J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Oct;22(5):815-819. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.815.
House Dust Mite Induces Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 in EoL-1 Human Eosinophilic Leukemic Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics and Institute of Allergy, Biomolecule Secretion Research Center, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Parasitology, Institute of Tropical Medicine, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. myeong@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 1713286
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.815
Abstract
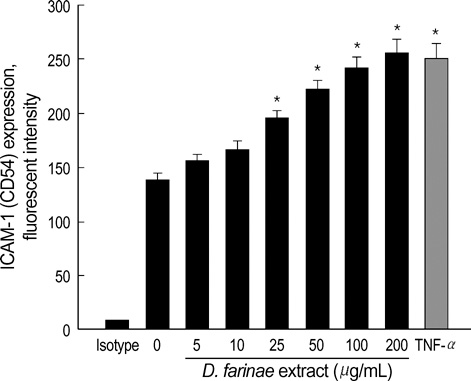
- The house dust mite (HDM) is considered to be the most common indoor allergen associated with bronchial asthma. In this study, we investigated whether crude extract of the HDM Dermatophagoides farinae could activate human eosinophilic leukemic cells (EoL-1) to induce upregulation of cell-surface adhesion molecules. When EoL-1 cells were incubated with D. farinae extract, expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) significantly increased on the cell surfaces compared to cells incubated with medium alone. In contrast, surface expression of CD11b and CD49d in EoL-1 cells was not affected by D. farinae extract. In addition, pretreatment of cells with NF- kappaB inhibitor (MG-132) or JNK inhibitor (SP600125) significantly inhibited ICAM-1 expression promoted by HDM extract. However, neither p38 MAP kinase inhibitor nor MEK inhibitor prevented HDM-induced ICAM-1 expression in EoL-1 cells. These results suggest that crude extract of D. farinae induces ICAM-1 expression in EoL-1 cells through signaling pathways involving both NF- kappaB and JNK.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Anthracenes/pharmacology
Antigens, CD11b/biosynthesis
Cell Line, Tumor
Cell Membrane/metabolism
Eosinophils/*metabolism
Flow Cytometry/methods
*Gene Expression Regulation
Humans
Integrin alpha4/biosynthesis
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1/*metabolism
Leukemia/*metabolism
Leupeptins/pharmacology
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 8/metabolism
NF-kappa B/metabolism
Pyroglyphidae
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases/metabolism
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bousquet J, Chanez P, Lacoste JY, Barnéon G, Ghavanian N, Enander I, Venge P, Ahlstedt S, Simony-Lafontaine J, Godard P, et al. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1990. 323:1033–1039.
Article2. Jagels MA, Daffern PJ, Zuraw BL, Hugli TE. Mechanisms and regulation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte and eosinophil adherence to human airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999. 21:418–427.
Article3. Tang ML, Fiscus LC. Important roles for L-selectin and ICAM-1 in the development of allergic airway inflammation in asthma. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2001. 14:203–210.4. van de Stolpe A, van der Saag PT. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Mol Med. 1996. 74:13–33.
Article5. Wong CK, Ip WK, Lam CW. Interleukin-3, -5, and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced adhesion molecule expression on eosinophils by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003. 29:133–147.
Article6. Cheung PF, Wong CK, Ip WK, Lam CW. IL-25 regulates the expression of adhesion molecules on eosinophils: mechanism of eosinophilia in allergic inflammation. Allergy. 2006. 61:878–885.
Article7. Platts-Mills TA, Vervloet D, Thomas WR, Aalberse RC, Chapman MD. Indoor allergens and asthma: report of the Third International Workshop. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997. 100:S2–S24.8. Herbert CA, King CM, Ring PC, Holgate ST, Stewart GA, Thompson PJ, Robinson C. Augmentation of permeability in the bronchial epithelium by the house dust mite allergen Der p1. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995. 12:369–378.
Article9. Schulz O, Sewell HF, Shakib F. Proteolytic cleavage of CD25, the alpha subunit of the human T cell interleukin 2 receptor, by Der p 1, a major mite allergen with cysteine protease activity. J Exp Med. 1998. 187:271–275.10. Coward WR, Sagara H, Wilson SJ, Holgate ST, Church MK. Allergen activates peripheral blood eosinophil nuclear factor-κB to generate granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor, tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-8. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004. 34:1071–1078.11. Pomerantz JL, Baltimore D. Two pathways to NF-κB. Mol Cell. 2002. 10:693–695.
Article12. Ip WK, Wong CK, Lam CW. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human eosinophilic leukaemia EoL-1 cells is mediated by the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003. 33:241–248.13. Ree HI, Jeon SH, Lee IY, Hong CS, Lee DK. Fauna and geographical distribution of house dust mites in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1997. 35:9–17.
Article14. Holden NS, Catley MC, Cambridge LM, Barnes PJ, Newton R. ICAM-1 expression is highly NF-kappaB-dependent in A549 cells. No role for ERK and p38 MAPK. Eur J Biochem. 2004. 271:785–791.15. Lin FS, Lin CC, Chien CS, Luo SF, Yang CM. Involvement of p42/p44 MAPK, JNK, and NF-κB in IL-1 β-induced ICAM-1 expression in human pulmonary epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2005. 202:464–473.16. Wong CK, Li ML, Wang CB, Ip WK, Tian YP, Lam CW. House dust mite allergen Der p 1 elevates the release of inflammatory cytokines and expression of adhesion molecules in co-culture of human eosinophils and bronchial epithelial cells. Int Immunol. 2006. 18:1327–1335.
Article17. Horie S, Okubo Y, Hossain M, Momose T, Suzuki J, Isobe M, Sekiguchi M. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on eosinophils is involved in eosinophil protein X release induced by cytokines. Immunology. 1997. 90:301–307.
Article18. Takashi S, Okubo Y, Horie S. Contribution of CD54 to human eosinophil and neutrophil superoxide production. J Appl Physiol. 2001. 91:613–622.
Article19. Mengelers HJ, Maikoe T, Brinkman L, Hooibrink B, Lammers JW, Koenderman L. Immunophenotyping of eosinophils recovered from blood and BAL of allergic asthmatics. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994. 149:345–351.
Article20. Azuma M, Nakamura Y, Sano T, Okano Y, Sone S. Adhesion molecule expression on eosinophils in idiopathic eosinophilic pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 1996. 9:2494–2500.
Article21. Hansel TT, Braunstein JB, Walker C, Blaser K, Bruijnzeel PL, Virchow JC Jr, Virchow C Sr. Sputum eosinophils from asthmatics express ICAM-1 and HLA-DR. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991. 86:271–277.
Article22. Mastrandrea F, Nicotra MR, De Vita L, Coradduzza G, Minardi A, Scarcia G, Manelli M, Cadario G, Parmiani S, Natali PG. Mite antigens enhance ICAM-1 and induce VCAM-1 expression on human umbilical vein endothelium. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2003. 31:259–264.
Article23. Asokananthan N, Graham PT, Stewart DJ, Bakker AJ, Eidne KA, Thompson PJ, Stewart GA. House dust mite allergens induce proinflammatory cytokines from respiratory epithelial cells: the cysteine protease allergen, Der p 1, activates protease-activated receptor (PAR)-2 and inactivates PAR-1. J Immunol. 2002. 169:4572–4578.
Article24. Miike S, Kita H. Human eosinophils are activated by cysteine protease and release inflammatory mediators. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 111:704–713.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Th2 Responses Elicited by Nasal Epithelial Cells Exposed to House Dust Mite Extract
- Effects of Mycoplasma Pneumoniae on Activation of Human Eosinophilic Leukaemia EoL-1 Cells
- Effects of Hyperosmolar Stimuli on Activation of Human Eosinophilic Leukaemia EoL-1 Cells
- Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in human primary lung cancers
- Expression of cell adhesion molecules on positive reaction site of patch test with Dermatophagoides farinae in atopic dermatitis patients