Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2012 Dec;15(4):243-249.
Efficacy of Early Infliximab Treatment for Pediatric Crohn's Disease: A Three-year Follow-up
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea. i101016@skku.edu
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Myongji Hospital, College of Medicine, Kwandong University, Goyang, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the efficacy of early infliximab use and to follow the progress of pediatric cases of Crohn's disease for 3 years.
METHODS
We reviewed the medical records of 28 pediatric patients who had been treated with infliximab for Crohn's disease. Eighteen patients (the 'top-down' group) received infliximab and azathioprine for induction and maintenance therapy for the first year, and then were treated with azathioprine for 2 additional years. Ten patients who were refractory to conventional therapy were categorized in the 'step-up' group. All patients were followed for at least 36 months. Treatment efficacy was assessed by the relapse rate using the pediatric Crohn's disease activity index (PCDAI) score in each group at 12, 24, and 36 months. Blood samples were available from 10 patients, and were used to assess antibody to infliximab (ATI).
RESULTS
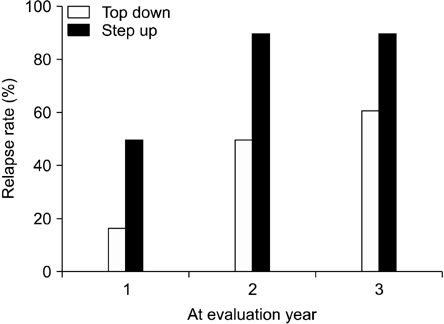
The relapse rate in 'top-down' group was lower than that in 'step-up' group at 1, 2, and 3 years. But, just the relapse rate at the 2 years was significantly different. At 3 years, the relapse rate according to different characteristic variables (sex, age at diagnosis, involvement, PCDAI at diagnosis) was not significantly different. Only one patient treated with infliximab had an adverse event, consisting of dyspnea and tachycardia. ATI was not detected in the blood samples from 10 patients.
CONCLUSION
Early induction with infliximab at diagnosis ('top-down' therapy) is effective for reducing the relapse rate compared to conventional therapies in pediatric Crohn's disease possibly for up to 3 years.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cosnes J, Cattan S, Blain A, Beaugerie L, Carbonnel F, Parc R, et al. Long-term evolution of disease behavior of Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2002. 8:244–250.
Article2. Solberg IC, Vatn MH, Høie O, Stray N, Sauar J, Jahnsen J, et al. IBSEN Study Group. Clinical course in Crohn's disease: results of a Norwegian population-based ten-year follow-up study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 5:1430–1438.
Article3. Munkholm P, Langholz E, Davidsen M, Binder V. Disease activity courses in a regional cohort of Crohn's disease patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995. 30:699–706.
Article4. Xavier RJ, Podolsky DK. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2007. 448:427–434.
Article5. Van Assche G, Dignass A, Reinisch W, van der Woude CJ, Sturm A, De Vos M, et al. European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO). The second European evidence-based Consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn's disease: special situations. J Crohns Colitis. 2010. 4:63–101.
Article6. Lichtenstein GR, Hanauer SB, Sandborn WJ. Practice Parameters Committee of American College of Gastroenterology. Management of Crohn's disease in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. 104:465–483.
Article7. Kozuch PL, Hanauer SB. General principles and pharmacology of biologics in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2006. 35:757–773.
Article8. Hanauer SB, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR, Mayer LF, Schreiber S, Colombel JF, et al. ACCENT I Study Group. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn's disease: the ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet. 2002. 359:1541–1549.
Article9. Peyrin-Biroulet L, Deltenre P, de Suray N, Branche J, Sandborn WJ, Colombel JF. Efficacy and safety of tumor necrosis factor antagonists in Crohn's disease: meta-analysis of placebo-controlled trials. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. 6:644–653.
Article10. Kim SH, Yang S, Kim KJ, Kim EH, Yoon SM, Ye BD, et al. Efficacy of infliximab in the treatment of Korean patients with Crohns disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2009. 54:108–116.
Article11. Hyams JS, Markowitz J, Wyllie R. Use of infliximab in the treatment of Crohn's disease in children and adolescents. J Pediatr. 2000. 137:192–196.
Article12. Kugathasan S, Werlin SL, Martinez A, Rivera MT, Heikenen JB, Binion DG. Prolonged duration of response to infliximab in early but not late pediatric Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000. 95:3189–3194.
Article13. Hyams JS, Lerer T, Griffiths A, Pfefferkorn M, Kugathasan S, Evans J, et al. Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Collaborative Research Group. Long-term outcome of maintenance infliximab therapy in children with Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009. 15:816–822.
Article14. Kim MJ, Lee JS, Lee JH, Kim JY, Choe YH. Infliximab therapy in children with Crohn's disease: a one-year evaluation of efficacy comparing 'top-down' and 'step-up' strategies. Acta Paediatr. 2011. 100:451–455.
Article15. Lee JS, Lee JH, Lee JH, Lee HJ, Kim MJ, Lee HJ, et al. Efficacy of early treatment with infliximab in pediatric Crohn's disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. 16:1776–1781.
Article16. Lee JH, Lee HJ, Park SE, Choe YH. Infliximab: the benefit for refractory Crohn disease andtop-down induction therapy in severe Crohn disease. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. 11:28–35.
Article17. IBD Working Group of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. Inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents: recommendations for diagnosis--the Porto criteria. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 41:1–7.18. Hyams J, Markowitz J, Otley A, Rosh J, Mack D, Bousvaros A, et al. Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Collaborative Research Group. Evaluation of the pediatric Crohn disease activity index: a prospective multicenter experience. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 41:416–421.
Article19. Adişen E, Aral A, Aybay C, Gürer MA. Anti-infliximab antibody status and its relation to clinical response in psoriatic patients: A pilot study. J Dermatol. 2010. 37:708–713.
Article20. Van Limbergen J, Russell RK, Drummond HE, Aldhous MC, Round NK, Nimmo ER, et al. Definition of phenotypic characteristics of childhood-onset inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2008. 135:1114–1122.
Article21. Choi KD, Song HJ, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS. Efficacy and safety of treatment with infliximab in Crohn's disease-the experience of single center in Korea. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005. 46:48–55.22. Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Reinisch W, Mantzaris GJ, Kornbluth A, Rachmilewitz D, et al. SONIC Study Group. Infliximab, azathioprine, or combination therapy for Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2010. 362:1383–1395.
Article23. Baldassano R, Braegger CP, Escher JC, DeWoody K, Hendricks DF, Keenan GF, et al. Infliximab (REMICADE) therapy in the treatment of pediatric Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003. 98:833–838.
Article24. Stephens MC, Shepanski MA, Mamula P, Markowitz JE, Brown KA, Baldassano RN. Safety and steroid-sparing experience using infliximab for Crohn's disease at a pediatric inflammatory bowel disease center. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003. 98:104–111.
Article25. Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Long-Fox A, Charles P, Bijl H, et al. Repeated therapy with monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994. 344:1125–1127.
Article26. Jwa YJ, Kim NH, Park HJ, Park JS, Bae WK, Kim KA, et al. A case of psoriasis induced by infliximab treatment for Crohn's disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010. 56:324–328.
Article27. Na SY, Shim JO. Biological therapy for inflammatory bowel disease in children. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012. 15:13–18.
Article28. Kim MJ, Choe YH. Change in the treatment strategy for pediatric Crohn's disease. Korean J Pediatr. 2010. 53:830–833.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adalimumab Treatment in Pediatric-Onset Crohn's Disease Patients after Infliximab Failure: A Single Center Study
- Change in the treatment strategy for pediatric Crohn's disease
- Recent Trends of Infliximab Treatment for Crohn's Disease
- Factors Affecting Surgical Treatment With Infliximab Therapy in Perianal Fistula With Crohn Disease
- Clinical efficacy of adalimumab versus infliximab and the factors associated with recurrence or aggravation during treatment of anal fistulas in Crohn's disease