Korean J Lab Med.
2011 Jul;31(3):162-166. 10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.3.162.
Leptin:Adiponectin Ratio and Metabolic Syndrome in the General Japanese Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, Clinical Research Institute for Endocrine and Metabolic Disease, National Hospital Organization Kyoto Medical Center, Kyoto, Japan. kazukotani@jichi.ac.jp
- 2Department of Clinical Laboratory Medicine, Jichi Medical University, Shimotsuke-City, Tochigi, Japan.
- KMID: 1735848
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.3.162
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Circulating leptin:adiponectin ratio (L:A) is a potential surrogate marker for cardiometabolic diseases; however, the relationship of the L:A with the occurrence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) has not yet been fully explored in the general Japanese population.
METHODS
We enrolled 678 Japanese subjects (208 men and 470 women, mean age: 58.8+/-14.4 [SD] yr; mean body mass index: 23.6+/-3.3 kg/m2) in this study, and determined their MetS status by using the National Cholesterol Education Program-Adult Treatment Panel (NCEP-ATP) recommendations with minor modifications for the Japanese population. Biochemical markers such as leptin and adiponectin present in blood were measured. The statistical analyses performed were gender-based.
RESULTS
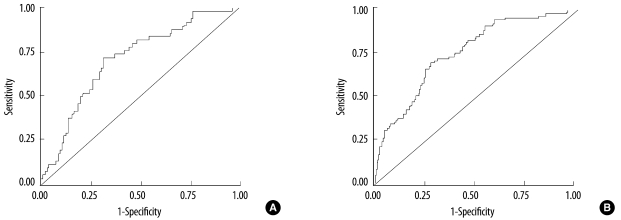
A in subjects with MetS was significantly higher than that in subjects without MetS, regardless of gender. The L:A also showed a significant and gradual increase corresponding to the increase in the number of components of MetS present in both the genders (trend P<0.01). The cut-off level of the L:A to detect MetS was 0.59 (sensitivity: 0.72, specificity: 0.70) in men and 1.04 (sensitivity: 0.72, specificity: 0.69) in women.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that the L:A can serve as a clinically useful marker for detecting MetS characteristics in the general Japanese population. The clinical application of this laboratory index for detecting MetS should be assessed in future studies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Evaluation of the Performance of an Adiponectin ELISA-based Test and Establishing Serum Adiponectin Reference Intervals for Korean Population
Yongjung Park, Young Ran Kim, Hyon-Suk Kim
Lab Med Online. 2013;3(4):242-252. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2013.3.4.242.
Reference
-
1. Klein BE, Klein R, Lee KE. Components of the metabolic syndro-me and risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes in beaver dam. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:1790–1794. PMID: 12351479.
Article2. Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, Niskanen LK, Kumpusalo E, Tuomilehto J, et al. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA. 2002; 288:2709–2716. PMID: 12460094.
Article3. McNeill AM, Rosamond WD, Girman CJ, Golden SH, Schmidt MI, East HE, et al. The metabolic syndrome and 11-year risk of incident cardiovascular disease in the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:385–390. PMID: 15677797.
Article4. Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. 2002; 287:356–359. PMID: 11790215.
Article5. Park HS, Kim SM, Lee JS, Lee J, Han JH, Yoon DK, et al. Prevalen-ce and trends of metabolic syndrome in Korea: Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 1998-2001. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007; 9:50–58. PMID: 17199718.
Article6. Satoh N, Naruse M, Usui T, Tagami T, Suganami T, Yamada K, et al. Leptin-to-adiponectin ratio as a potential atherogenic index in obese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:2488–2490. PMID: 15451921.
Article7. Kotani K, Sakane N, Saiga K, Kurozawa Y. Leptin : adiponectin ratio as an atherosclerotic index in patients with type 2 diabetes : relationship of the index to carotid intima-media thickness. Diabetologia. 2005; 48:2684–2686. PMID: 16261311.
Article8. Inoue M, Maehata E, Yano M, Taniyama M, Suzuki S. Correlation between the adiponectin-leptin ratio and parameters of insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism. 2005; 54:281–286. PMID: 15736103.
Article9. Inoue M, Yano M, Yamakado M, Maehata E, Suzuki S. Relationship between the adiponectin-leptin ratio and parameters of insulin resistance in subjects without hyperglycemia. Metabolism. 2006; 55:1248–1254. PMID: 16919546.
Article10. Taniguchi A, Nakai Y, Fukushima M, Kawamura H, Imura H, Nagata I, et al. Pathogenic factors responsible for glucose intolerance in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes. 1992; 41:1540–1546. PMID: 1446794.
Article11. Examination Committee of Criteria for 'Obesity Disease' in Japan. Japan Society for the Study of Obesity. New criteria for 'obesity disease' in Japan. Circ J. 2002; 66:987–992. PMID: 12419927.12. Kawamoto R, Tomita H, Oka Y, Ohtsuka N, Kamitani A. Metabo-lic syndrome and carotid atherosclerosis: role of elevated blood pressure. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2005; 12:268–275. PMID: 16205023.
Article13. Schisterman EF, Faraggi D, Reiser B, Hu J. Youden index and the optimal threshold for markers with mass at zero. Stat Med. 2008; 27:297–315. PMID: 17624866.
Article14. Beltowski J. Leptin and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2006; 189:47–60. PMID: 16580676.
Article15. Oh DK, Ciaraldi T, Henry RR. Adiponectin in health and disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007; 9:282–289. PMID: 17391153.
Article16. Tarnopolsky MA, Ruby BC. Sex differences in carbohydrate metabolism. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2001; 4:521–526. PMID: 11706287.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlations of Leptin, Adiponectin and Leptin/Adiponectin Ratio with Metabolic Disorders in the Childhood Obesity
- Impact of Serum Leptin to Adiponectin Ratio on Regression of Metabolic Syndrome in High-Risk Individuals: The ARIRANG Study
- The relationship between leptin adiponectin ratio and insulin resistance in healthy children
- Effects of Obesity on the Physiological Levels of Adiponectin, Leptin and Diagnostic Indices of Metabolic Syndrome in Male Workers
- Relationships among Serum Adiponectin, Leptin and Vitamin D Concentrations and the Metabolic Syndrome in Farmers