Efficacy of Infliximab in the Treatment of Korean Patients with Crohn's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. sky@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1775965
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2009.54.2.108
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
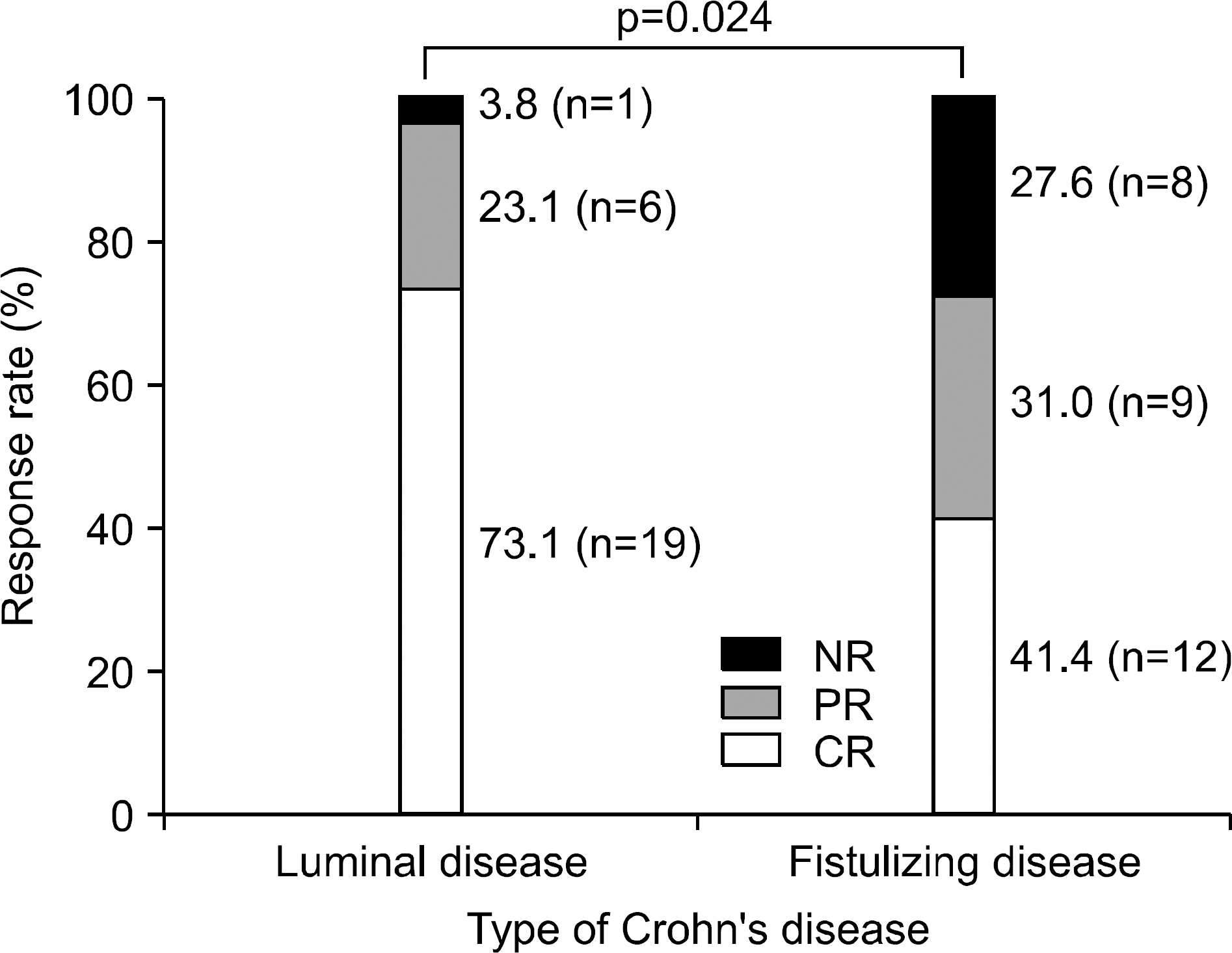
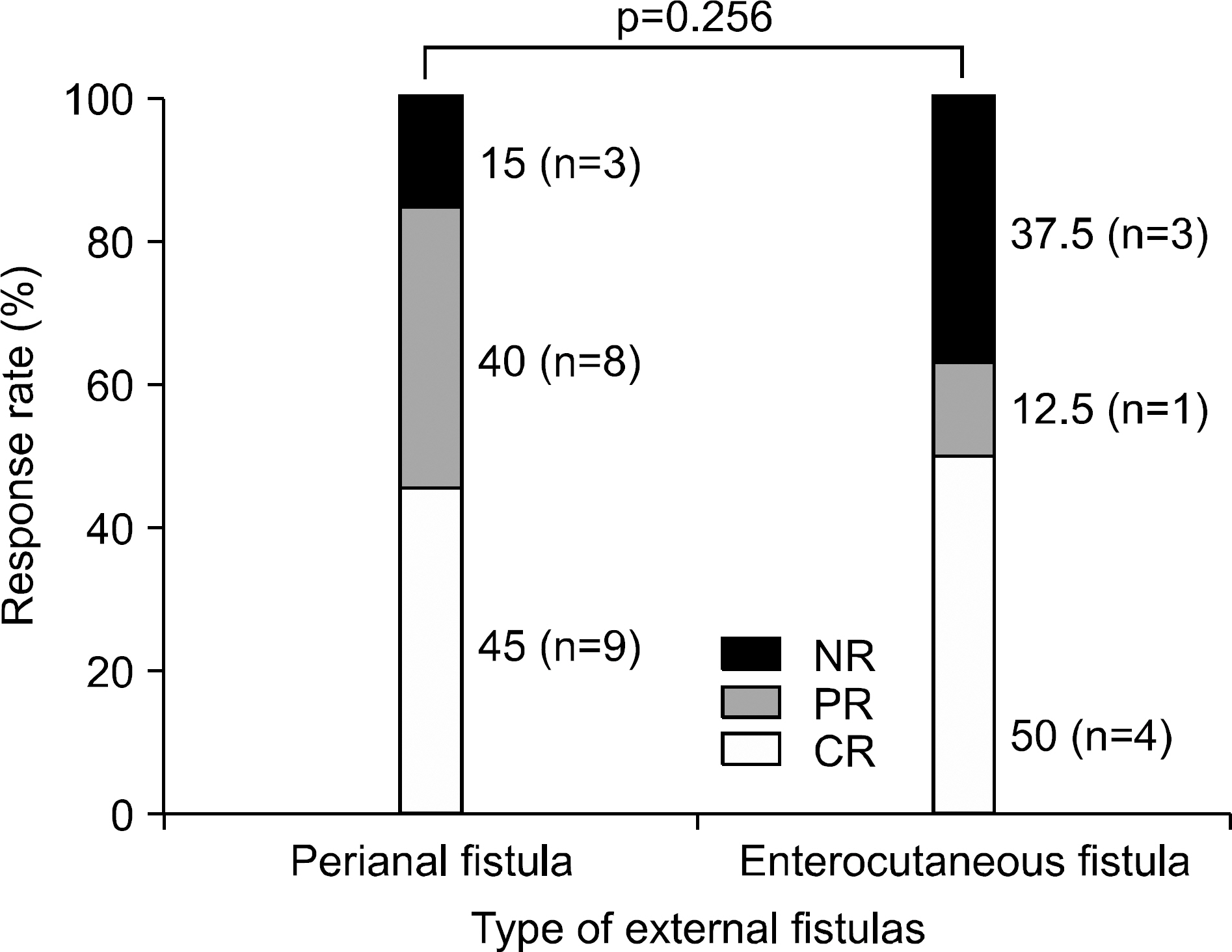
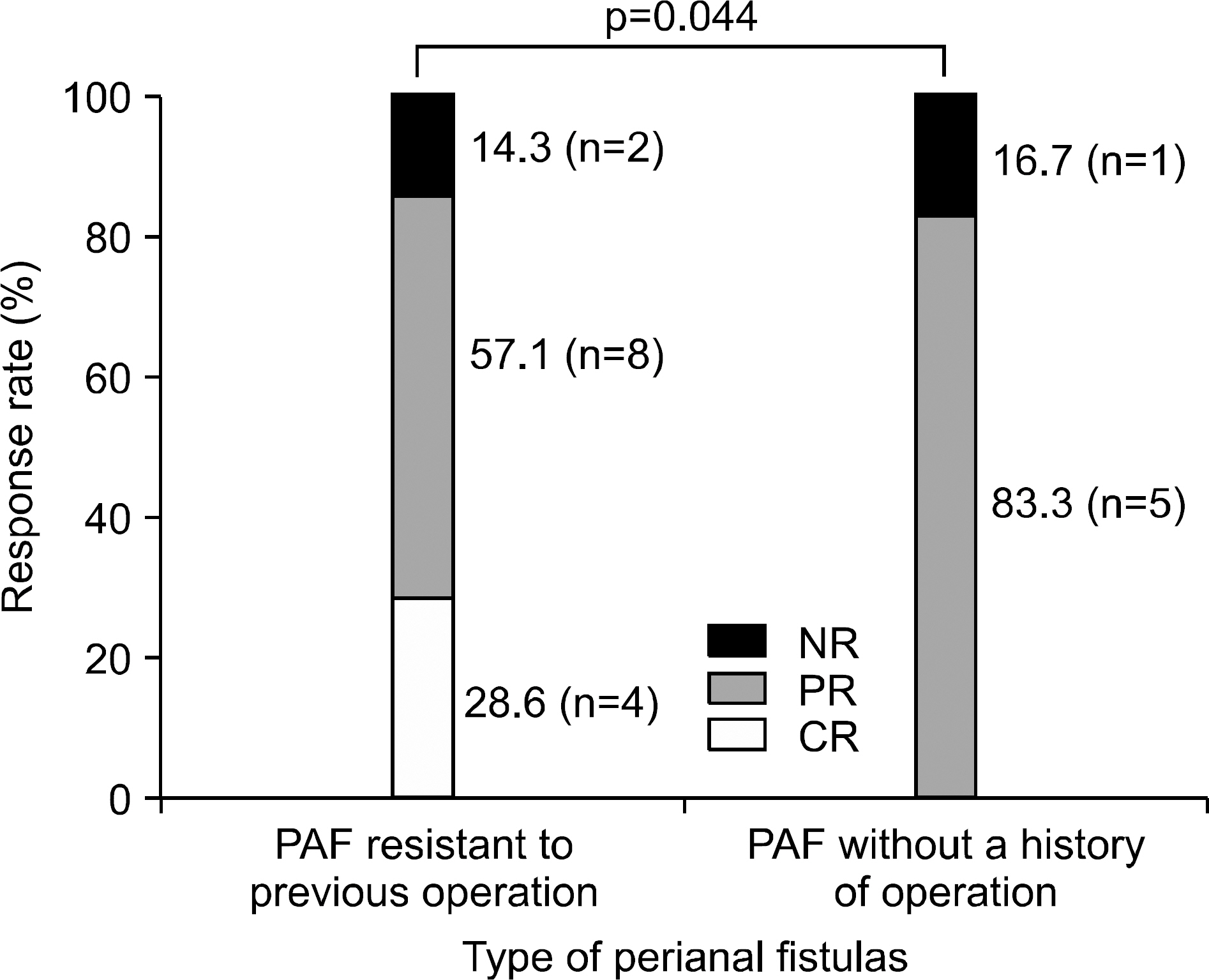
Infliximab has been proven to be effective for refractory luminal and fistulizing Crohn's disease (CD). We performed this study to demonstrate the efficacy of infliximab in Korean CD patients. METHODS: Medical records of 40 CD patients who had been treated with infliximab were reviewed retrospectively. RESULTS: Among 40 patients, 11 (27.5%) patients were treated for refractory luminal disease, 14 (35%) for fistulizing disease, and 15 (37.5%) for both types. Clinical response rate was higher in 26 patients with refractory luminal disease (Complete response (CR), 73.1%; Partial response (PR), 23.1%) than in 29 patients with fistulizing disease (CR, 41.4%; PR, 31%) (p=0.024). The clinical response rate tended to be higher in 28 patients with external fistulas (CR, 46.4%; PR, 32.2%) than 4 patients with internal fistulas (PR, 25%; NR, 75%) (p=0.064). Among patients with external fistulas, the response rate of 8 patients with enterocutaneous fistulas (CR, 50%; PR, 12.5%) was not different from 20 patients with perianal fistulas (CR, 45%; PR, 40%). Among 20 patients with perianal fistulas, the response rate of 6 patients with perianal fistulas without a history of operation (CR, 83.3%; PR, 0%) was higher than 14 patients with perianal fistulas resistant to previous surgical treatment (CR, 28.6%; PR, 57.1%) (p=0.044). As for adverse reaction, 7 patients experienced mild infusion reaction, and 2 patients developed serious infection. CONCLUSIONS: Infliximab is more effective for refractory luminal disease than for fistulizing disease. In addition, clinical responses to infliximab are different according to subtypes of fistulas. These findings should be considered for the proper use of infliximab.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Efficacy of Early Infliximab Treatment for Pediatric Crohn's Disease: A Three-year Follow-up
Yun Seok Lee, Sang Hun Baek, Mi Jin Kim, Yoo Min Lee, Yoon Lee, Yon Ho Choe
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012;15(4):243-249. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2012.15.4.243.Life-Threatening Lower Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage in Pediatric Crohn's Disease
Earl Kim, Yunkoo Kang, Mi Jung Lee, Young Nyun Park, Hong Koh
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2013;16(1):53-60. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2013.16.1.53.Long-term Efficacy and Predictors of Response to Infliximab in Korean Patients with Crohn's Disease
Kang-Moon Lee
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2013;61(5):241-242. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2013.61.5.241.Clinical Outcome of Treatment with Infliximab in Crohn's Disease: A Single-Center Experience
Yeon-Ju Kim, Jung-Wook Kim, Chang Kyun Lee, Hyun Jin Park, Jae-Jun Shim, Jae Young Jang, Suk Ho Dong, Hyo Jong Kim, Byung-Ho Kim, Young Woon Chang
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2013;61(5):270-278. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2013.61.5.270.
Reference
-
1. Yang SK, Yun S, Kim JH, et al. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in the Songpa-Kangdong district, Seoul, Korea, 1986-2005: a KASID study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008; 14:542–549.
Article2. Faubion WA Jr, Loftus EV Jr, Harmsen WS, Zinsmeister AR, Sandborn WJ. The natural history of corticosteroid therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Gastroenterology. 2001; 121:255–260.
Article3. Munkholm P, Langholz E, Davidsen M, Binder V. Frequency of glucocorticoid resistance and dependency in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1994; 35:360–362.
Article4. Candy S, Wright J, Gerber M, Adams G, Gerig M, Goodman R. A controlled double blind study of azathioprine in the management of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1995; 37:674–678.
Article5. Sandborn W, Sutherland L, Pearson D, May G, Modigliani R, Prantera C. Azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine for inducing remission of Crohn's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. CD000545.6. Targan SR, Hanauer SB, van Deventer SJ, et al. A short-term study of chimeric monoclonal antibody cA2 to tumor necrosis factor alpha for Crohn's disease. Crohn's Disease cA2 Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337:1029–1035.7. Present DH, Rutgeerts P, Targan S, et al. Infliximab for the treatment of fistulas in patients with Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999; 340:1398–1405.
Article8. Rutgeerts P, Van Assche G, Vermeire S. Optimizing anti-TNF treatment in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:1593–1610.
Article9. Choi KD, Song HJ, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS. Efficacy and safety of treatment with infliximab in Crohn's disease-the experience of single center in Korea. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005; 46:48–55.10. Lee KM, Kim JS, Shin DH, et al. Effect of infliximab in the treatment of refractory inflammatory bowel disease with complication. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004; 44:259–266.11. Park SH, Jeen YT, Chun HR, et al. A case of refractory pediatric Crohn's disease with a successful treatment by infliximab therapy. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005; 46:297–301.12. Ricart E, Panaccione R, Loftus EV, Tremaine WJ, Sandborn WJ. Infliximab for Crohn's disease in clinical practice at the Mayo Clinic: the first 100 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:722–729.
Article13. Hanauer SB, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn's disease: the ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet. 2002; 359:1541–1549.
Article14. Sands BE, Anderson FH, Bernstein CN, et al. Infliximab maintenance therapy for fistulizing Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:876–885.
Article15. Orlando A, Colombo E, Kohn A, et al. Infliximab in the treatment of Crohn's disease: predictors of response in an Italian multicentric open study. Dig Liver Dis. 2005; 37:577–583.
Article16. Parsi MA, Lashner BA, Achkar JP, Connor JT, Brzezinski A. Type of fistula determines response to infliximab in patients with fistulous Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:445–449.
Article17. Miehsler W, Reinisch W, Kazemi-Shirazi L, et al. Infliximab: lack of efficacy on perforating complications in Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2004; 10:36–40.18. Kim JY, Yang SK, Byeon JS, et al. The incidence and natural history of perianal fistulas in Korean patients with Crohn's disease. Intest Res. 2006; 4:22–31.19. Kim HD, Kim CG, Kim JW, et al. Clinical features and therapeutic responses of perianal lesions in Crohn's disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2003; 42:128–133.20. Bell SJ, Williams AB, Wiesel P, Wilkinson K, Cohen RC, Kamm MA. The clinical course of fistulating Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 17:1145–1151.
Article21. Schwartz DA, Pemberton JH, Sandborn WJ. Diagnosis and treatment of perianal fistulas in Crohn disease. Ann Intern Med. 2001; 135:906–918.
Article22. Regueiro M, Mardini H. Treatment of perianal fistulizing Crohn's disease with infliximab alone or as an adjunct to exam under anesthesia with seton placement. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2003; 9:98–103.
Article23. Topstad DR, Panaccione R, Heine JA, Johnson DR, MacLean AR, Buie WD. Combined seton placement, infliximab infusion, and maintenance immunosuppressives improve healing rate in fistulizing anorectal Crohn's disease: a single center experience. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003; 46:577–583.24. Sandborn WJ, Fazio VW, Feagan BG, Hanauer SB. AGA technical review on perianal Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2003; 125:1508–1530.
Article25. Lionetti P, Bronzini F, Salvestrini C, et al. Response to infliximab is related to disease duration in paediatric Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 18:425–431.
Article26. Parsi MA, Achkar JP, Richardson S, et al. Predictors of response to infliximab in patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2002; 123:707–713.
Article27. Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, Enns R, et al. Adalimumab induction therapy for Crohn disease previously treated with infliximab: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2007; 146:829–838.28. Cheifetz A, Smedley M, Martin S, et al. The incidence and management of infusion reactions to infliximab: a large center experience. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98:1315–1324.
Article29. Keane J, Gershon S, Wise RP, et al. Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha-neutralizing agent. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:1098–1104.30. Wolfe F, Michaud K, Anderson J, Urbansky K. Tuberculosis infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and the effect of infliximab therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50:372–379.
Article31. Rutgeerts P, D'Haens G, Targan S, et al. Efficacy and safety of retreatment with anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody (infliximab) to maintain remission in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1999; 117:761–769.
Article32. Colombel JF, Loftus EV Jr, Tremaine WJ, et al. The safety profile of infliximab in patients with Crohn's disease: the Mayo clinic experience in 500 patients. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:19–31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Affecting Surgical Treatment With Infliximab Therapy in Perianal Fistula With Crohn Disease
- Recent Trends of Infliximab Treatment for Crohn's Disease
- Adalimumab Treatment in Pediatric-Onset Crohn's Disease Patients after Infliximab Failure: A Single Center Study
- Adalimumab or infliximab: which is better for perianal fistula in Crohn's disease?
- Efficacy of Early Infliximab Treatment for Pediatric Crohn's Disease: A Three-year Follow-up