Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2012 Jun;16(3):219-224. 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.3.219.
Gap Junction Contributions to the Goldfish Electroretinogram at the Photopic Illumination Level
- Affiliations
-
- 1Natural Sciences Section, Department of Medical Lifescience, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea. cjung@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1768017
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.3.219
Abstract
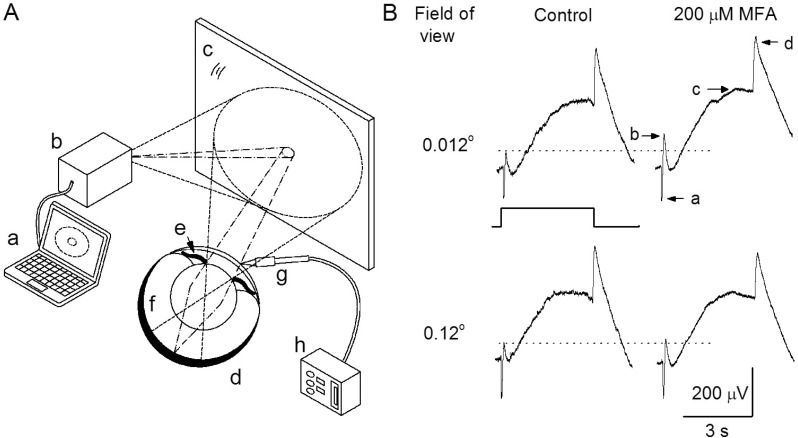
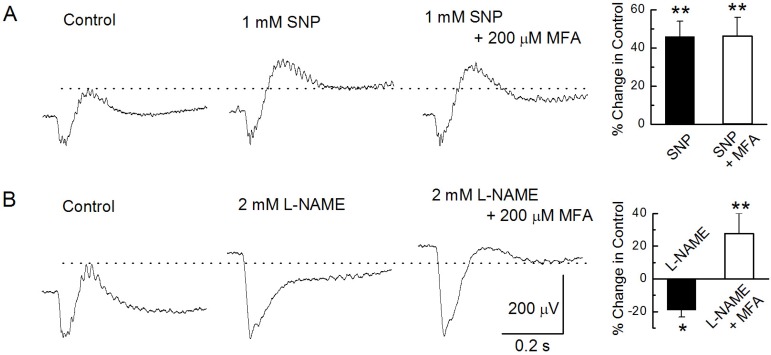
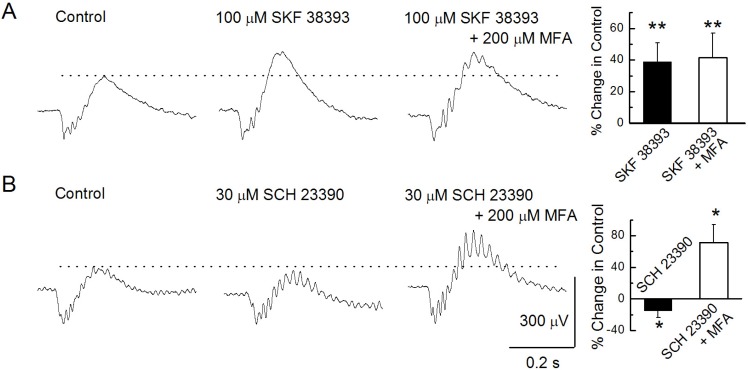
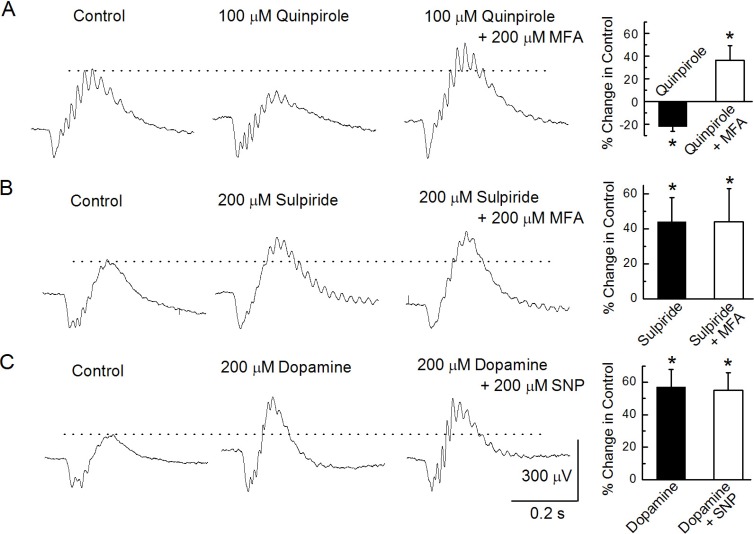
- Understanding how the b-wave of the electroretinogram (ERG) is generated by full-field light stimulation is still a challenge in visual neuroscience. To understand more about the origin of the b-wave, we studied the contributions of gap junctions to the ERG b-wave. Many types of retinal neurons are connected to similar and different neighboring neurons through gap junctions. The photopic (cone-dominated) ERG, stimulated by a small light beam, was recorded from goldfish (Carassius auratus) using a corneal electrode. Data were obtained before and after intravitreal injection of agents into the eye under a photopic illumination level. Several agents were used to affect gap junctions, such as dopamine D1 and D2 receptor agonists and antagonists, a nitric oxide (NO) donor, a nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor, the gap junction blocker meclofenamic acid (MFA), and mixtures of these agents. The ERG b-waves, which were enhanced by MFA, sodium nitroprusside (SNP), SKF 38393, and sulpiride, remained following application of a further injection of a mixture with MFA. The ERG b-waves decreased following NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), SCH 23390, and quinpirole administration but were enhanced by further injection of a mixture with MFA. These results indicate that gap junction activity influences b-waves of the ERG related to NO and dopamine actions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
2,3,4,5-Tetrahydro-7,8-dihydroxy-1-phenyl-1H-3-benzazepine
Benzazepines
Dopamine
Electrodes
Eye
Gap Junctions
Goldfish
Humans
Intravitreal Injections
Light
Lighting
Meclofenamic Acid
Neurons
Neurosciences
NG-Nitroarginine Methyl Ester
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase
Nitroprusside
Quinpirole
Retinal Neurons
Sulpiride
Tissue Donors
2,3,4,5-Tetrahydro-7,8-dihydroxy-1-phenyl-1H-3-benzazepine
Benzazepines
Dopamine
Meclofenamic Acid
NG-Nitroarginine Methyl Ester
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase
Nitroprusside
Quinpirole
Sulpiride
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Bisphenol A and 4-
tert -Octylphenol Inhibit Cx46 Hemichannel Currents
Seunghoon Oh
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015;19(1):73-79. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.1.73.
Reference
-
1. Bloomfield SA, Völgyi B. The diverse functional roles and regulation of neuronal gap junctions in the retina. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009; 10:495–506. PMID: 19491906.
Article2. Werblin FS, Dowling JE. Organization of the retina of the mudpuppy, Necturus maculosus. II. Intracellular recording. J Neurophysiol. 1969; 32:339–355. PMID: 4306897.
Article3. Kaneko A. Receptive field organization of bipolar and amacrine cells in the goldfish retina. J Physiol. 1973; 235:133–153. PMID: 4778132.
Article4. Naka KI, Nye PW. Role of horizontal cells in organization of the catfish retinal receptive field. J Neurophysiol. 1971; 34:785–801. PMID: 5097157.
Article5. Marchiafava PL. Horizontal cells influence membrane potential of bipolar cells in the retina of the turtle. Nature. 1978; 275:141–142. PMID: 692683.
Article6. Arai I, Tanaka M, Tachibana M. Active roles of electrically coupled bipolar cell network in the adult retina. J Neurosci. 2010; 30:9260–9270. PMID: 20610761.
Article7. Cook JE, Becker DL. Gap junctions in the vertebrate retina. Microsc Res Tech. 1995; 31:408–419. PMID: 8534902.
Article8. Marc RE, Liu WL, Muller JF. Gap junctions in the inner plexiform layer of the goldfish retina. Vision Res. 1988; 28:9–24. PMID: 3414003.
Article9. Saito T, Kujiraoka T. Characteristics of bipolar-bipolar coupling in the carp retina. J Gen Physiol. 1988; 91:275–287. PMID: 3373179.10. DeVries SH, Schwartz EA. Modulation of an electrical synapse between solitary pairs of catfish horizontal cells by dopamine and second messengers. J Physiol. 1989; 414:351–375. PMID: 2558170.
Article11. DeVries SH, Schwartz EA. Hemi-gap-junction channels in solitary horizontal cells of the catfish retina. J Physiol. 1992; 445:201–230. PMID: 1380084.
Article12. Lu C, McMahon DG. Modulation of hybrid bass retinal gap junctional channel gating by nitric oxide. J Physiol. 1997; 499:689–699. PMID: 9130165.
Article13. Lasater EM, Dowling JE. Dopamine decreases conductance of the electrical junctions between cultured retinal horizontal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1985; 82:3025–3029. PMID: 3857632.
Article14. Piccolino M, Neyton J, Gerschenfeld HM. Decrease of gap junction permeability induced by dopamine and cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in horizontal cells of turtle retina. J Neurosci. 1984; 4:2477–2488. PMID: 6092564.
Article15. Hedden WL Jr, Dowling JE. The interplexiform cell system. II. Effects of dopamine on goldfish retinal neurones. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978; 201:27–55. PMID: 27790.16. Murakami M, Miyachi EI, Takahadhi KI. Modulation of gap juctions between horizontal cells by second messengers. Prog Retinal Eye Res. 1995; 14:197–221.17. McMahon DG, Brown DR. Modulation of gap-junction channel gating at zebrafish retinal electrical synapses. J Neurophysiol. 1994; 72:2257–2268. PMID: 7533830.
Article18. Baldridge WH, Ball AK, Miller RG. Dopaminergic regulation of horizontal cell gap junction particle density in goldfish retina. J Comp Neurol. 1987; 265:428–436. PMID: 3693614.
Article19. Stell WK. Inputs to bipolar cell dendrites in goldfish retina. Sens Processes. 1978; 2:339–349. PMID: 755290.20. Saito T, Kondo H, Toyoda J. Rod and cone signals in the on-center bipolar cell: their different ionic mechanisms. Vision Res. 1978; 18:591–595. PMID: 664343.
Article21. Malchow RP, Yazulla S. Separation and light adaptation of rod and cone signals in the retina of the goldfish. Vision Res. 1986; 26:1655–1666. PMID: 3617507.
Article22. Hughes A, Saszik S, Bilotta J, Demarco PJ Jr, Patterson WF 2nd. Cone contributions to the photopic spectral sensitivity of the zebrafish ERG. Vis Neurosci. 1998; 15:1029–1037. PMID: 9839967.
Article23. Hood DC, Finkelstein MA. Boff KR, Kaufman L, Thomas JP, editors. Sensitivity to light. Handbook of Perception and Human Performance. 1986. New York: Wiley;p. 5-1–5-66.24. Kim SH, Jung CS. The role of the pattern edge in goldfish visual motion detection. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010; 14:413–417. PMID: 21311683.
Article25. Liu CR, Xu L, Zhong YM, Li RX, Yang XL. Expression of connexin 35/36 in retinal horizontal and bipolar cells of carp. Neuroscience. 2009; 164:1161–1169. PMID: 19778581.
Article26. O'Brien J, al-Ubaidi MR, Ripps H. Connexin 35: a gap-junctional protein expressed preferentially in the skate retina. Mol Biol Cell. 1996; 7:233–243. PMID: 8688555.27. Condorelli DF, Parenti R, Spinella F, Trovato Salinaro A, Belluardo N, Cardile V, Cicirata F. Cloning of a new gap junction gene (Cx36) highly expressed in mammalian brain neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1998; 10:1202–1208. PMID: 9753189.
Article28. Veruki ML, Hartveit E. Meclofenamic acid blocks electrical synapses of retinal AII amacrine and on-cone bipolar cells. J Neurophysiol. 2009; 101:2339–2347. PMID: 19279153.
Article29. Pan F, Mills SL, Massey SC. Screening of gap junction antagonists on dye coupling in the rabbit retina. Vis Neurosci. 2007; 24:609–618. PMID: 17711600.
Article30. Tomita T, Yanagida T. Origins of the ERG waves. Vision Res. 1981; 21:1703–1707. PMID: 7336605.
Article31. Koriyama Y, Yasuda R, Homma K, Mawatari K, Nagashima M, Sugitani K, Matsukawa T, Kato S. Nitric oxide-cGMP signaling regulates axonal elongation during optic nerve regeneration in the goldfish in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem. 2009; 110:890–901. PMID: 19457064.32. Villani L, Guarnieri T. Localization of nitric oxide synthase in the goldfish retina. Brain Res. 1996; 743:353–356. PMID: 9017268.
Article33. Liepe BA, Stone C, Koistinaho J, Copenhagen DR. Nitric oxide synthase in Müller cells and neurons of salamander and fish retina. J Neurosci. 1994; 14:7641–7654. PMID: 7527846.34. Yazulla S, Lin ZS. Differential effects of dopamine depletion on the distribution of [3H]SCH 23390 and [3H]spiperone binding sites in the goldfish retina. Vision Res. 1995; 35:2409–2414. PMID: 8594810.35. Harsanyi K, Mangel SC. Activation of a D2 receptor increases electrical coupling between retinal horizontal cells by inhibiting dopamine release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992; 89:9220–9224. PMID: 1357661.
Article36. Van Buskirk R, Dowling JE. Isolated horizontal cells from carp retina demonstrate dopamine-dependent accumulation of cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1981; 78:7825–7829. PMID: 6278491.
Article37. Lasater EM. Retinal horizontal cell gap junctional conductance is modulated by dopamine through a cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987; 84:7319–7323. PMID: 2823257.
Article38. Huppé-Gourgues F, Coudé G, Lachapelle P, Casanova C. Effects of the intravitreal administration of dopaminergic ligands on the b-wave amplitude of the rabbit electroretinogram. Vision Res. 2005; 45:137–145. PMID: 15581915.
Article39. Hedden WL Jr, Dowling JE. The interplexiform cell system. II. Effects of dopamine on goldfish retinal neurones. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978; 201:27–55. PMID: 27790.40. Dowling JE, Ehinger B. Synaptic organization of the dopaminergic neurons in the rabbit retina. J Comp Neurol. 1978; 180:203–220. PMID: 207745.
Article41. Dowling JE, Ehinger B. The interplexiform cell system. I. Synapses of the dopaminergic neurons of the goldfish retina. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978; 201:7–26. PMID: 27792.42. Hampton CK, Redburn DA. Autoradiographic analysis of 3H-glutamate, 3H-dopamine, and 3H-GABA accumulation in rabbit retina after kainic acid treatment. J Neurosci Res. 1983; 9:239–251. PMID: 6133958.43. Yazulla S, Zucker CL. Synaptic organization of dopaminergic interplexiform cells in the goldfish retina. Vis Neurosci. 1988; 1:13–29. PMID: 2908724.
Article44. Djamgoz MB, Wagner HJ. Localization and function of dopamine in the adult vertebrate retina. Neurochem Int. 1992; 20:139–191. PMID: 1304857.
Article45. Negishi K, Teranishi T, Kato S. The dopamine system of the teleost fish retina. Prog Ret Res. 1990; 9:1–48.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of the Pattern Edge in Goldfish Visual Motion Detection
- Photopic Negative Response (PhNR) in Normal Subjects
- Photopic Electroretinogram in Adult Diabetics
- The Change of Contrast Sensitivity in Amblyopic Patient after Occlusion Therapy using ACV
- ON and OFF Responses of the Electroretinogram in Patients with Glaucoma