Yonsei Med J.
2005 Apr;46(2):268-274. 10.3349/ymj.2005.46.2.268.
In Vitro Bioassay of Endotoxin Using Fluorescein as a pH Indicator in a Macrophage Cell Culture System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Engineering, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjc@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Medical Devices & Radiation Health, Korea Food & Drug Administration, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Microbiology, National Institute of Health Sciences, Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 1734054
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2005.46.2.268
Abstract
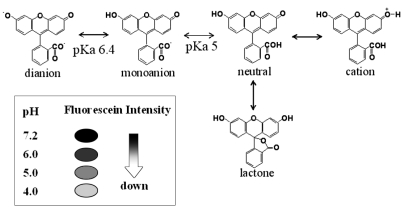
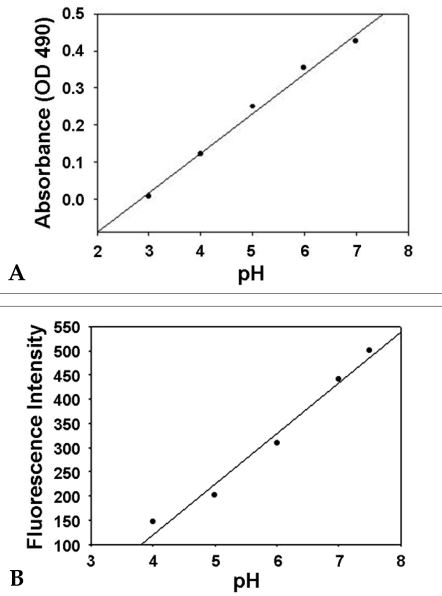
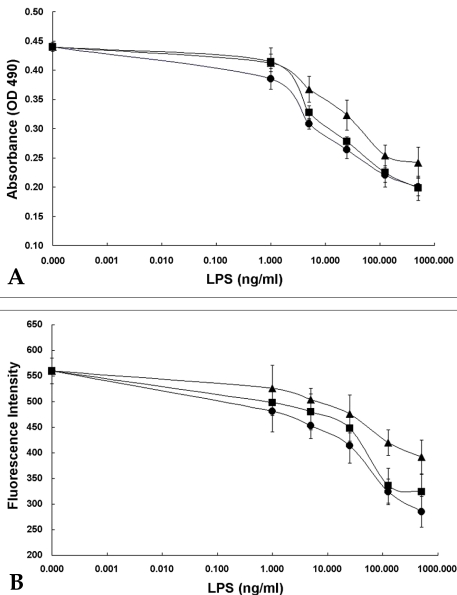
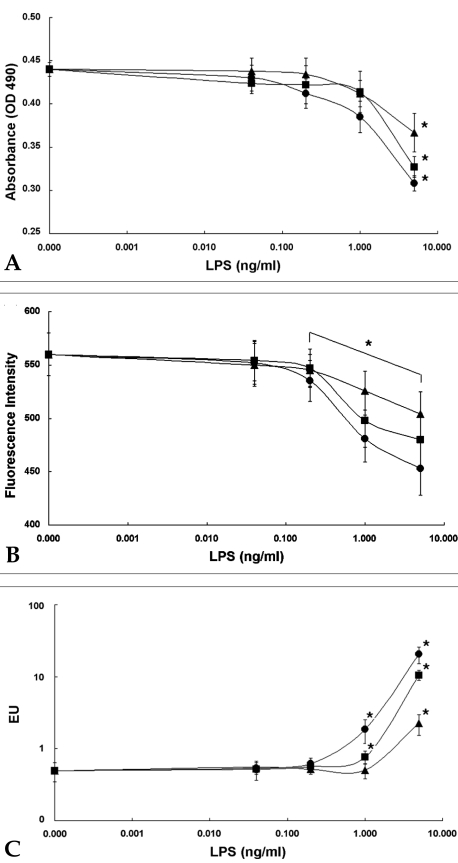
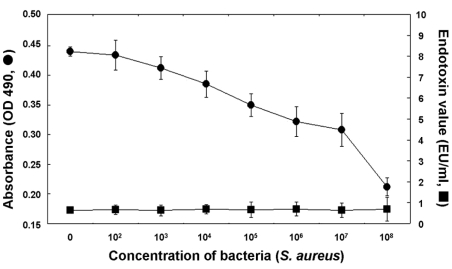
- Based on the biological activity of endotoxin, we propose a possible new method for detecting endotoxin using a pH- indication system of macrophage culture media. After RAW 264.7 macrophage cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the addition of fluorescein to the LPS-treated media reproductively reduced its absorption and emission spectra (it was a dose-dependent reduction). The advantages of this LPS- detection method were compared with the Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) test by using purified bacterial LPS (Salmonella minnessota, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa). Additionally, the absorption and fluorescence intensity of fluorescein, following treatment of RAW 264.7 cells with a high concentration of Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-positive, lysed bacteria), could not generally be detected by the LAL test, but they were found to be reduced, in a dose-response relationship, with this new system. The macrophage culture system-method might be a good supplement to the LAL assay for detection of LPS, Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS. Receptor-dependent mechanisms of cell stimulation by bacterial endotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995; 13:437–457. PMID: 7542010.
Article2. Iwanaga S, Morita T, Harada T, Nakamura S, Niwa M, Takada K, et al. Chromogenic substrates for horseshoe crab clotting enzyme. Its application for the assay of bacterial endotoxins. Haemostasis. 1978; 7:183–188. PMID: 658779.3. Iwanaga S. The limulus clotting reaction. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993; 5:74–82. PMID: 8452677.
Article4. Rietschel ET, Brade H, Brade L, Brandenburg K, Schade U, Seydel U, et al. Lipid A, the endotoxic center of bacterial lipopolysaccharides: relation of chemical structure to biological activity. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987; 231:25–53. PMID: 3588622.5. Laude-Sharp M, Haeffner-Cavaillon N, Caroff M, Lantreibecq F, Pusineri C, Kazatchkine MD. Dissociation between the interleukin 1-inducing capacity and Limulus reactivity of lipopolysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria. Cytokine. 1990; 2:253–258. PMID: 2129502.
Article6. Eperon S, De Groote D, Werner-Felmayer G, Jungi TW. Human monocytoid cell lines as indicators of endotoxin: comparison with rabbit pyrogen and Limulus amoebocyte lysate assay. J Immunol Methods. 1997; 207:135–145. PMID: 9368640.
Article7. Werner-Felmayer G, Baier-Bitterlich G, Fuchs D, Hausen A, Murr C, Reibnegger G, et al. Detection of bacterial pyrogens on the basis of their effects on gamma interferon-mediated formation of neopterin or nitrite in cultured monocyte cell lines. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1995; 2:307–313. PMID: 7664177.
Article8. Jungi TW. A turbidimetric assay in an ELISA reader for the determination of mononuclear phagocyte procoagulant activity. J Immunol Methods. 1990; 133:21–29. PMID: 2212688.
Article9. McCoy KL. Contribution of endosomal acidification to antigen processing. Semin Immunol. 1990; 2:239–246. PMID: 1983337.10. Mellman I, Fuchs R, Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986; 55:663–700. PMID: 2874766.
Article11. Sjoback R, Nygren J, Kubista M. Absorption and Fluorescence Properties of Fluorescein. Spectrochim Acta A. 1995; 51:7–12.12. Cooper JF. Validation of bacterial endotoxin test methods. LAL Times. 1999; 6:1–4.13. U.S.FDA, Guideline on validation of the Limulus amebocyte lysate test as an in-process endotoxin test for human and animal parenteral drugs, biological products and medical devices, DHHS, Dec. 1987 and Interim Guidance, 1991. FDA Interim Guidance. 1991.14. Levin J, Tomasulo PA, Oser RS. Detection of endotoxin in human blood and demonstration of an inhibitor. J Lab Clin Med. 1970; 75:903–911. PMID: 5421075.15. Takagi K, Moriya A, Tamura H, Nakahara C, Tanaka S, Fujita V, et al. Quantitative measurement of endotoxin in human blood using synthetic chromogenic substrate for horseshoe crab clotting enzyme: a comparison of methods of blood sampling and treatment. Thromb Res. 1981; 23:51–57. PMID: 7302922.
Article16. Peterson AA, Munford RS. Dephosphorylation of the lipid A moiety of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide by mouse macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987; 55:974–978. PMID: 3030936.17. Ulevitch RJ. Berry LJ, editor. Interaction of bacterial lipopolysaccharide and plasma high density lipoproteins. Handbook of endotoxin. 1985. Amsterdam: Elsvier;p. 372–388.18. Urbaschek B, Becker KP, Ditter B, Urbaschek R. Leive L, editor. Quantification of endotoxin and sample-related interferences in human plasma and cerebrospinal fluid by using a kinetic Limulus amoebocyte lysate microtiter test. Microbiology. 1985. Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology;p. 39–42.19. Eperon S, Jungi TW. The use of human monocytoid lines as indicators of endotoxin. J Immunol Methods. 1996; 194:121–129. PMID: 8765165.
Article20. Kreutz M, Ackermann U, Hauschildt S, Krause SW, Riedel D, Bessler W, et al. A comparative analysis of cytokine production and tolerance induction by bacterial lipopeptides, lipopolysaccharides and Staphylococcus aureus in human monocytes. Immunology. 1997; 92:396–401. PMID: 9486114.21. Johannsen L, Obal F Jr, Kapas L, Kovalzon V, Krueger JM. Somnogenic activity of muramyl peptide-derived immune adjuvants. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1994; 16:109–116. PMID: 8181899.
Article22. Himanen JP, Pyhala L, Olander RM, Merimskaya O, Kuzina T, Lysyuk O, et al. Biological activities of lipoteichoic acid and peptidoglycan-teichoic acid of Bacillus subtilis 168 (Marburg). J Gen Microbiol. 1993; 139:2659–2665. PMID: 8277249.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Study of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines in Endotoxin Induced Uveitis
- Changes of Endotoxin Concentration in Dialysis Solution During Hemodialysis
- The Role of Oxygen Free Radicals from Endothelial Cells in Endotoxin-induced Endothelial Cell Cytotoxicity
- Establishment of Three Dimensional In Vitro Laboratory Model in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: Spheroid Model and Raft Culture Model
- The Effects of Inline Intravenous Filtration on Bacteria, Candida and Bacterial Endotoxin Retentions