J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Apr;22(2):298-304. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.298.
Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Triggers Apoptotic Signal for B16 Melanoma Cells via ERK and Caspase Activation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Dermatology, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, 911-1 Mock-dong, Yangcheon-gu, Seoul, Korea. kbmyung@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 1713191
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.298
Abstract
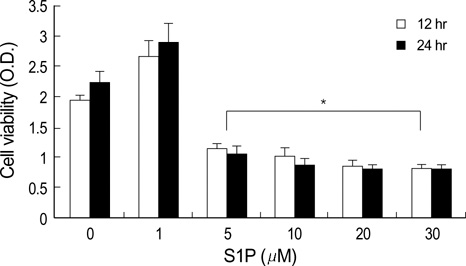
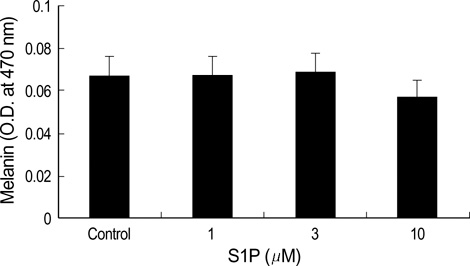
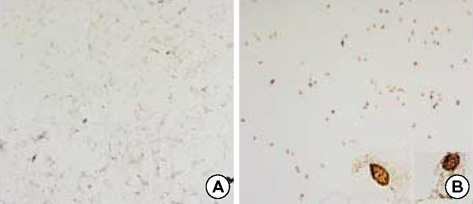
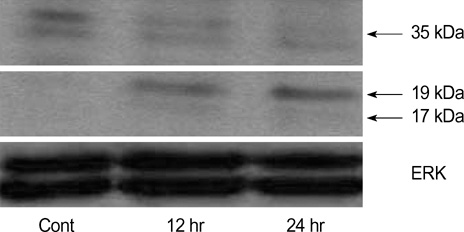
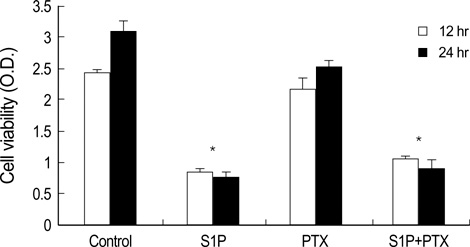
- The bioactive sphingolipid metabolite sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), recently was reported to induce apoptosis of some cancer cells and neurons, although it generally known to exert mitogenic and antiapoptotic effects. In this study, we investigated the effects of S1P on the cell growth, melanogenesis, and apoptosis of cultured B16 mouse melanoma cells. In results, S1P was found to induce apoptosis in B16 melanoma cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner, but exerted minimal effects on melanogenesis. Although receptors of sphingosine 1-phosphate (endothelial differentiation gene 1 [Edg]/S1P1, Edg5/S1P2, Edg3/S1P3) were expressed in B16 melanoma cells, they were shown not to be associated with S1P-induced apoptosis. In addition, pertussis toxin did not block the apoptotic effects of S1P on B16 melanoma cells. S1P induced caspase-3 activation and the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation. Interestingly, the ERK pathway inhibitor, UO126, reversed the apoptotic effects of S1P on B16 melanoma cells. These results suggest that S1P induced apoptosis of B16 melanoma cells via an Edg receptor-independent, pertussis toxin-insensitive pathway, and appears to be associated with the ERK and caspase-3 activation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Sphingosine/administration & dosage/*analogs & derivatives
Signal Transduction/drug effects
Mice
Melanoma/*enzymology/*pathology
Lysophospholipids/*administration & dosage
Extracellular Signal-Regulated MAP Kinases/*metabolism
Enzyme Activation/drug effects
Cell Line
Caspase 3/*metabolism
Apoptosis/*drug effects
Animals
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sigal YJ, McDermott MI, Morris AJ. Integral membrane lipid phosphatases/ phosphotransferases: common structure and diverse functions. Biochem J. 2005. 387:281–293.2. Spiegel S, Milstein S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate, signaling inside and out. FEBS Lett. 2000. 476:55–57.3. Pyne S, Pyne NJ. Sphingosine 1-phosphate signalling in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 2000. 349:385–402.
Article4. Spiegel S, Cuvillier O, Edsall LC, Kohama T, Menzeleev R, Olah Z, Olivera A, Pirianov G, Thomas DM, Tu Z, Van Brocklyn JR, Wang F. Sphingosine 1-phosphate in cell growth and cell death. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. 845:11–18.5. Goetzl EJ, An S. Diversity of cellular receptors and functions for the lysophospholipid growth factors lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate. FASEB J. 1998. 12:1589–1598.
Article6. Yatomi Y, Igarashi Y, Yang L, Hisano N, Qi R, Asazuma N, Satoh K, Ozaki Y, Kume S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate, a bioactive sphingolipid abundantly stored in platelets, is a normal constituent of human plasma and serum. J Biochem (Tokyo). 1997. 121:969–973.
Article7. Ruwisch L, Schafer-Korting M, Kleuser B. An improved high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of sphingosine-1-phosphate in complex biological materials. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001. 363:358–363.
Article8. Tokumura A. A family of phospholipid autacoids: occurrence, metabolism, and bioactions. Prog Lipid Res. 1995. 34:151–184.
Article9. Spiegel S, Milstein S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate, a key cell signaling molecule. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:25851–25854.
Article10. Fukushima N, Ishii I, Contos JJ, Weiner JA, Chun J. Lysophospholipid receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001. 41:507–534.11. Chun J, Goetzl EJ, Hla T, Igarashi Y, Lynch KR, Moolenaar W, Pyne S, Tigyi G. International union of pharmacology. XXXIV. Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature. Pharmacol Rev. 2002. 54:265–269.
Article12. An S, Goetzl EJ, Lee H. Signaling mechanisms and molecular characteristics of G protein-coupled receptors for lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine-1-phosphate. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1998. 31:147–157.13. Lee MJ, Van Brocklyn JR, Thangada S, Liu CH, Hand AR, Menzeleev R, Spiegel S, Hla T. Sphingosine-1-phosphate as a ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1. Science. 1998. 279:1552–1555.
Article14. Okamoto H, Takuwa N, Gonda K, Okazaki H, Chang K, Yatomi Y, Shigematsu H, Takuwa Y. EDG1 is a functional sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor that is linked via a Gi/o to multiple signaling pathways, including phospholipase C activation, Ca2+ mobilization, Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, and adenylate cyclase inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1998. 273:27104–27110.15. Van Brocklyn JR, Lee MJ, Menzeleev R, Olivera A, Edsall L, Cuvillie O, Thomas DM, Coopman PJ, Thangada S, Liu CH, Hla T, Spiegel S. Dual actions of sphingosine-1-phosphate: extracellular through the Gi-coupled receptor Edg-1 and intracellular to regulate proliferation and survival. J Cell Biol. 1998. 142:229–240.16. Zondag GC, Postma FR, Etten IV, Verlaan I, Moolenaar WH. Sphingosine 1-phosphate signalling through the G-protein-coupled receptor Edg-1. Biochem J. 1998. 330:605–609.
Article17. Okamoto H, Takuwa N, Yatomi Y, Gonda K, Shigematsu H, Takuwa Y. EDG3 is a functional receptor specific for sphingosine 1-phosphate and sphingosylphosphorylcholine with signaling characteristics distinct from EDG1 and AGR16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. 260:203–208.
Article18. Gonda K, Okamoto H, Takuwa N, Yatomi Y, Okazaki H, Sakurai T, Kimura S, Sillard R, Harii K, Takuwa Y. The novel sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor AGR16 is coupled via pertussis toxin-sensitive and -insensitive G-proteins to multiple signalling pathways. Biochem J. 1999. 337:67–75.
Article19. Hung WC, Chuang LY. Induction of apoptosis by sphingosine-1-phosphate in human hepatoma cells is associated with enhanced expression of bax gene product. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996. 229:11–15.
Article20. Hong G, Baudhuin LM, Xu Y. Sphingosine-1-phosphate modulates growth and adhesion of ovarian cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 1999. 460:513–518.
Article21. Moore AN, Kampfl AW, Zhao X, Hayes RL, Dash PK. Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces apoptosis of cultured hippocampal neurons that requires protein phosphatases and activator protein-1 complexes. Neuroscience. 1999. 94:405–415.
Article22. Van Brocklyn JR, Tu Z, Edsall L, Schmidt RR, Spiegel S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced cell rounding and neurite retraction are mediated by the G protein-coupled receptor H218. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:4626–4632.
Article23. Davaille J, Gallois C, Habib A, Li L, Mallat A, Tao J, Levade T, Lotersztajn S. Antiproliferative properties of sphingosine 1-phosphate in human hepatic myofibroblasts. A cyclooxygenase-2 mediated pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:34628–34633.24. Gennero I, Fauvel J, Nieto M, Cariven C, Gaits F, Briand-Mesange F, Chap H, Salles JP. Apoptotic effect of sphingosine 1-phosphate and increased sphingosine 1-phosphate hydrolysis on mesangial cells cultured at low cell density. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:12724–12734.
Article25. Kim DS, Hwang ES, Lee JE, Kim SY, Park KC. Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes mouse melanocyte survival via ERK and Akt activation. Cell Signal. 2003. 15:919–926.
Article26. Daugas E, Nochy D, Ravagnan L, Loeffler M, Susin SA, Zamzami N, Kroemer G. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): a ubiquitous mitochondrial oxidoreductase involved in apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2000. 476:118–123.
Article27. Davaille J, Li L, Mallat A, Lotersztajn S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate triggers both apoptotic and survival signals for human hepatic myofibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:37323–37330.28. Liu H, Toman RE, Goparaju SK, Maceyka M, Nava VE, Sankala H, Payne SG, Bektas M, Ishii I, Chun J, Milstein S, Spiegel S. Sphingosine kinase type 2 is a putative BH3-only protein that induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:40330–40336.
Article29. Lee JS, Jung JH, Kim TH, Seo JS. Changes of gene expression in NIH3T3 cells exposed to osmotic and oxidative stresses. Genomics Inform. 2004. 2:67–74.30. Kim MY, Liang GH, Kim JA, Kim YJ, Oh S, Suh SH. Sphingosine-1-phosphate activates BKCa channels independently of G protein-coupled receptor in human endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006. 290:C1000–C1008.31. Stanciu M, Wang Y, Kentor R, Burke N, Watkins S, Kress G, Reynolds I, Klann E, Angiolieri MR, Johnson JW, DeFranco DB. Persistent activation of ERK contributes to glutamate-induced oxidative toxicity in a neuronal cell line and primary cortical neuron cultures. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:12200–12206.
Article32. Namura S, Iihara K, Takami S, Nagata I, Kikuchi H, Matsushita K, Moskowitz MA, Bonventre JV, Alessandrini A. Intravenous administration of MEK inhibitor U0126 affords brain protection against forebrain ischemia and focal cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001. 98:11569–11574.
Article33. Cagnol S, Van Obberghen-Schilling E, Chambard JC. Prolonged activation of ERK1,2 induces FADD-independent caspase 8 activation and cell death. Apoptosis. 2006. 11:337–346.
Article34. Bektas M, Jolly PS, Muller C, Eberle J, Spiegel S, Geilen CC. Sphingosine kinase activity counteracts ceramide-mediated cell death in human melanoma cells: role of Bcl-2 expression. Oncogene. 2005. 24:178–187.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prolonged ERK Activation of S1P on B16 Melanoma Cells
- Caspases Activation in Ultraviolet B-induced Apoptosis of G361 Human Melanoma Cell Line
- The Study of the Cytotoxic Mechanism of Cisplatin in HeLa Cells
- Requirement of ERK Activation in Hypoxia Induced Caspase Activation and Apoptosis of Cultured Tubular Cells
- Identification of sphingosine 1-phosphate level and MAPK/ERK signaling in pancreatic β cells