Colon Cancers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea. taejung@mail.dongguk.ac.kr
- 2Department of General Surgery, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
- KMID: 1777097
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2009.50.6.818
Abstract
- PURPOSE
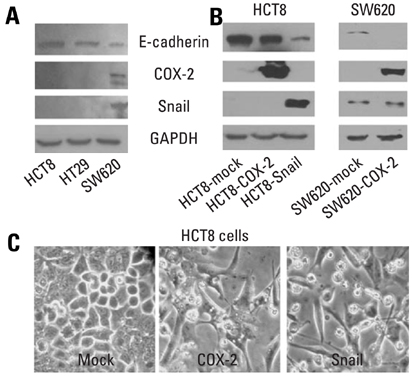
Down-regulation of E-cadherin is a hallmark of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). EMT progression in cancer cells is associated with the loss of certain epithelial markers and the acquisition of a mesenchymal phenotype, as well as migratory activities. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression is associated with tumor invasion and metastasis in colon cancer. This study investigated the relationship between E-cadherin and COX-2 in colon cancer cells and human colon tumors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Colon cancer cell lines and immunohistochemistry were used.
RESULTS
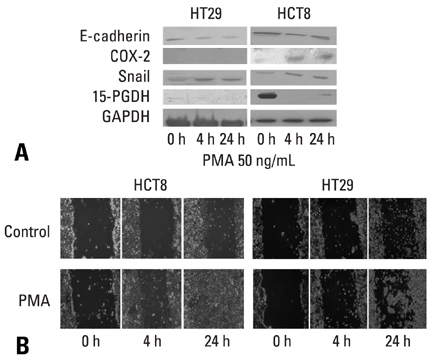
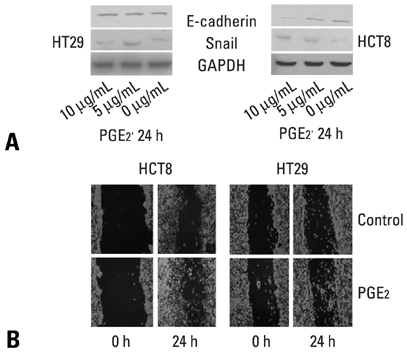
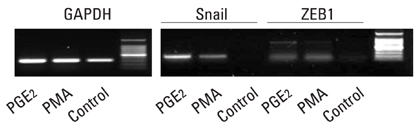
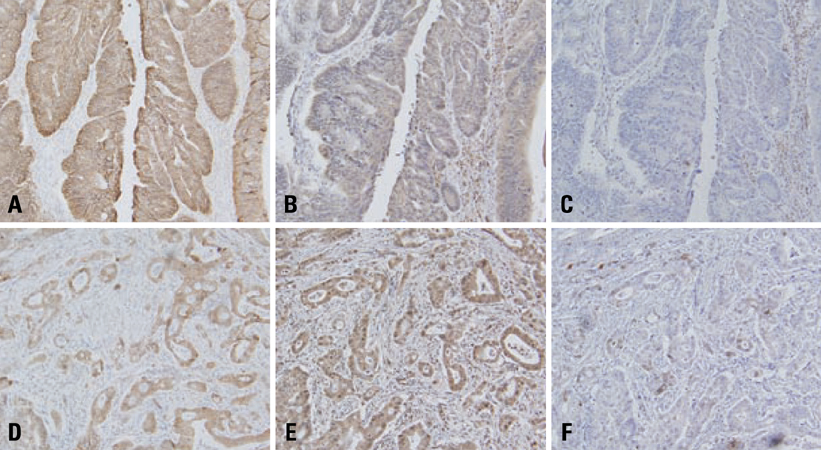
E-cadherin expression was inversely related to the expressions of COX-2 and Snail in colon cancer cells. Ectopic expression of COX-2 or Snail reduced E-cadherin and induced a scattered, flattened phenotype with few intercellular contacts in colon cancer cells. Treatment of cancer cells with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate increased the expressions of COX-2 and Snail, decreased 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase expression, and increased the cells' motility. In addition, exposure to prostaglandin E2 increased Snail expression and cell motility, and decreased E-cadherin expression. Membranous E-cadherin expression was lower in adenomas and cancers than in the adjacent, non-neoplastic epithelium. In contrast, the expressions of Snail and COX-2 were higher in cancers than in normal tissues and adenomas. The expressions of COX-2 and Snail increased in areas with abnormal E-cadherin expression. Moreover, COX-2 expression was related to higher tumor stages and was significantly higher in nodal metastatic lesions than primary cancers.
CONCLUSION
This study suggests that COX-2 may have a role in tumor metastasis via EMT.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Blotting, Western
Cadherins/genetics/metabolism
Cell Differentiation/genetics/physiology
Cell Line, Tumor
Cell Movement/drug effects/genetics
Colonic Neoplasms/*metabolism/*pathology
Cyclooxygenase 2/genetics/metabolism/*physiology
Dinoprostone/pharmacology
Epithelial Cells/*cytology/metabolism
Epithelium/*metabolism
Female
HT29 Cells
Homeodomain Proteins/genetics/metabolism
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Male
Mesoderm/*cytology/*metabolism
Middle Aged
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
Tetradecanoylphorbol Acetate/pharmacology
Transcription Factors/genetics/metabolism
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Role of Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition in the Gastroenterology
Sung Moo Kim, Joung-Ho Han, Seon Mee Park
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010;56(2):69-77. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2010.56.2.69.
Reference
-
1. Brown JR, DuBois RN. COX-2: a molecular target for colorectal cancer prevention. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:2840–2855.
Article2. Wang D, Dubois RN. Prostaglandins and cancer. Gut. 2006. 55:115–122.
Article3. Vleminckx K, Kemler R. Cadherins and tissue formation: integrating adhesion and signaling. Bioessays. 1999. 21:211–220.
Article4. Thiery JP. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002. 2:442–454.
Article5. Guarino M, Rubino B, Ballabio G. The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology. Pathology. 2007. 39:305–318.
Article6. Peinado H, Portillo F, Cano A. Transcriptional regulation of cadherins during development and carcinogenesis. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. 48:365–375.
Article7. Barrallo-Gimeno A, Nieto MA. The Snail genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: implications in development and cancer. Development. 2005. 132:3151–3161.
Article8. Tsujii M, DuBois RN. Alterations in cellular adhesion and apoptosis in epithelial cells overexpressing prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2. Cell. 1995. 83:493–501.
Article9. Dohadwala M, Yang SC, Luo J, Sharma S, Batra RK, Huang M, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent regulation of E-cadherin: prostaglandin E (2) induces transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and snail in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2006. 66:5338–5345.
Article10. Mann JR, Backlund MG, Buchanan FG, Daikoku T, Holla VR, Rosenberg DW, et al. Repression of prostaglandin dehydrogenase by epidermal growth factor and snail increases prostaglandin E2 and promotes cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2006. 66:6649–6656.
Article11. Barberà MJ, Puig I, Domínguez D, Julien-Grille S, Guaita-Esteruelas S, Peiró S, et al. Regulation of Snail transcription during epithelial to mesenchymal transition of tumor cells. Oncogene. 2004. 23:7345–7354.
Article12. Bellovin DI, Bates RC, Muzikansky A, Rimm DL, Mercurio AM. Altered localization of p120 catenin during epithelial to mesenchymal transition of colon carcinoma is prognostic for aggressive disease. Cancer Res. 2005. 65:10938–10945.
Article13. Hirohashi S. Inactivation of the E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion system in human cancer. Am J Pathol. 1998. 153:333–339.
Article14. Noda M, Tatsumi Y, Tomizawa M, Takama T, Mitsufuji S, Sugihara H, et al. Effects of etodolac, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on the expression of E-cadherin-catenin complexes in gastrointestinal cell lines. J Gastroenterol. 2002. 37:896–904.
Article15. Chang YW, Marlin JW, Chance TW, Jakobi R. RhoA mediates cyclooxygenase-2 signaling to disrupt the formation of adherens junctions and increase cell motility. Cancer Res. 2006. 66:11700–11708.
Article16. Jungck M, Grünhage F, Spengler U, Dernac A, Mathiak M, Caspari R, et al. E-cadherin expression is homogeneously reduced in adenoma from patients with familial adenomatous polyposis: an immunohistochemical study of E-cadherin, beta-catenin and cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2004. 19:438–445.17. Ohta T, Takahashi M, Ochiai A. Increased protein expression of both inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in human colon cancers. Cancer Lett. 2006. 239:246–253.
Article18. Zhang H, Sun XF. Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 correlates with advanced stages of colorectal cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002. 97:1037–1041.19. Nosho K, Yoshida M, Yamamoto H, Taniguchi H, Adachi Y, Mikami M, et al. Association of Ets-related transcriptional factor E1AF expression with overexpression of matrix metalloproteinases, COX-2 and iNOS in the early stage of colorectal carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2005. 26:892–899.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Aberrant Expression of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Markers in Early Gastric Cancer: Clinical Application
- Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Tumor Microvessel Density in Colorectal Cancer
- Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Drug Resistance and Metastasis of Lung Cancer
- Natural Compound Shikonin Induces Apoptosis and Attenuates Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Radiation-Resistant Human Colon Cancer Cells